Abstract
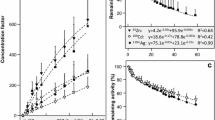
The clam Gafrarium pectinatum was investigated to assess its usefulness as a bioindicator species of metal mining contamination in the New Caledonia lagoon. The uptake and depuration kinetics of Ag, Cd, Co, Cr, and Zn were determined following exposures via seawater, sediment, and food using highly sensitive radiotracer techniques (110mAg, 109Cd, 51Cr, 57Co, and 65Zn). When the clams were exposed to dissolved metals, Co, Zn, and Ag were readily incorporated in their tissues (concentration factors (CF) ranging from 181 to 4982 after 28 days of exposure) and all metals were strongly retained (biological half-lives always >2 months). The estimated transfer factor (TF) in clam tissues after a 35-day sediment exposure was 1 to 4 orders of magnitude lower than the estimated CF, indicating a lower bioavailability of sediment-bound metals than dissolved ones. Once incorporated, metals taken up from sediment and seawater were retained longer than metals ingested with food, indicating that the uptake pathway influences the storage processes of metals in clam tissues. Compilation of our data into a global bioaccumulation model indicated that, except for Ag that essentially originated from food (92%), sediment was the main source of metal bioaccumulation in the clam (more than 80%). These results highlight that bioaccumulation processes strongly depend from one metal to the other. The overall efficient bioaccumulation and retention capacities of the clam G. pectinatum confirm its usefulness as a bioindicator species that can provide time-integrated information about ambient contamination levels in the tropical marine coastal environment.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ambatsian P, Fernex F, Bernat M, Parron C, Lecolle J (1997) High metal inputs to closed seas: the New Caledonian lagoon. J Geochem Explor 59(1):59–74
Berthet B, Amiard J-C, Amiard-Triquet C et al (1992) Bioaccumulation toxicity and physico-chemical speciation of silver in bivalve molluscs: ecotoxicological and health consequences. Sci Total Environ 125:97–122
Bird ECF, Dubois JP, Iltis JA (1984) The impacts of opencast mining on the rivers and coasts of New Caledonia. The United Nations University, Tokyo, p 53
Bonnet X, Briand MJ, Brischoux F et al (2014) Anguilliform fish reveal large scale contamination by mine trace elements in the coral reefs of New Caledonia. Sci Total Environ 470–471:876–882. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.10.027
Borovicka J, Randa Z, Jelínek E et al (2007) Hyperaccumulation of silver by Amanita strobiliformis and related species of the section Lepidella. Mycol Res 111:1339–1344. doi:10.1016/j.mycres.2007.08.015
Boyden CR (1977) Effect of size upon metal content of shellfish. J Mar Biol Assoc United Kingdom 57:675–714
Bruland KD (1983) Trace elements in seawater. In: Chester R (ed) Riley JP. Chem. Oceanogr. Academic Press, London, pp 157–201
Cheung KH, Gu J-D (2003) Reduction of chromate (CrO42-) by an enrichment consortium and an isolate of marine sulfate-reducing bacteria. Chemosphere 52:1523–1529
Chong K, Wang W-X (2000a) Assimilation of cadmium, chromium and zinc by the green mussel Perna viridis and the clam Ruditapes philippinarum. Environ Toxicol Chem 19:1660–1667
Chong K, Wang W-X (2000b) Bioavailability of sediment-bound Cd, Cr and Zn to the green mussel Perna viridis and the Manila clam Ruditapes philippinarum. J Exp Mar Bio Ecol 255:75–92
Dalvi A, Bacon W, Osborne R (2004) The past and the future of nickel laterites
Decho AW, Luoma SN (1991) Time-courses in the retention of food material in the bivalves Potamocorbula amurensis and Macoma balthica: significance to the absorption of carbon and chromium. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 78:303–314
