Abstract
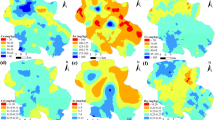
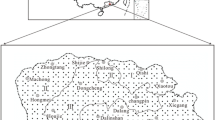
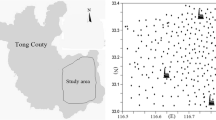
In this study, 234 soil samples were recently collected from Gaoqing County (a typical area of the lower Yellow River) to determine the contents of As, Cd, Cr, Cu, Hg, Ni, Pb, and Zn. Multivariate statistical analyses such as correlation analysis, principal components analysis, and one-way ANOVA were applied to identify the source of metals in the soil. Geostatistical methods were used to analyze the spatial structure and distribution of the metals. The results indicated that the mean contents of all metals exceeded the background value of the lower Yellow River, especially for As, Cu, and Hg (1.23, 1.20, and 1.29 times that of the BV, respectively), indicating that these metals were enriched in the study area to different degrees. The results derived from multivariate analysis suggested that As, Cd, Cr, Cu, Ni, Pb, and Zn were mainly controlled by the combination of human activities and soil parent material, and the human activities included industrial emissions, traffic emissions, and agricultural practices. In addition, Hg mainly originated from anthropogenic inputs, such as textile printing, plastics processing, and petrochemical engineering. The contents of metals in different types of land use and parent materials are clearly different. The mean content for eight elements in urban construction land was significantly higher than that of the other land use types; in addition to Hg, the mean content of the other elements was the highest in the lacustrine deposit. The elements of As, Cd, Cr, Cu, Ni, Pb, and Zn had similar hotspots in the urban area, indicating the significant human influence. In addition, these seven metals showed high values in the southeast lacustrine deposit area. The high-value areas of Hg were concentrated in the southwest and northeast study area, which were consistent with the spatial pattern of the industrial sites.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acosta JA, Faz A, Martinez-Martinez S (2010) Identification of heavy metal sources by multivariable analysis in a typical Mediterranean city (SE Spain). Environ Monit Assess 169(14):519–530
Bednářová Z, Kalina J, Hájek O (2016) Spatial distribution and risk assessment of metals in agricultural soils. Geoderma 284:113–121
Bo LJ, Wang DJ, Li TL, Li Y, Zhang G, Wang C, Zhang SQ (2015) Accumulation and risk assessment of heavy metals in water, sediments, and aquatic organisms in rural rivers in the Taihu Lake region, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:6721–6731
Bonanno G, Borg JA, Di Martino V (2017) Levels of heavy metals in wetland and marine vascular plants and their biomonitoring potential: a comparative assessment. Sci Total Environ 576:796–806
Cai LM, Ma J, Zhou YZ (2008) Multivariate geostatistics and GIS-based approach to study the spatial distribution and sources of heavy metals in agricultural soil in the Pearl River Delta, China. Environ Sci 29(12):3496–3502
Cai LM, Xu ZC, Ren MZ, Guo Q, Hu X, Hu G, Wan H, Peng P (2012) Source identification of eight hazardous heavy metals in agricultural soils of Huizhou, Guangdong Province, China. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 78:2–8
Chen TB, Zheng YM, Lei M, Huang ZC, Wu HT, Chen H, Fan KK, Yu K, Wu X, Tian QZ (2005) Assessment of heavy metal pollution in surface soils of urban parks in Beijing, China. Chemosphere 60(4):542–551
Chen XD, Lu XW, Yang G (2012) Sources identification of heavy metals in urban topsoil from inside the Xi’an Second Ringroad, NW China using multivariate statistical methods. Catena 98:73–78
Cheng QL, Wang RL, Huang WH, Wang WL, Li XD (2015) Assessment of heavy metal contamination in the sediments from the Yellow River Wetland National Nature Reserve (the Sanmenxia section), China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:8586–8593
Cui YJ, Zhu YG, Zhai RH, Chen DY, Huang YZ, Qiu Y, Liang JZ (2004) Transfer of metals from soil to vegetables in an area near a smelter in Nanning, China. Environ Int 30(6):785–791
Dai B, Lv JS, Zhan JC (2015) Assessment of sources, spatial distribution and ecological risk of heavy metals in soils in a typical industry-based City of Shandong Province, eastern China. Environ Sci 36(2):507–515 (in Chinese)
Facchinelli A, Sacchi E, Mallen L (2001) Multivariate statistical and GIS-based approach to identify heavy metal sources in soils. Environ Pollut 114:313–324
Franco-Uria A, Lopez-Mateo C, Roca E (2009) Source identification of heavy metals in pastureland by multivariate analysis in NW Spain. J Hazard Mater 165:1008–1015
