Abstract
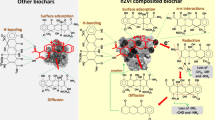
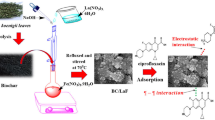
The adsorption removal of levofloxacin (LEV), a widely used fluoroquinolone antibiotic, by using the biochars derived from the pyrolysis of pine wood chip pretreated with cerium trichloride was investigated through batch sorption experiments and multiple characterization techniques. The differences in the basic physicochemical properties between Ce-impregnated biochars and the pristine biochars were confirmed by the analysis of elemental compositions, specific surface areas, energy dispersive spectrometry, X-ray diffraction, and thermo-gravimetry. FT-IR spectra of the pre- and post-sorption biochars confirmed the chemical adsorption for LEV sorption onto the biochars. Large shifts in the binding energy of Ce3d, O1s, C1s, and N1s regions on the pre- and post-sorption biochars indicated the surface complexation of LEV molecule onto the biochars. The binding species of Ce4+ and Ce3+ identified by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy reflect the role of Ce oxides during sorption. Batch adsorption showed the significant enhancement of adsorption capacity for LEV after the Ce modification. Batch adsorption kinetic data fitted well with the pseudo-second-order model. Both the Langmuir and the Freundlich models reproduced the isotherm data well. Findings from this work indicated that Ce-impregnated biochars can be effective for the removal of aqueous LEV.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brigante M, Schulz PC (2012a) Adsorption of the antibiotic minocycline on cerium(IV) oxide: effect of pH, ionic strength and temperature. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 156:138–144
Brigante M, Schulz PC (2012b) Cerium(IV) oxide: synthesis in alkaline and acidic media, characterization and adsorption properties. Chem Eng J 191:563–570
Datsyuk V, Kalyva M, Papagelis K, Parthenios J, Tasis D, Siokou A, Kallitsis I, Galiotis C (2008) Chemical oxidation of multiwalled carbon nanotubes. Carbon 46:833–840
Dawood S, Sen TK (2012) Removal of anionic dye Congo red from aqueous solution by raw pine and acid-treated pine cone powder as adsorbent: equilibrium, thermodynamic, kinetics, mechanism and process design. Water Res 46:1933–1946
Ding W, Dong X, Ime IM, Gao B, Ma LQ (2014) Pyrolytic temperatures impact lead sorption mechanisms by bagasse biochars. Chemosphere 105:68–74
Filgueiras AL, Paschoal D, Dos Santos HF, Sant'Ana AC (2015) Adsorption study of antibiotics on silver nanoparticle surfaces by surface-enhanced Raman scattering spectroscopy. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 136(Pt B):979–985
Guo X, Dong H, Yang C, Zhang Q, Liao C, Zha F, Gao L (2016) Application of goethite modified biochar for tylosin removal from aqueous solution. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 502:81–88
Hamid S, Chowdhury Z, Zain S (2014) Base catalytic approach: a promising technique for the activation of biochar for equilibrium sorption studies of copper, Cu(II) ions in single solute system. Materials 7:2815–2832
Hu J, Wang W, Zhu Z, Chang H, Pan F, Lin B (2007) Quantitative structure-activity relationship model for prediction of genotoxic potential for quinolone antibacterials. Environ Sci Technol 41:4806–4812
Hu X, Ding Z, Zimmerman AR, Wang S, Gao B (2015) Batch and column sorption of arsenic onto iron-impregnated biochar synthesized through hydrolysis. Water Res 68:206–216
Jin Z, Li J, Shi L, Ji Y, Zhong Z, Su F (2015) One-pot hydrothermal growth of raspberry-like CeO2 on CuO microsphere as copper-based catalyst for Rochow reaction. Appl Surf Sci 359:120–129
Jing X-R, Wang Y-Y, Liu W-J, Wang Y-K, Jiang H (2014) Enhanced adsorption performance of tetracycline in aqueous solutions by methanol-modified biochar. Chem Eng J 248:168–174