Gissi F, Stauber JL, Binet MT et al (2016) A review of nickel toxicity to marine and estuarine tropical biota with particular reference to the South East Asian and Melanesian region. Environ Pollut 218:1308–1323. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2016.08.089
Greger M (2004) Metal availability, uptake, transport and accumulation in plants. In: MNV P (ed) Heavy met. stress plants from biomol. to ecosyst, 2nd edn. Springer, Berlin, pp 1–27
Griscom SB, Fisher NS, Luoma SN (2000) Geochemical influences on assimilation of sediment-bound metals in clams and mussels. Environ Sci Technol 34:91–99
Griscom SB, Fisher NS, Aller RC, Lee BG (2002a) Effects of gut chemistry in marine bivalves on the assimilation of metals from ingested sediment particles. J Mar Res 60:101–120
Griscom SB, Fisher NS, Luoma SN (2002b) Kinetic modeling of Ag, Cd and Co bioaccumulation in the clam Macoma balthica: quantifying dietary and dissolved sources. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 240:127–141
Hansen DJ, Berry WJ, Mahony JD et al (1996) Predicting the toxicity of metal-contaminated field sediments using interstitial concentration of metals and acid-volatile sulfide normalizations. Environ Toxicol Chem 15:2080–2094
Hédouin L, Metian M, Teyssié J-L et al (2006) Allometric relationships in the bioconcentration of heavy metals by the edible tropical clam Gafrarium tumidum. Sci Total Environ 366:154–163
Hédouin L, Pringault O, Metian M et al (2007) Nickel bioaccumulation in bivalves from the New Caledonia lagoon: seawater and food exposure. Chemosphere 66:1449–1457
Hédouin L, Bustamante P, Churlaud C et al (2008a) Trends in concentrations of selected metalloid and metals in two bivalves from the coral reefs in the SW lagoon of New Caledonia. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 72:372–381
Hédouin L, Bustamante P, Fichez R, Warnau M (2008b) The tropical brown alga Lobophora variegata as a bioindicator of mining contamination in the New Caledonia lagoon: a field transplantation study. Mar Environ Res 66:438–444
Hédouin L, Gomez Batista M, Metian M et al (2010a) Metal and metalloid bioconcentration capacity of two tropical bivalves for monitoring the impact of land-based mining activities in the New Caledonia lagoon. Mar Pollut Bull 61:554–567
Hédouin L, Metian M, Lacoue-Labarthe T et al (2010b) Influence of food on the assimilation of selected metals in tropical bivalves from the New Caledonia lagoon: qualitative and quantitative aspects. Mar Pollut Bull 61:568–575
Hédouin L, Metian M, Teyssié J-L et al (2010c) Delineation of heavy metal contamination pathways (seawater, food and sediment) in tropical oysters from New Caledonia using radiotracer techniques. Mar Pollut Bull 61:542–553. doi:10.1016/j.marpolbul.2010.06.037
Hédouin L, Pringault O, Bustamante P et al (2011) Validation of two tropical marine bivalves as bioindicators of mining contamination in the New Caledonia lagoon: transplantation experiments. Water Res 45:483–496
Hédouin L, Metian M, Teyssié JL et al (2016) Bioaccumulation of 63Ni in the scleractinian coral Stylophora pistillata and isolated Symbiodinium using radiotracer techniques. Chemosphere 156:420–427
Howe PL, Reichelt-Brushett AJ, Clark MW (2014) Effects of Cd, Co, Cu, Ni and Zn on asexual reproduction and early development of the tropical sea anemone Aiptasia pulchella. Ecotoxicology 23:1593–1606. doi:10.1007/s10646-014-1299-2
IAEA (2004) Sediments distribution coefficients and concentration factors for biota in the marine environment. International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA), Vienna, Austria 95 p
