Abstract
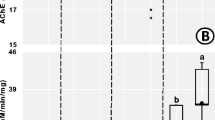
Earthworms are important and useful soil organisms, but in agricultural soils, they are potentially exposed to a wide variety of pesticides. Insecticides represent the highest threat to earthworms and many are neurotoxic. There is a need for a reliable, relevant, simple biomarker to assess the sub-lethal effects of neurotoxic insecticides on earthworms under laboratory or field conditions. The Aporrectodea caliginosa earthworms were exposed to 0 (control), 0.5×, 1× (normal field application rate), and 5× concentrations of a carbamate (Pirimor®) and an organophosphate (Lorsban®) insecticides. The nerve conduction velocity (NCV) of the medial giant fibers of A. caliginosa earthworm was recorded on days 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, and 7 to quantify sub-lethal neurotoxic effects. Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) enzyme activity of A. caliginosa homogenates was measured at the conclusion of the experiment. Pirimor® but not Lorsban® induced a significant decrease in NCV on days 3, 4, and 7 at 1× and 5× doses. A significant dose-dependent decrease was observed on AChE activity to Pirimor® at the doses used but not Lorsban®. A clear relationship is observed between AChE activity and NCV in the case of Pirimor®. This study showed that NCV is a sensitive biomarker that correlates well with classical biomarker measurements such as AChE enzyme activity. This technique could be used to study the impact of insecticides on earthworms and also their recovery.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Areti A, Komirishetty P, Kumar A (2017) Carvedilol prevents functional deficits in peripheral nerve mitochondria of rats with oxaliplatin-evoked painful peripheral neuropathy. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 322:97–103
Bate A (2015) Speciation and the effects of silver nanoparticles on the earthworm Aporrectodea caliginosa. MSc Dissertation. Lincoln University, Lincoln Christchurch, New Zealand
Belzunces LP, Gauthier M, Colin M-E (1992) Acetylcholinesterase in Apis mellifera head during post-embryonic development. Existence of a glycoinositol-anchored membrane form at eary pupal stages. Comp Biochem Physiol B Comp Biochem 103(1):57–63
Bembridge JD (1998) Recommendations from the second international workshop on earthworm ecotoxicology. In: Sheppard SC, Bembridge JD, Holmstrup M, Posthuma L (eds) Amsterdam, Netherlands, April 1997. Advances in earthworm ecotocicology. SETAC, Pensacola, pp 389–398
Capowiez Y, Bastardie F, Costagliola G (2006) Sublethal effects of imidacloprid on the burrowing behaviour of two earthworm species: modifications of the 3D burrow systems in artificial cores and consequences on gas diffusion in soil. Soil Biol Biochem 38(2):285–293
Collange B, Wheelock C, Rault M, Mazzia C, Capowiez Y, Sanchez-Hernandez JC (2010) Inhibition, recovery and oxime-induced reactivation of muscle esterases following chlorpyrifos exposure in the earthworm Lumbricus terrestris. Environ Pollut 158(6):2266–2272
Drewes C, Lingamneni A (1992) Use of earthworms in eco-neurotoxicity testing: sublethal effects of carbofuran in Lumbricus terrestris. In: Greig-Smith PW, Becker H, Edwards PJ, Heimbach F (eds) Ecotoxicology of earthworms. Intercept Ltd, Andover, pp 63–72
Drewes C, McFall J (1980) Longitudinal variations in the efficacy of lateral giant fiber to giant motor neuron transmission in intact earthworms. Comp Biochem Physiol A Physiol 66(2):315–321
Drewes C, McFall J, Vining E, Pallas S (1980) Longitudinal variations in MGF-mediated giant motor neuron activity and rapid escape shortening in intact earthworms. Comp Biochem Physiol A Physiol 67(4):659–665
Drewes CD, Vining EP, Callahan CA (1988) Electrophysiological detection of sublethal neurotoxiceffects in intact earthworms. In: Edwards CA, Neuhauser EF (eds) Earthworms in waste and environmental management. SPB Academic Publishing, The Hague, pp 355–356
Drewes CD, Vining EP, Callahan CA (1984) Non-invasive electrophysiological monitoring: a sensitive method for detecting sublethal neurotoxicity in earthworms. Environ Toxicol Chem 3(4):599–607
Ecobichon DJ (2001) Carbamate insecticides. In: Krieger RI, Krieger WC (eds) Handbook of pesticide toxicology, 2nd Edn. Academic Press, London, pp 1087–1106
Ellman GL, Courtney KD, Andres V, Featherstone RM (1961) A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem Pharmacol 7(2):88–95
