Abstract
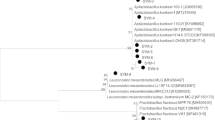
The development of novel antimicrobial drugs, as well as the discovery of novel compounds able to promote honeybee’s growth, represents major challenges for modern entomology. The main aim of this study was to investigate whether Brevibacillus laterosporus isolated from the digestive tract of Saudi honeybees, Apis mellifera, was able to stimulate colony strength parameters of honeybees and to evaluate its ability to produce antimicrobial agents. Honeybees were collected in Dirab, Riyadh Region, Saudi Arabia, and microorganisms were isolated and identified by 16S ribosomal RNA analysis. Microscopic identification of the microorganism in its native state was facilitated by atomic force microscopy at high-resolution imaging. Active biological compounds were produced by submerged fermentation with B. laterosporus. The fermented broth was subjected to extraction and purification, and then semi-pure compounds were analyzed by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. The effectiveness of the crude extract and semi-pure compounds as antimicrobial agents was evaluated by susceptibility assays. More than 22% of the microorganisms isolated from the digestive tract of healthy honeybees have been identified as B. laterosporus, this kind of species has a unique shape and morphological structure. The cyclic dipeptide cyclo(Leu-Pro) produced by B. laterosporus showed biological activity against several pathogenic microorganisms. Furthermore, the total counts of workers, closed brood, and open brood, as well as the production of bee pollen and honey, were better in honeybees treated with a B. laterosporus suspension. The data indicated that the B. laterosporus strain isolated from a healthy honeybee might be a novel probiotic and a producer of important biological compounds.







Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
09 July 2018
The original publication of this paper contains a mistake. The correct affiliation no. 3 is shown in this paper.
References
Alharbi NS, Khaled JM, Alzaharni KE, Mothana RA, Alsaid MS, Alhoshan M, Dass LA, Kadaikunnan S, Alobaidi AS (2017) Effects of Piper cubeba L essential oil on methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: an AFM and TEM study. J Mol Recognit 30
Benelli G (2017) Plant-borne compounds and nanoparticles: challenges for medicine, parasitology and entomology—GREEN-NANO-PEST&DRUGS. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9960-y
Biavati B, Castagnoli P, Crociani F, Trovatelli L (1984) Species of the Bifidobacterium in the feces of infants. Microbiologica 7:341
Corby-Harris V, Maes P, Anderson KE (2014) The bacterial communities associated with honey bee (Apis mellifera) foragers. PLoS One 9:e95056
De Oliveira EJ, Rabinovitch L, Monnerat RG, Passos LKJ, Zahner V (2004) Molecular characterization of Brevibacillus laterosporus and its potential use in biological control. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:6657–6664
Delaplane KS, van der Steen J, Guzman-Novoa E (2013) Standard methods for estimating strength parameters of Apis mellifera colonies. J Apic Res 52:1–12
Desjardine K, Pereira A, Wright H, Matainaho T, Kelly M, Andersen RJ (2007) Tauramamide, a lipopeptide antibiotic produced in culture by Brevibacillus laterosporus isolated from a marine habitat: structure elucidation and synthesis. J Nat Prod 70:1850–1853
Evans JD, Lopez DL (2004) Bacterial probiotics induce an immune response in the honey bee (Hymenoptera: Apidae). J Econ Entomol 97:752–756
Forsgren E, Olofsson TC, Vásquez A, Fries I (2010) Novel lactic acid bacteria inhibiting Paenibacillus larvae in honey bee larvae. Apidologie 41:99–108
Fuller R (1991) Probiotics in human medicine. Gut 32:439
Geraylou Z, Vanhove MP, Souffreau C, Rurangwa E, Buyse J, Ollevier F (2014) In vitro selection and characterization of putative probiotics isolated from the gut of Acipenser baerii (Brandt, 1869). Aquac Res 45:341–352
Graz M, Hunt A, Jamie H, Grant G, Milne P (1999) Antimicrobial activity of selected cyclic dipeptides. Die Pharmazie 54:772–775
Hadrich I, Makni F, Neji S, Cheikhrouhou F, Bellaaj H, Elloumi M, Ayadi A, Ranque S (2012) Amphotericin B in vitro resistance is associated with fatal Aspergillus flavus infection. Med Mycol 50:829–834
Hassi M, El Guendouzi S, Haggoud A, David S, Ibnsouda S, Houari A, Iraqui M (2012) Antimycobacterial activity of a Brevibacillus laterosporus strain isolated from a Moroccan soil. Braz J Microbiol 43:1516–1522