Jaffré T, Pillon Y, Thomine S, Merlot S (2013) The metal hyperaccumulators from New Caledonia can broaden our understanding of nickel accumulation in plants. Front Plant Sci 4:279. doi:10.3389/fpls.2013.00279
Labrosse P, Fichez R, Farman R, Adams T (2000) New Caledonia. In: Sheppard CRC (ed) Seas Millenn. An Environ. Eval, Pergamon, Amsterdam, pp 723–736
Laganier R (1991) Erosion, transport and sedimentation processes associated with open-coast mining in New Caledonia: interac- tions with weather and climate. ORSTOM, South Pacific environments: interactions with weather and climate, New Zealand; p 83–5
Landrum PF, Lee H, Lydy MJ (1992) Toxicokinetics in aquatic systems: model comparisons and use in hazard assessment. Environ Toxicol Chem 11:1709–1725
Lee BG, Luoma SN (1998) Influence of microalgal biomass on absorption efficiency of Cd, Cr and Zn by two bivalves from San Francisco Bay. Limnol Oceanogr 43:1455–1466
Luoma SN (1989) Can we determine the biological availability of sediment-bound trace elements? Hydrobiologia 176(177):379–396
Mayer LM, Chen Z, Findlay RH et al (1996) Bioavailability of sedimentary contaminants subject to deposit-feeder digestion. Environ Sci Technol 30:2641–2645
Metian M, Warnau M (2008) The tropical brown alga Lobophora variegata: a prospective bioindicator for Ag contamination in tropical coastal waters. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 81:455–458
Metian M, Hédouin L, Barbot C et al (2005) Use of radiotracer techniques to study subcellular distribution of metals and radionuclides in bivalves from the Noumea lagoon, New Caledonia. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 75:89–93
Metian M, Warnau M, Oberhänsli F et al (2007) Interspecific comparison of Cd bioaccumulation in European Pectinidae (Chlamys varia and Pecten maximus). J Exp Mar Bio Ecol 353:58–67
Metian M, Bustamante P, Cosson RP et al (2008a) Investigation of Ag in the king scallop Pecten maximus using field and laboratory approaches. J Exp Mar Bio Ecol 367:53–60
Metian M, Bustamante P, Hédouin L, Warnau M (2008b) Accumulation of nine metals and one metalloid in the tropical scallop Comptopallium radula from coral reefs in New Caledonia. Environ Pollut 152:543–552
Metian M, Hédouin L, Giron E et al (2008c) The brown alga Lobophora variegata, a bioindicator species for surveying metal contamination in tropical marine environments. J Exp Mar Bio Ecol 362:49–54
Metian M, Bustamante P, Hédouin L et al (2009a) Delineation of heavy metal uptake pathways (seawater and food) in the variegated scallop Chlamys varia using radiotracer techniques. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 375:161–171
Metian M, Hédouin L, Warnau M, Bustamante P (2009b) Bioaccumulation kinetics of essential metals (Co, Mn and Zn) in the king scallop Pecten maximus: relative contribution of seawater, food and sediment pathways. Mar Biol 156:2063–2075
Metian M, Hédouin L, Eltayeb MM et al (2010) Metal and metalloid bioaccumulation in the Pacific blue shrimp Litopenaeus stylirostris (Stimpson) from New Caledonia: laboratory and field studies. Mar Pollut Bull 61:576–584. doi:10.1016/j.marpolbul.2010.06.035
Metian M, Warnau M, Chouvelon T et al (2013) Trace element bioaccumulation in reef fish from New Caledonia: influence of trophic groups and risk assessment for consumers. Mar Environ Res 87–88:26–36. doi:10.1016/j.marenvres.2013.03.001
Ng TY-T, Wang W-X (2004) Detoxification and effects of Ag, Cd, and Zn pre-exposure on metal uptake kinetics in the clam Ruditapes philippinarum. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 268:161–172
Ratte HT (1999) Bioaccumulation and toxicity of silver compounds: a review. Environ Toxicol Chem 18:89–108
Reinfelder JR, Fisher NS (1991) The assimilation of elements ingested by marine copepods. Science 251:794–796