Gooneratne R, Buser A, Lindsay P, Wellby M (2011) Ecotoxicological assessment of acid mine drainage: electrophysiological changes in earthworm (Aporrectodea caliginosa) and aquatic oligochaete (Lumbriculus variegatus). J Environ Monit 13(5):1360–1365
Gupta S, Sundararaman V (1991) Correlation between burrowing capability and AChE activity in the earthworm, Pheretima posthuma, on exposure to carbaryl. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 46(6):859–865
Hirano T, Tamae K (2011) Earthworms and soil pollutants. Sensors 11(12):11157–11167
Jordaan MS, Reinecke SA, Reinecke AJ (2012) Acute and sublethal effects of sequential exposure to the pesticide azinphos-methyl on juvenile earthworms (Eisenia andrei). Ecotoxicology 21(3):649–661
Jouni F, Sanchez-Hernandez JC, Mazzia C, Jobin M, Capowiez Y, Rault M (2018) Interspecific differences in biochemical and behavioral biomarkers in endogeic earthworms exposed to ethyl parathion. Chemosphere 202:85–93
Kammenga JEDR, Donker MH, Kohler H-R, Simonsen V, Triebskorn R, Weeks JM (2000) Biomarkers in terrestrial invertebrates for ecotoxicological soil risk assessment. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol 164:93–147
Markwell MAK, Haas SM, Bieber L, Tolbert N (1978) A modification of the Lowry procedure to simplify protein determination in membrane and lipoprotein samples. Anal Biochem 87(1):206–210
Millot N (1943) The visceral nervous system of the earthworm: I. Nerve controlling the tone of the alimentary canal. Proc R Soc B 131:271–295
Morcillo SM, Yela J, Capowiez Y, Mazzia C, Rault M, Sanchez-Hernandez JC (2013) Avoidance behaviour response and esterase inhibition in the earthworm, Lumbricus terrestris, after exposure to chlorpyrifos. Ecotoxicology 22(4):597–607
O'Gara B, Vining E, Drewes C (1982) Electrophysiological correlates of rapid escape reflexes in intact earthworms, Eisenia foetida. I. Functional development of giant nerve fibers during embryonic and postembryonic periods. J Neurobiol 13(4):337–353
Olvera-Velona A, Capowiez Y, Mascle O, Ortiz-Hernandez L, Benoit P (2008) Assessment of the toxicity of ethyl-parathion to earthworms (Aporrectodea caliginosa) using behavioural, physiological and biochemical markers. Appl Soil Ecol 40(3):476–483
Paoletti M, Sommaggio D, Favretto M, Petruzzelli G, Pezzarossa B, Barbafieri M (1998) Earthworms as useful bioindicators of agroecosystem sustainability in orchards and vineyards with different inputs. Appl Soil Ecol 10(1):137–150
Pelosi C, Barot S, Capowiez Y, Hedde M, Vandenbulcke F (2014) Pesticides and earthworms. A review. Agron Sustain Dev 34(1):199–228
Pelosi C, Toutous L, Chiron F, Dubs F, Hedde M, Muratet A, Ponge J-F, Salmon S, Makowski D (2013) Reduction of pesticide use can increase earthworm populations in wheat crops in a European temperate region. Agric Ecosyst Environ 181:223–230
Pereira JL, Antunes SC, Ferreira AC, Goncalves F, Pereira R (2010) Avoidance behavior of earthworms under exposure to pesticides: is it always chemosensorial? J Environ Sci Health B 45(3):229–232
Prosser CL, Zimmerman GL (1943) Effects of drugs on the hearts of Arenicola and Lumbricus. Physiol Zool 16(1):77–83
Rault M, Collange B, Mazzia C, Capowiez Y (2008) Dynamics of acetylcholinesterase activity recovery in two earthworm species following exposure to ethyl-parathion. Soil Biol Biochem 40(12):3086–3091
Sanchez-Hernandez JC (2006) Earthworm biomarkers in ecological risk assessment. Rev Environ ContamToxicol 188:85–126
Scott-Fordsmand JJ, Weeks JM (2000) Biomarkers in earthworms. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol 165:117–159
Sheppard SC, Evenden WG (1992) Optimized design for earthworm survival tests in soil. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 49(5):648–655
Subaraja M, Vanisree AJ (2016) Neurotransmission, structural and conduction velocity changes in cerebral ganglions of Lumbricus terrestris on exposure to acrylamide. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 23(17):17123–31
Wu K (1939) On the physiology and pharmacology of the earthworm gut. J Exp Biol 16(2):184–197
Acknowledgements
Christophe Mazzia thanks the Scientific Committee of the University of Avignon for a fellowship to conduct this research at Lincoln University, New Zealand.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mazzia, C., Munir, K., Wellby, M. et al. Nerve conduction velocity as a non-destructive biomarker in the earthworm Aporrectodea caliginosa exposed to insecticides. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25, 24362–24367 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2469-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2469-1