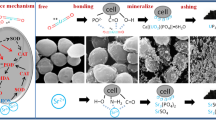
Abstract
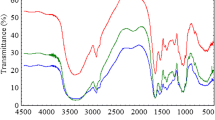
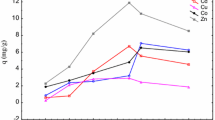
In this study, the Saccharomyces cerevisiae (S. cerevisiae) was modified by γ-ray. The RNA-seq results reflect that the high γ-ray energies could change some gene fragments, such as deletion, recombination, and mutation. The biosorption of strontium ions (Sr2+) to different types of S. cerevisiae (S. cerevisiae (K-0), modified S. cerevisiae (Y-7), and non-living S. cerevisiae (H-K)) from the simulated high-level liquid waste (S-HLLW) was assessed at different experimental conditions. The sorption experimental results show that, under an appropriate condition, γ-ray radiation can enhance its biosorption capacity slightly of Sr2+ to S. cerevisiae. The maximum metal uptake and efficiency of Y-7 under S-HLLW were 11.656 mg g−1 and 37.91% at 32 h (wet weight), respectively. They decreased to 9.46 mg g−1 and 30.76% under radiation conditions. SEM-EDX and TEM analysis indicates that Sr2+ was adsorbed both on the cellular surface and the inner parts of the cells. Our experimental results fit well to the Langmuir and Freundlich model isotherms (r2 > 0.94), and the maximum biosorption capacity values reached qmax > 24.74 mg g−1 at 32 °C. Negative values of ΔG0 and positive values of ΔH0 were observed, indicating the spontaneous and endothermic nature of Sr2+ biosorption on modified S. cerevisiae. The biosorption kinetics follow a pseudo-second-order equation at 32 °C (r2 > 0.94). The desorption efficiency of Sr2+ adsorbed onto Y-7 was 7.65 ± 0.52%, 76.51 ± 2.13%, and 65.62 ± 2.42% by deionized water, 1 M HCl, and 0.1 M EDTA-Na, respectively. However, they were lower than H-K (18.82, 83.32, and 73.32%). Our findings demonstrate that living S. cerevisiae (Y-7) is a promising sorbent material for the treatment of radioactive process streams.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anders S, Huber W (2010) Differential expression analysis for sequence count data. Genome Biol 11:R106
Bahieldin A, Atef A, Sabir JSM, Gadalla NO, Edris S, Alzohairy AM, Radhwan NA, Baeshen MN, Ramadan AM, Eissa HF, Hassan SM, Baeshen NA, Abuzinadah O, al-Kordy MA, el-Domyati FM, Jansen RK (2015) RNA-Seq analysis of the wild barley (H. spontaneum) leaf transcriptome under salt stress. C R Biol 338(5):285–297
Bailly du Bois P, Laguionie P, Boust D, Korsakissok I, Didier D, Fiévet B (2012) Estimation of marine source-term following Fukushima Dai-ichi accident. J Environ Radioactiv 114(12):2–9
Chen C, Wang J (2008) Removal of Pb2+, ag+, Cs+ and Sr2+ from aqueous solution by brewery’s waste biomass. J Hazard Mater 151(1):65–70
Chen C, Wang J (2016) Uranium removal by novel graphene oxide-immobilized Saccharomyces cerevisiae gel beads. J Environ Radioactiv 162:134–145
Chepelev I, Wei G, Tang Q, Zhao K (2009) Detection of single nucleotide variations in expressed exons of the human genome using RNA-Seq. Nucleic Acids Res 37(16):e106–e106
Clarke PH (1985) The scientific study of bacteria, 1780–1980. In: The scientific study of bacteria, 1780–1980. Springer, Berlin
Dabbagh R, Ghafourian H, Baghvand A, Nabi G, Riahi H, Ahmadi Faghih M (2007) Bioaccumulation and biosorption of stable strontium and 90Sr by Oscillatoria homogenea cyanobacterium. J Radioanal Nucl Ch 272(1):53–59
Dai Q, Zhang W, Dong F, Yulian Z, Wu X (2014) Effect of γ-ray radiation on the biosorption of strontium ions to baker’s yeast. Chem Eng J 249:226–235
Deák T, Beuchat LR (1996) Handbook of food spoilage yeasts. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Eccles H (1995) Removal of heavy metals from effluent streams—why select a biological process? Int Biodeter Biodegr 35(1–3):5–16