Luo Y, Xu L, Rysz M, Wang Y, Zhang H, Alvarez PJ (2011) Occurrence and transport of tetracycline, sulfonamide, quinolone, and macrolide antibiotics in the Haihe river basin, China. Environmental science & technology 45:1827–1833
Ma Y, Liu WJ, Zhang N, Li YS, Jiang H, Sheng GP (2014) Polyethylenimine modified biochar adsorbent for hexavalent chromium removal from the aqueous solution. Bioresour Technol 169:403–408
Mehrjouei M, Müller S, Möller D (2014) Treatment of pyrolysis wastewater using heterogeneous advanced oxidation processes. Environmental Progress & Sustainable Energy 33:178–183
Mohanad JMR, Muna YAA (2014) Adsorption of levofloxancine antibacterial from contaminated water by non-conventional low cost natural waste materials. Journal of Engineering 20:88–104
Mullins DR (2015) The surface chemistry of cerium oxide. Surf Sci Rep 70:42–85
Nagao M, Sudat Y (1989) Adsorption of benzene, toluene, and chlorobenzene on titanium dioxide. Langmuir 5:42–47
Peng L, Ren Y, Gu J, Qin P, Zeng Q, Shao J, Lei M, Chai L (2014) Iron improving bio-char derived from microalgae on removal of tetracycline from aqueous system. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 21:7631–7640
Rajapaksha AU, Chen SS, Tsang DCW, Zhang M, Vithanage M, Mandal S, Gao B, Bolan NS, Ok YS (2016) Engineered/designer biochar for contaminant removal/immobilization from soil and water: potential and implication of biochar modification. Chemosphere 148:276–291
Ramola S, Mishra T, Rana G, Srivastava RK (2014) Characterization and pollutant removal efficiency of biochar derived from bagasse, bamboo and tyre. Environ Monit Assess 186:9023–9039
Speltini A, Sturini M, Maraschi F, Profumo A (2010) Fluoroquinolone antibiotics in environmental waters: sample preparation and determination. J Sep Sci 33:1115–1131
Wang S, Gao B, Li Y, Mosa A, Zimmerman AR, Ma LQ, Harris WG, Migliaccio KW (2015a) Manganese oxide-modified biochars: preparation, characterization, and sorption of arsenate and lead. Bioresour Technol 181:13–17
Wang Y, Lu J, Wu J, Liu Q, Zhang H, Jin S (2015b) Adsorptive removal of fluoroquinolone antibiotics using bamboo biochar. Sustainability 7:12947–12957
Wang Z, Guo H, Shen F, Yang G, Zhang Y, Zeng Y, Wang L, Xiao H, Deng S (2015c) Biochar produced from oak sawdust by lanthanum (La)-involved pyrolysis for adsorption of ammonium (NH4(+)), nitrate (NO3(-)), and phosphate (PO4(3-)). Chemosphere 119:646–653
Xiao W, Guo Q, Wang EG (2003) Transformation of CeO2(1 1 1) to Ce2O3(0 0 0 1) films. Chem Phys Lett 368:527–531
Yao H, Lu J, Wu J, Lu Z, Wilson PC, Shen Y (2012) Adsorption of fluoroquinolone antibiotics by wastewater sludge biochar: role of the sludge source. Water Air Soil Pollut 224
Yi S, Gao B, Sun Y, Wu J, Shi X, Wu B, Hu X (2016) Removal of levofloxacin from aqueous solution using rice-husk and wood-chip biochars. Chemosphere 150:694–701
Zhang S-J, Huang Y-P, Liu Z-S, Duan H-Q (2011) Via protoporphyrin to the synthesis of levofloxacin-imprinted polymer. Polym Adv Technol 22:286–292
Zhou J-H, Sui Z-J, Zhu J, Li P, Chen D, Dai Y-C, Yuan W-K (2007) Characterization of surface oxygen complexes on carbon nanofibers by TPD, XPS and FT-IR. Carbon 45:785–796
Acknowledgments
This work was partially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China-Xinjiang Project (U1503282) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41372234).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 1583 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yi, S., Sun, Y., Hu, X. et al. Porous nano-cerium oxide wood chip biochar composites for aqueous levofloxacin removal and sorption mechanism insights. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25, 25629–25637 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-8342-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-8342-1