Hroncova Z, Havlik J, Killer J, Doskocil I, Tyl J, Kamler M, Titera D, Hakl J, Mrazek J, Bunesova V (2015) Variation in honey bee gut microbial diversity affected by ontogenetic stage, age and geographic location. PLoS One 10:e0118707
Hudzicki J (2009) Kirby-Bauer disk diffusion susceptibility test protocol. American Society for Microbiol
Karaman I, Şahin F, Güllüce M, Öǧütçü H, Şengül M, Adıgüzel A (2003) Antimicrobial activity of aqueous and methanol extracts of Juniperus oxycedrus L. J Ethnopharmacol 85:231–235
Kim HM, Hwang CY, Cho BC (2010) Arcobacter marinus sp. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 60:531–536
Martin-Laurent F, Philippot L, Hallet S, Chaussod R, Germon J, Soulas G, Catroux G (2001) DNA extraction from soils: old bias for new microbial diversity analysis methods. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:2354–2359
Moran NA, Hansen AK, Powell JE, Sabree ZL (2012) Distinctive gut microbiota of honey bees assessed using deep sampling from individual worker bees. PLoS One 7:e36393
Olofsson TC, Vásquez A (2009) Phylogenetic comparison of bacteria isolated from the honey stomachs of honey bees Apis mellifera and bumble bees Bombus spp. J Apic Res 48:233–237
Otero MC, Nader-Macías ME (2006) Inhibition of Staphylococcusaureus by H2O2-producing Lactobacillus gasseri isolated from the vaginal tract of cattle. Anim Reprod Sci 96:35–46
Pares S, Mouz N, Petillot Y, Hakenbeck R, Dideberg O (1996) X-ray structure of Streptococcus pneumoniae PBP2x, a primary penicillin target enzyme. Nat Struct Mol Biol 3:284–289
Pfaller M, Diekema D (2012) Progress in antifungal susceptibility testing of Candida spp. by use of Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute broth microdilution methods, 2010 to 2012. J Clin Microbiol 50:2846–2856
Saikia R, Gogoi D, Mazumder S, Yadav A, Sarma R, Bora T, Gogoi B (2011) Brevibacillus laterosporus strain BPM3, a potential biocontrol agent isolated from a natural hot water spring of Assam, India. Microbiol Res 166:216–225
Shida O, Takagi H, Kadowaki K, Komagata K (1996) Proposal for two new genera, Brevibacillus gen nov and Aneurinibacillus gen nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 46:939–946
Singer S (1996) The utility of strains of morphological group II Bacillus. Adv Appl Microbiol 42:219–261
Soto A, Martín V, Jiménez E, Mader I, Rodríguez JM, Fernández L (2014) Lactobacilli and bifidobacteria in human breast milk: influence of antibiotherapy and other host and clinical factors. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 59:78–88
Ström K, Sjögren J, Broberg A, Schnürer J (2002) Lactobacillus plantarum MiLAB 393 produces the antifungal cyclic dipeptides cyclo (L-Phe-L-Pro) and cyclo (L-Phe-trans-4-OH-L-Pro) and 3-phenyllactic acid. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:4322–4327
Tajabadi N, Mardan M, Manap MYA, Shuhaimi M, Meimandipour A, Nateghi L (2011) Detection and identification of Lactobacillus bacteria found in the honey stomach of the giant honeybee Apis dorsata. Apidologie 42:642–649
Vaseeharan B, Ramasamy P (2003) Control of pathogenic Vibrio spp. by Bacillus subtilis BT23, a possible probiotic treatment for black tiger shrimp Penaeus monodon. Lett Appl Microbiol 36:83–87
Winston ML (1991) The biology of the honey bee. Harvard University Press
Wu M, Sugimura Y, Takaya N, Takamatsu D, Kobayashi M, Taylor D, Yoshiyama M (2013) Characterization of bifidobacteria in the digestive tract of the Japanese honeybee, Apis cerana japonica. J Invertebr Pathol 112:88–93
Yang X, Huang E, Yuan C, Zhang L, Yousef AE (2016) Isolation and structural elucidation of brevibacillin, an antimicrobial Lipopeptide from Brevibacillus laterosporus that combats drug-resistant Gram-positive bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 82:2763–2772
Acknowledgements
This project was funded by (KACST) King Abdulaziz City for Science and Technology, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, Award Number (LGP-34-112).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khaled, J.M., Al-Mekhlafi, F.A., Mothana, R.A. et al. Brevibacillus laterosporus isolated from the digestive tract of honeybees has high antimicrobial activity and promotes growth and productivity of honeybee’s colonies. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25, 10447–10455 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0071-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0071-6