Reinfelder JR, Fisher NS (1994) The assimilation of elements ingested by marine planktonic bivalve larvae. Limnol Oceanogr 39:12–20
Reinfelder J, Wang W-X, Luoma SN, Fisher NS (1997) Assimilation efficencies and turnover rates of trace elements in marine bivalves: a comparison of oysters, clams and mussels. Mar Biol 129:443–452
Reinfelder JR, Fisher NS, Luoma SN et al (1998) Trace element trophic transfer in aquatic organisms: a critique of the kinetic model approach. Sci Total Environ 219:117–135
Rodriguez y Baena AM, Metian M, Teyssié J-L et al (2006) Experimental evidence for 234Th bioaccumulation in three Antarctic crustaceans: potential implications for particle flux studies. Mar Chem 100:354–365. doi:10.1016/j.marchem.2005.10.022
Sañudo-Wilhelmy SA, Flegal R (1992) Anthropogenic silver in the southern California bight: a new tracer of sewage in coastal waters. Environ Sci Technol 26:2147–2151
Selck H, Forbes VE, Forbes TL (1998) Toxicity and toxicokinetics of cadmium in Capitella sp. I: relative importance of water and sediment as routes of cadmium uptake. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 164:167–178
Shanmugam P, Neelamani S, Ahn YH et al (2007) Assessment of the levels of coastal marine pollution of Chennai city, Southern India. Water Resour Manag 21:1187–1206. doi:10.1007/s11269-006-9075-6
Thomann RV, Mahony JD, Mueller R (1995) Steady-state model of biota sediment accumulation factor for metals in two marine bivalves. Environ Toxicol Chem 14:1989–1998
Wang W-X, Fisher NS (1996) Assimilation of trace elements and carbon by the mussel Mytilus edulis: effects of food composition. Limnol Oceanogr 41:197–207
Wang W-X, Fisher NS (1999) Assimilation efficiencies of chemical contaminants in aquatic invertebrates: a synthesis. Environ Toxicol Chem 18:2034–2045
Wang W-X, Fisher NS, Luoma SN (1996) Kinetic determinations of trace element bioaccumulation in the mussel Mytilus edulis. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 140:91–113
Warnau M, Fowler SW, Teyssié J-L (1996) Biokinetics of selected heavy metals and radionuclides in two marine macrophytes: the seagrass Posidonia oceanica and the alga Caulerpa taxifolia. Mar Environ Res 41:343–362
Warren L, Tessier A, Hare L (1998) Modelling cadmium accumulation by benthic invertebrates in situ: the relative contribution of sediment and overlying water reservoirs to organism cadmium concentrations. Limnol Oceanogr 43:1442–1454
Whicker FW, Schultz V (1982) Radioecology: nuclear energy and the environment. CRC Press, Florida
Wise SS, Xie H, Fukuda T et al (2014) Hexavalent chromium is cytotoxic and genotoxic to hawksbill sea turtle cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 279:113–118. doi:10.1016/j.taap.2014.06.008
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA). The support of French Ecosphère Continentale et Côtière—Programme National Environnement Côtier (EC2CO-PNEC) and the Institut de Recherche pour le Développement (IRD) is also acknowledged. The IAEA is grateful for the support provided to its Environment Laboratories by the Government of the Principality of Monaco. LH was beneficiary of a PhD grant (CIFRE, France) supported by the Goro Nickel Company, New Caledonia. MW is an Honorary Senior Research Associate of the National Fund for Scientific Research (NFSR, Belgium).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Georg Steinhauser
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hédouin, L., Metian, M., Teyssié, JL. et al. High contribution of the particulate uptake pathway to metal bioaccumulation in the tropical marine clam Gafrarium pectinatum . Environ Sci Pollut Res 25, 11206–11218 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-8562-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-8562-z