Han DM, Cheng JP, Hu XF, Jiang ZY (2017) Spatial distribution, risk assessment and source identification of heavy metals in sediments of the Yangtze River Estuary, China. Mar Pollut Bull 115:141–148
Hu Y, Cheng H (2016) A method for apportionment of natural and anthropogenic contributions to heavy metal loadings in the surface soils across large-scale regions. Environ Pollut 214:400–409
Huang SS, Liao QL, Hua M (2007) Survey of heavy metal pollution and assessment of agricultural soil in Yangzhong district, Jiangsu Province, China. Chemosphere 67:2148–2155
Li W, Xu B, Song Q (2014) The identification of ‘hotspots’ of heavy metal pollution in soil–rice systems at a regional scale in eastern China. Sci Total Environ 472:407–420
Li HH, Chen LJ, Yu L (2017) Pollution characteristics and risk assessment of human exposure to oral bio accessibility of heavy metals via urban street dusts from different functional areas in Chengdu, China. Sci Total Environ 586:1076–1084
Liu JL, Feng XB, Yin RS, Zhu W, Li ZG (2011) Mercury distributions and mercury isotope signatures in sediments of Dongjiang, the Pearl River Delta, China. Chem Geol 287:81–89
Liu Y, Ma ZW, Lv JS (2016) Identifying sources and hazardous risks of heavy metals in topsoils of rapidly urbanizing East China. J Geogr Sci 26:735–749
Lu AX, Wang JH, Qin XY (2012) Multivariate and geostatistical analyses of the spatial distribution and origin of heavy metals in the agricultural soils in Shunyi, Beijing, China. Sci Total Environ 425:66–74
Lu Y, Zhu F, Chen J (2007) Chemical fractionation of heavy metals in urban soils of Guangzhou, China. Environ Monit Assess 134: 429–439
Lu J, Li A, Huang P (2017) Distribution, sources and contamination assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments of the South Yellow Sea and northern part of the East China Sea. Mar Pollut Bull 124(1): 470–479
Lv JS, Zhang ZL, Liu Y, Dai JR, Wang X (2012) Sources identification and hazardous risk delineation of heavy metals contamination in Rizhao City. Acta Geograph Sin 67(7):971–984
Lv JS, Liu Y, Zhang ZL (2013) Factorial kriging and stepwise regression approach to identify environmental factors influencing spatial multi-scale variability of heavy metals in soils. J Hazard Mater 261:387–397
Lv JS, Zhang ZL, Li S et al (2014a) Assessing spatial distribution, sources, and potential ecological risk of heavy metals in surface sediments of the Nansi Lake, Eastern China. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 299(3):1671–1681
Lv JS, Liu Y, Zhang ZL (2014b) Multivariate geostatistical analyses of heavy metals in soils: spatial multi-scale variations in Wulian, Eastern China. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 107:140–147
Lv J, Liu Y, Zhang Z (2015a) Distinguishing anthropogenic and natural sources of trace elements in soils undergoing recent 10-year rapid urbanization: a case of Donggang, Eastern China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22(14):10539–10550
Lv JS, Zhang ZL, Liu Y (2015b) Identifying the origins and spatial distributions of heavy metals in soils of Ju county (Eastern China) using multivariate and geostatistical approach. J Soils Sediments 15:163–178
Ma XL, Zuo H, Tian MJ, Zhang LY, Meng J, Zhou XN (2016) Assessment of heavy metals contamination in sediments from three adjacent regions of the Yellow River using metal chemical fractions and multivariate analysis techniques. Chemosphere 144:264–272
Mico C, Recatala L, Peris A, Sanchez J (2006) Assessing heavy metalsources in agricultural soils of an European Mediterranean area bymultivariate analysis. Chemosphere 65:863–872
Naji A, Sohrabi T (2015) Distribution and contamination pattern of heavy metals from surface sediments in the southern part of Caspian Sea, Iran. Chem Spec Bioavailab 27(1):29–43
Nanos N, Rodríguez Martín JA (2012) Multiscale analysis of heavy metal contents in soils: spatial variability in the Duero river basin (Spain). Geoderma 189:554–562
Pan HY, Lu XW, Lei K (2017) A comprehensive analysis of heavy metals in urban road dust of Xi'an, China: contamination, source apportionment and spatial distribution. Sci Total Environ 609:1361–1369
Rinklebe J, Shaheen SM (2017) Geochemical distribution of Co, Cu, Ni, and Zn in soil profiles of Fluvisols, Luvisols, Gleysols, and Calcisols originating from Germany and Egypt. Geoderma 307:122–138
Rodríguez Martín JA, Nanos N (2016) Soil as an archive of coal-fired power plant mercury deposition. J Hazard Mater 308:131–138
Rodríguez Martín JA, Arias ML, Grau Corbi JM (2006) Heavy metals contents in agricultural top soils in the Ebro basin (Spain). Application of the multivariate geostatistical methods to study spatial variations. Environ Pollut 144:1001–1012
