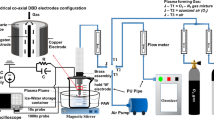
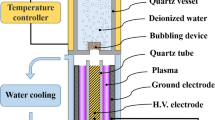
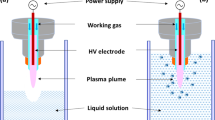
Abstract
Broad biological activities of “plasma-activated water” (PAW) have drawn great attentions recently. Treatment of water using gas discharge plasma led to acidic solutions with excellent and broad antibacterial activity. Because PAW caused severe membrane damages in bacteria and diffused freely in extracellular matrix, PAW also demonstrated good anti-biofilm activity. However, further studies revealed that trace amounts of metal ions (mainly copper and zinc) in PAW brought by plasma treatment played key roles in bacteria inactivation. The contribution of metal ions to the antibacterial activity varied among PAWs from different working gases. However, solution acidification caused by reactive species in plasma was essential. The experimental results demonstrated that potential artifacts in reported biological activities of PAWs should be considered.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abushelaibi A (2005) Antimicrobial effects of copper and brass ions on the growth of Listeria monocytogenes at different temperatures, pH and nutrients. Doctoral dissertation, Colorado State University
Akhavan O, Ghaderi E (2010) Cu and CuO nanoparticles immobilized by silica thin films as antibacterial materials and photocatalysts. Surf Coat Technol 205:219–223
Akhavan O, Ghaderi E (2011) Copper oxide nanoflakes as highly sensitive and fast response self-sterilizing biosensors. J Mater Chem 21:12935–12940
Chen TP, Su TL, Liang JF (2017) Plasma-activated solutions for bacteria and biofilm inactivation. Curr Bioact Compd 13(1):59–65
Díaz-Visurraga J, Gutiérrez C, von Plessing C, Garcia A (2011) Metal nanostructures as antibacterial agents. Sci Technol Microb Pathog Proc Int Conf Antimicrob Res 3:210–218
Dizaj SM, Lotfipour F, Barzegar-Jalali M, Zarrintan MH, Adibkia K (2014) Antimicrobial activity of the metals and metal oxide nanoparticles. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl 44:278–284
Donlan RM (2011) Biofilm elimination on intravascular catheters: important considerations for the infectious disease practitioner. Clin Infect Dis 52(8):1038–1045
Ercan UK, Wang H, Ji H, Fridman G, Brooks AD, Joshi SG (2013) Nonequilibrium plasma-activated antimicrobial solutions are board-spectrum and retain their efficacies for extended period of time. Plasma Process Polym 10(6):544–555
Ikawa S, Kitano K, Hamaguchi S (2010) Effects of pH on bacterial inactivation in aqueous solutions due to low-temperature atmospheric pressure plasma application. Plasma Process Polym 7(1):33–42
Joaquin JC, Kwan C, Abramzon N, Vandervoort K, Brelles-Marino G (2009) Is gas discharge plasma a new solution to the old problem of biofilm inactivation? Microbiology 155(3):724–732
Joshi SG, Paff M, Friedman G, Fridman G, Fridman A, Brooksm AD (2010) Control of methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus in planktonic form and biofilms: a biocidal efficacy study of nonthermal dielectric-barrier discharge plasma. Am J Infect Control 38(4):293–301
Julák J, Scholtz V, Kotúčová S, Janoušková O (2012) The persistent microbicidal effect in water exposed to the corona discharge. Phys Med 28(3):230–239
Kamgang-Youbi G, Herry JM, Bello-Feotaine MN, Brisset JL, Doubla A, Naïtali M (2007) Evidence of temporal postdischarge decontamination of bacteria by gliding electric discharges: application to Hafnia alvei. Appl Environ Microbiol 73(15):4791–3796
Kamgang-Youbi G, Herry JM, Brisset JL, Bellon-Fontaine MN, Doubla A, Naїtali M (2008) Impact on disinfection efficiency of cell load and of planktonic/adherent/detached state: case of Hafnia alvei inactivation by plasma activated water. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 81(3):449–457