Farooq U, Kozinski JA, Khan MA, Athar M (2010) Biosorption of heavy metal ions using wheat based biosorbents—a review of the recent literature. Bioresour Technol 101(14):5043–5053
Gipps J, Coller B (1980) Effect of physical and culture conditions on uptake of cadmium by Chlorella pyrenoidosa. Mar Freshw Res 31(6):747–755
Ho Y, Wase DJ, Forster C (1996) Kinetic studies of competitive heavy metal adsorption by sphagnum moss peat. Environ Technol 17(1):71–77
Hu W, Dong F, Yang G, Peng X, Huang X, Liu M, Zhang J (2017) Synergistic interface behavior of strontium adsorption using mixed microorganisms. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 12:1–10
Izumida TKF (1990) Precipitates formation behavior in simulated high level liquid waste of fuel reprocessing. J Nucl Sci Technol 27(3):267–274
Kapoor A, Viraraghavan T (1995) Fungal biosorption—an alternative treatment option for heavy metal bearing wastewaters: a review. Bioresour Technol 53(3):195–206
Kubota MFT (1980) Formation of precipitate in high-level liquid waste from nuclear fuel reprocessing. J Nucl Sci Technol 17(10):783–790
Lan T, Feng Y, Liao J, Li X, Ding C, Zhang D, Yang J, Zeng J, Yang Y, Tang J, Liu N (2014) Biosorption behavior and mechanism of cesium-137 on Rhodosporidium fluviale strain UA2 isolated from cesium solution. J Environ Radioactiv 134:6–13
Li CC, Chung HP, Wen HW, Chang CT, Wang YT, Chou FI (2015) The radiation resistance and cobalt biosorption activity of yeast strains isolated from the Lanyu low-level radioactive waste repository in Taiwan. J Environ Radioactiv 146:80–87
Liu J, Sheng H, Xu Y, Feng K (2008) Effect of Fe on the growth of Scenedesmus quadricauda. Environ Pollut Control 8:61–64
Liu M, Dong F, Yan X, Zeng W, Hou L, Pang X (2010) Biosorption of uranium by Saccharomyces cerevisiae and surface interactions under culture conditions. Bioresour Technol 101(22):8573–8580
Liu M, Dong F, Kang W, Sun S, Wei H, Zhang W, Nie X, Guo Y, Huang T, Liu Y (2014) Biosorption of strontium from simulated nuclear wastewater by Scenedesmus spinosus under culture conditions: adsorption and bioaccumulation processes and models. International Int J Env Res Pub He 11(6):6099–6118
Luo H, Dai S, Bonnesen PV (2004) Solvent extraction of Sr2+ and Cs+ based on room-temperature ionic liquids containing monoaza-substituted crown ethers. Anal Chem 76(10):2773–2779
Marešová J, Pipíška M, Rozložník M, Horník M, Remenárová L, Augustín J (2011) Cobalt and strontium sorption by moss biosorbent: modeling of single and binary metal systems. Desalination 266(1):134–141
Mei LI, Jin XU, Liu ZL, Jun XU (2004) Strontium stress on marine microalgae dicrateria inornata growth and antioxidant enzymes activities. Oceano Limnol Sin 35:467–472
Merroun M, Chekroun KB, Arias J, Gonzalez-Munoz M (2003) Lanthanum fixation by Myxococcus xanthus: cellular location and extracellular polysaccharide observation. Chemosphere 52(1):113–120
Nie X, Dong F, Liu M, Sun S, Yang G, Zhang W, Qin Y, Ma J, Huang R, Gong J (2016) Removel of uranium from aqueous solutions by Spirodela Punctata as the mechanism of biomineralization. Procedia Environ Sci 31:382–391
Nilchi A, Hadjmohammadi MR, Garmarodi SR, Saberi R (2009) Studies on the adsorption behavior of trace amounts of 90Sr2+, 140La3+, 60Co2+, Ni2+and Zr4+ cations on synthesized inorganic ion exchangers. J Hazard Mater 167(1–3):531–535
Parab H, Devi PSR, Shenoy N, Kumar SD, Bhardwaj YK, Reddy AVR (2016) Gamma irradiation stability studies of coir pith: a lignocellulosic biosorbent for strontium. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 308(1):323–328
Petin VG, Kim JK (2014) Survival and recovery of yeast cells after combined treatment with ionizing radiation and heat. Radiat Res 161(1):56–63