Rodríguez Martín JA, Ramos-Miras JJ, Boluda R (2013) Spatial relations of heavy metals in arable and greenhouse soils of a Mediterranean environment region (Spain). Geoderma 200:180–188
Rodríguez JA, Nanos N, Grau JM, Gil L (2008) Multiscale analysis of heavy metal contents in Spanish agricultural topsoils. Chemosphere 70:1085–1096
Saleem M, Iqbal J, Shah MH (2013) Study of seasonal variations and risk assessment of selected metals in sediments from Mangla Lake, Pakistan. J Geochem Explor 125:144–152
Sollitto D, Romic M, Castrignano A (2010) Assessing heavy metal contamination in soils of the Zagreb region (Northwest Croatia) using multivariate geostatistics. Catena 80:182–194
Stafilov T, Sajn R, Alijagic J (2013) Distribution of arsenic, antimony, and thallium in soil in Kavadarci and its surroundings, Republic of Macedonia. Soil Sediment Contam 22:105–118
State Environmental Protection Administration of China (1997) Environmental quality standard for soils (GB15618–1995). Standards Press of China, Beijing
Sun Y, Zhou Q, Xie X (2010) Spatial, sources and risk assessment of heavy metal contamination of urban soils in typical regions of Shenyang, China. J Hazard Mater 174(1):455–462
Sun CY, Liu JS, Wang Y (2013) Multivariate and geostatistic analysis of the spatial distribution and sources of heavy metals in agricultural soil in Dehui, Northeast China. Chemosphere 92(5):517–523
Wang GY, Pan M, Liu XD (1992) On the relationship between the concentrations of elements in soil and the types of soil-forming parent material in Shandong Province, China. Acta Acta Sci Nat Univ Pekin 28(4):475–485 (in Chinese)
Wang X, Sato T, Xing B (2005) Health risks of heavy metals to the general public in Tianjin, China via consumption of vegetables and fish. Sci Total Environ 350(1):28–37
Wang JJ, Zhao HW, Zhong XP, Kong SF, Liu YS, Zeng H (2011) Investigation of mercury levels in soil around a municipal solid waste incinerator in Shenzhen, China. Environ Earth Sci 64:1001–1010
Wang CL, Xia XQ, Zhao XQ (2012) Distribution and migration regularity of soil heavy metal pollution along the Xiaoqing watershed, Shandong Province. Geol China 39(2):530–538 (in Chinese)
Wang F, Wu QY, Lv JS (2016) Spatial characteristics and environmental risk of heavy metals in typical gold mining area of Shandong Province. Environ Sci 37(8):3144–3150 (in Chinese)
Xu XD, Cao ZM, Zhang ZX (2016) Spatial distribution and pollution assessment of heavy metals in the surface sediments of the Bohai and Yellow Seas. Mar Pollut Bull 110:596–602
Yalcin MG, Tumuklu A, Sonmez M (2010) Application of multivariate statistical approach to identify heavy metal sources in bottom soil of the Seyhan River (Adana), Turkey. Environ Monit Assess 164:311–322
Yang P G, Mao R Z, Shao H B, Gao Y (2009) An investigation on the distribution of eight hazardous heavy metals in the suburban farmland of China. J Hazard Mater 167: 1246-1251
Yuan X, Zhang L, Li J, Wang C (2014) Sediment properties and heavy metal pollution assessment in the river, estuary and lake environments of a fluvial plain, China. Catena 119:52–60
Zhang CS (2006) Using multivariate analyses and GIS to identify pollutants and their spatial patterns in urban soils in Galway, Ireland. Environ Pollut 142:501–511
Zhang CS, Tang Y, Luo L, Xu WL (2009) Outlier identification and visualization for Pb concentrations in urban soils and its implications for identification of potential contaminated land. Environ Pollut 157:3083–3090
Zhao Y, Wang ZG, Sun WX (2010) Spatial interrelations and multi-scale sources of soil heavy metal variability in a typical urban-rural transition area in Yangtze River Delta region of China. Geoderma 156:216–227
Zhu JX, Wang QF, Yu HL (2016) Heavy metal deposition through rainfall in Chinese natural terrestrial ecosystems: evidences from national-scale network monitoring. Chemosphere 164:128–133
Funding
This study was jointly supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.41601549, 41701604), Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (No.ZR2016DQ11), and Open Foundation of Estuarine and Coastal State Key Laboratory (SKLEC-KF201710).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Severine Le Faucheur
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lv, J., Yu, Y. Source identification and spatial distribution of metals in soils in a typical area of the lower Yellow River, eastern China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25, 21106–21117 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2256-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2256-z