Kamgang-Youbi G, Herry JM, Meyleuc T, Brisset JL, Bello-Feotaine MN, Doubla A, Naïtali M (2009) Microbial inactivation using plasma-activated water obtained by gliding electric discharges. Lett Appl Microbiol 48(1):13–18
Kamgang-Youbi G, Naitali M, Herry JM, Hnatiuc E, Brisset JL (2010) Direct and post-discharges in environmental applications of cold plasmas. OPTIM 2010: 12th international conference on optimization of electrical and electronic equipment, 1336–1342
Kharidia R, Liang JF (2011) The activity of a small lytic peptide PTP-7 on Staphylococcus aureus biofilms. J Microbiol 49(4):663–668
Lin YSE, Vidic RD, Stout JE, Victor LY (1996) Individual and combined effects of copper and silver ions on inactivation of Legionella pneumophila. Water Res 30(8):1905–1913
Machala Z, Tarabova B, Hensel K, Spetlikova E, Sikurova L, Lukes P (2013) Formation of ROS and RNS in water electro-sprayed through transient spark discharge in air and their bactericidal effects. Plasma Process Polym 10(7):649–659
Naïtali M, Kamgang-Youbi G, Herry JM, Bellon-Fotaine MN, Brisset JL (2010) Combined effects of long-living chemical species during microbial inactivation using atmospheric plasma-treated water. Appl Environ Microbiol 76(22):7662–7664
National Nosocomial Infections Surveillance (2003) National Nosocomial Infections Surveillance (NNIS) system report, data summary from January 1992 through June 2003. Am J Infect Control 31:481–498
Oehmigen K, Hähnel M, Brandenburg R, Wilke C, Weltmann KD, Von Woedtke T (2010) The Role of acidification for antimicrobial activity of atmospheric pressure plasma in liquids. Plasma Process Polym 7(3–4):250–257
Patel R (2005) Biofilms and antimicrobial resistance. Clin Orthop Relat Res 437:41–47
Pavlovich MJ, Chang HW, Sakiyama Y, Clark DS, Grave DB (2013) Ozone correlates with antibacterial effects from indirect air dielectric barrier discharge treatment of water. J Phys D Appl Phys 46(14):145202
Traba C, Liang JF (2011) Susceptibility of Staphylococcus aureus biofilms to reactive discharge gases. Biofouling 27(7):763–772
Traba C, Liang JF (2015) The inactivation of Staphylococcus aureus biofilms using low-power argon plasma in a layer-by-layer approach. Biofouling 31(1):39–48
Traba C, Chen L, Liang JF (2013a) Low power gas discharge plasma mediated inactivation and removal of biofilms formed on biomaterials. Curr Appl Phys 13:S12–S18
Traba C, Chen L, Liang D, Azzam R, Liang JF (2013b) Insights into discharge argon-mediated biofilm inactivation. Biofouling 29(10):1205–1213
Traylor MJ, Pavlovich MJ, Karim S, Hait P, Sakiyama Y, Clark DS, Graves DB (2011) Long-term antibacterial efficacy of air-plasma-activated water. J Phys D Appl Phys 44(47):472001
Zhang W, Zhang Y, Ji J, Zhao J, Yan Q, Chu PK (2006) Antimicrobial properties of copper plasma-modified polyethylene. Polymer 47:7441–7445
Zhang W, Zhang Y, Ji J, Zhao J, Yan Q, Huang A, Chu PK (2007) Antimicrobial properties of copper plasma-modified polyethylene. J Biomed Mater Res Part A 83A:838–844
Zhang Q, Liang Y, Feng H, Ma R, Tian Y, Zhang J, Fang J (2013) A study of oxidative stress induced by non-thermal plasma-activated water for bacterial damage. Appl Phys Lett 102(20):203701
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Dr. Christian Traba for his assistance in scanning electron microscopy and confocal microscopy.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Responsible editor: Bingcai Pan
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, TP., Liang, J. & Su, TL. Plasma-activated water: antibacterial activity and artifacts?. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25, 26699–26706 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9169-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9169-0