Petin VG, Evstratova ES, Kim JK (2014) Radiosensitivity, liquid-holding recovery and relative biological effectiveness of densely-ionizing radiation after repeated irradiation of yeast cells. Mutat Res-Gen Tox En 771(9):37–42
Qiu L, Feng J, Dai Y, Chang S (2017) Biosorption of the strontium ion by irradiated Saccharomyces cerevisiae under culture conditions. J Environ Radioactiv 172:52–62
Robalds A, Naja GM, Klavins M (2016) Highlighting inconsistencies regarding metal biosorption. J Hazard Mater 304:553–556
Shozugawa K, Nogawa N, Matsuo M (2012) Deposition of fission and activation products after the Fukushima Dai-ichi nuclear power plant accident. Environ Pollut 163(4):243–247
R.L. Smith J, P. Atmaji, Y. Hakuta z, M. Kawaguchi, T. Adschiri, K. Arai (1997) Recovery of metals from simulated high-level liquid waste with hydrothermal crystallization. J Supercrit Fluid 11(1):103–114
Sud D, Mahajan G, Kaur M (2008) Agricultural waste material as potential adsorbent for sequestering heavy metal ions from aqueous solutions—a review. Bioresour Technol 99(14):6017–6027
Tan Y, Feng J, Qiu L, Zhao Z, Zhang X, Zhang H (2017) The adsorption of Sr(II) and Cs(I) ions by irradiated Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Radioanal Nucl Ch 314(3):2271–2280
Tomioka N, Tanaka K, Uchiyama H, Yagi O, Kokufuta E (1998) Recovery of 137Cs by a bioaccumulation system using Rhodococcus erythropolis CS98. J Biosci Bioeng 85(6):604–608
Tu Y-J, You C-F, Chen Y-R, Huang C-P, Huang Y-H (2015) Application of recycled iron oxide for adsorptive removal of strontium. J Taiwan Inst Chem E 53:92–97
Wang L, Feng Z, Wang X, Wang X, Zhang X (2010) DEGseq: an R package for identifying differentially expressed genes from RNA-seq data. Bioinformatics 26(1):136–138
Wang L, Wan C, Lee D-J, Tay J-H, Chen X, Liu X, Zhang Y (2013) Adsorption–desorption of strontium from waters using aerobic granules. J Taiwan Inst Chem E 44:454–457
Wang T, Zheng X, Wang X, Lu X, Shen Y (2017) Different biosorption mechanisms of Uranium(VI) by live and heat-killed Saccharomyces cerevisiae under environmentally relevant conditions. J Environ Radioactiv 167:92–99
Weerasekara NA, Choo KH, Choi SJ (2013) Metal oxide enhanced microfiltration for the selective removal of Co and Sr ions from nuclear laundry wastewater. J Membrane Sci 447(22):87–95
Yaochuan Wang XG (1994) Lethal dose of Escherichia coli, Salmonella enteritidis, Staphylococcus aureus and Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nucl Agric Bull 15:171–174
Zhang AKE, Kumagai M (2006) Removal of Pd(II), Zr(IV), Sr(II), Fe(III), and Mo(VI) from simulated high level liquid waste by extraction chromatography utilizing the macroporous silica-based polymeric materials. Sep Purif Technol 50(1):35–44
Funding
Sponsored by the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (SBK2014041829), the graduate student innovation fund of Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics (kfjj201444), the environmental protection scientific research subject in Jiangsu province (Grant No. 2016003), the A Project Fund by the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (PAPD), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 11705089).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Georg Steinhauser
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qiu, L., Feng, J., Dai, Y. et al. Biosorption of strontium ions from simulated high-level liquid waste by living Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25, 17194–17206 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-1662-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-1662-6