Abstract
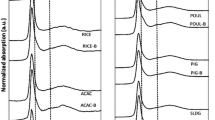
Converting swine manure to biochar is an effective way to recycle valuable nutrients, but there are few reports on its feasibility as a phosphorus (P) source. The objective of this study was to clarify the unique nature, including P speciation, of manure biochar products under various pyrolysis temperatures. We used solution 31P nuclear magnetic resonance and P K-edge X-ray adsorption near-edge spectroscopy (P XANES) to characterize P species in swine manure biochar. For every 100 °C increment starting from 300 °C, the P content in manure biochar increased by 2.16 to 3.37 g kg−1. However, above 400 °C, organic P species did not appear anymore, and only inorganic P, including orthophosphate and pyrophosphate, existed. P K-edge XANES spectra further showed all biochar samples had higher percentages of Ca3 (PO4)2 and NaP2O7, and lower percentages of FePO4, AlPO4, and inositol hexaphosphate compared to manure. Interestingly, percentages of Ca3(PO4)2, FePO4, and AlPO4 in MB400 (indicating manure pyrolysed at 400 °C) were comparable with those in MB700 while the percentage of NaP2O7 was higher in MB400. Phosphorus release from MB400 maintained a relatively high level at 0.33 g kg−1 during the whole 300-h observation period. These results suggest that with a suitable pyrolysis temperature, it was feasible for manure biochar to be a P source alternative.

ᅟ




Similar content being viewed by others
References
ASTM (2013) Standard test method for chemical analysis of wood charcoal. Am Soc Test Mater ASTM D1762–D1784. https://www.astm.org/Standards/D1762.htm
Cade–Menun BJ (2011) Characterizing phosphorus in animal waste with solution 31P NMR spectroscopy. In: He Z (ed) Environmental chemistry of animal manure. Nova Science Publisher. Inc, New York, pp 275–299
Cade–Menun BJ, Preston CM (1996) A comparison of soil extraction procedures for 31P NMR spectroscopy. Soil Sci 161:770–785
Cantrell KB, Hunt PG, Uchimiya M, Novak JM, Ro KS (2012) Impact of pyrolysis temperature and manure source on physicochemical characteristics of biochar. Bioresour Technol 107:419–428
Cao XD, Harris W (2010) Properties of dairy–manure–derived biochar pertinent to its potential use in remediation. Bioresour Technol 101:5222–5228
Gunes A, Inal A, Taskin MB, Sahin O, Kaya EC, Atakol O (2014) Effect of phosphorus-enriched biochar and poultry manure on growth and mineral composition of lettuce (Lactuca sativa L. cv.) grown in alkaline soil. Soil Use Manag 30(2):182–188
Gunes A, Inal A, Sahin O, Taskin MB, Atakol O, Yilmaz N (2015) Variations in mineral element concentrations of poultry manure biochar obtained at different pyrolysis temperatures, and their effects on crop growth and mineral nutrition. Soil Use Manag 31:429–437
Jin Y, Liang XQ, He MM, Liu Y, Tian GM, Shi JY (2016) Manure biochar influence upon soil properties, phosphorus distribution and phosphatase activities: a microcosm incubation study. Chemosphere 142:128–135
Liang XQ, Li L, Chen XY, Li H, Liu J, He MM, Ye YS, Tian GM, Lundy M (2013) Dissolved phosphorus losses by lateral seepage from swine manure amendments for organic rice production. Soil Sci Soc Am J 77(3):765–773
Liang Y, Cao XD, Zhao L, Xu XY, Harris W (2014) Phosphorus release from dairy manure, the manure-derived biochar, and their amended soil: effects of phosphorus nature and soil property. J Environ Qual 43(4):1504–1509
Mandal S, Sarkar B, Bolan N, Ok YS, Naidu R (2016) Enhancement of chromate reduction in soils by surface modified biochar. J Environ Manag 186:277–284
Marchetti R, Castelli F (2013) Biochar from swine solids and digestate influence nutrient dynamics and carbon dioxide release in soil. J Environ Qual 42(3):893–901
Muhammad N, Dai ZM, Xiao KC, Meng J, Brookes PC, Liu XM, Wang HZ, JJ W, JM X (2014) Changes in microbial community structure due to biochars generated from different feedstocks and their relationships with soil chemical properties. Geoderma 226:270–278
Silber A, Levkovitch I, Graber ER (2010) pH–dependent mineral release and surface properties of cornstraw biochar: agronomic implications. Environ Sci Technol 44(24):9318–9323
Tang XJ, Lou CL, Wang SX, YH L, Liu M, Hashmi MZ, Liang XQ, Li ZP, Liao YL, Qin WJ, Fan F, JM X, Brookes PC (2015) Effects of long-term manure applications on the occurrence of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs) in paddy soils: evidence from four field experiments in south of China. Soil Biol Biochem 90:179–187
Uchimiya M, Hiradate S (2014) Pyrolysis temperature-dependent changes in dissolved phosphorus speciation of plant and manure biochars. J Agric Food Chem 62(8):1802–1809
Uchimiya M, Bannon DI, Wartelle LH, Lima IM, Klasson KT (2012) Lead retention by broiler litter biochars in small arms range soil: impact of pyrolysis temperature. J Agric Food Chem 60(20):5035–5044
Wang Y, Lin YX, Chiu PC, Imhoff PT, Guo MX (2015) Phosphorus release behaviors of poultry litter biochar as a soil amendment. Sci Total Environ 512:454–463
Withers PJA, Sylvester-Bradley R, Jones DL, Healy JR, Talboys PJ (2014) Feed the crop not the soil: rethinking phosphorus management in the food chain. Environ Sci Technol 48:6523–6530
Zhao L, Cao XD, Zheng W, Wang Q, Yang F (2015) Endogenous minerals have influences on surface electrochemistry and ion exchange properties of biochar. Chemosphere 136:133–139
Funding
This study was supported by grants from the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2017YFD0800103), National Natural Science Foundation of China (41522108), and Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province (LR16B070001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Hailong Wang
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liang, X., Jin, Y., He, M. et al. Phosphorus speciation and release kinetics of swine manure biochar under various pyrolysis temperatures. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25, 25780–25788 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0640-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0640-8