Abstract
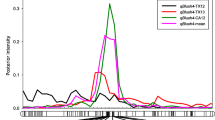
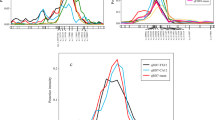
Bloom date is an important production trait in sour cherry (Prunus cerasus L.) as the risk of crop loss to floral freeze injury increases with early bloom time. Knowledge of the major loci controlling bloom date would enable breeders to design crosses and select seedlings with late bloom date. As sour cherry is a segmental allotetraploid, quantitative trait locus (QTL) analysis for bloom date was performed based on haplotype reconstruction by identifying the parental origins of marker alleles in sour cherry. A total of 338 sour cherry individuals from five F1 populations were genotyped using the cherry 6K Illumina Infinium® SNP array and phenotyped for bloom date in 3 years. A total of four QTLs were identified on linkage group (G)1, G2, G4, and G5, respectively. For these QTLs, 14 haplotypes constructed for the QTL regions were significantly associated with bloom date, accounting for 10.1–27.9% of the bloom date variation within individual populations. The three most significant haplotypes, which were identified for the G4 (G4-k), G2 (G2-j), and G1 (G1-c) QTLs, were associated with 2.8, 1.8, and 1.0 days bloom delay, respectively. These three haplotypes were also demonstrated to have additive effects on delaying bloom date for both individual and multiple QTLs. These results demonstrate that bloom date is under polygenic control in sour cherry; yet, pyramiding late blooming haplotypes for single and multiple QTLs would be an effective strategy to obtain later blooming offspring.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersen RL, Brown SK, Way RD, Livermore KG, Terry DE (1999) Sour cherry cultivar named ‘Surefire’. U.S. plant patent 11108P
Anderson JL, Seeley SD (1993) Bloom delay in deciduous fruits. Hortic Rev 15:97–144
Ballester J, Socias I, Company R, Arús P, deVicente MC (2001) Genetic mapping of a major gene delaying blooming time in almond. Plant Breed 120(3):268–270. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1439-0523.2001.00604.x
Beaver JA, Iezzoni AF (1993) Allozyme inheritance in tetraploid sour cherry (Prunus cerasus L.) J Am Soc Hortic Sci 118:873–877
Birchler JA, Newton KJ (1981) Modulation of protein levels in chromosomal dosage series of maize: the biochemical basis of aneuploid syndromes. Genetics 99(2):247–266
Bourke PM (2014) QTL analysis in polyploids: model testing and power calculations for an autotetraploid. In: Minor thesis (MSc) plant breeding, University and Research Centre, Wageningen
Cai L, Voorrips RE, van de Weg E, Peace P, Iezzoni A (2017) Genetic structure of a QTL hotspot on chromosome 2 in sweet cherry indicates positive selection for favorable haplotypes. Mol Breed 37(7):85. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-017-0689-6
Campoy JA, Ruiz D, Egea J, Rees DJG, Celton JM, Martinez-Gomez P (2011) Inheritance of flowering time in apricot (Prunus armeniaca L.) and analysis of linked quantitative trait loci (QTLs) using simple sequence repeat (SSR) markers. Plant Mol Biol Rep 29(2):404–410. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11105-010-0242-9
Castède S, Campoy JA, García JQ, Le Dantec L, Lafargue M, Barreneche T, Wenden B, Dirlewanger E (2014) Genetic determinism of phenological traits highly affected by climate change in Prunus avium: flowering data dissected into chilling and heat requirements. New Phytol 202(2):703–715. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.12658
Castède S, Campoy JA, Le Dantec L, Quero-García J, Barreneche T, Wenden B, Dirlewanger E (2015) Mapping of candidate genes involved in bud dormancy and flowering time in sweet cherry (Prunus avium). PLoS One 10(11):e0143250. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0143250
Churchill GA, Doerge RW (1994) Empirical threshold values for quantitative trait mapping. Genetics 138(3):963–971
De Franceschi P, Stegmeir T, Cabrera A, van der Knaap E, Rosyara UR, Sebolt AM, Dondini L, Dirlewanger E, Quero-Garcia J, Campoy JA, Iezzoni AF (2013) Cell number regulator genes in Prunus provide candidate genes for the control of fruit size in sweet and sour cherry. Mol Breed 32(2):311–326. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-013-9872-6
Dirlewanger E, Moing A, Rothan C, Svanella L, Pronier V, Guye A, Plomion C, Monet R (1999) Mapping QTLs controlling fruit quality in peach (Prunus persica (L.) Batsch). Theor Appl Genet 98(1):18–31. https://doi.org/10.1007/s001220051035
Dirlewanger E, Graziano E, Joobeur T, Garriga-Caldere F, Cosson P, Howard W, Arus P (2004) Comparative mapping and marker-assisted selection in Rosaceae fruit crops. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101(26):9891–9896. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0307937101
Dirlewanger E, Claverie J, Iezzoni AF, Wunsch A (2009) Sweet and sour cherry: linkage maps, QTL detection and marker assisted selection. In: Folta KM, Gardiner SE (eds) Genetics and Genomics of Rosaceae. Springer, New York, pp 291–313. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-0-387-77491-6_14
Dirlewanger E, Quero-García J, Le Dantec L, Lambert P, Ruiz D, Dondini L, Illa E, Quilot-Turion B, Audergon J-M, Tartarini S, Letourmy P, Arús P (2012) Comparison of the genetic determinism of two key phenological traits, flowering and maturity dates, in tree Prunus species: peach, apricot and sweet cherry. Heredity 109(5):280–292. https://doi.org/10.1038/hdy.2012.38
Fan S, Bielenberg DG, Zhebentyayeva TN, Reighard GL, Okie WR, Holland D, Abbott AG (2010) Mapping quantitative trait loci associated with chilling requirement, heat requirement and bloom date in peach (Prunus persica). New Phytol 185(4):917–930. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2009.03119.x
Guo M, Davis D, Birchler JA (1996) Dosage effects on gene expression in a maize ploidy series. Genetics 142(4):1349–1355
Hackett CA, Milne I, Bradshaw JE, Luo Z (2007) TetraploidMap for windows: linkage map construction and QTL mapping in autotetraploid species. J Hered 98(7):727–729. https://doi.org/10.1093/jhered/esm086
Iezzoni AF (1996) Sour cherry cultivars: objectives and methods of fruit breeding and characteristics of principal commercial cultivars. In: Webster AD, Looney NE (eds) Cherries: Crop physiology, production and uses. University Press, Cambridge, pp 223–241
Illumina Inc. (2010) GenomeStudio genotyping module v1.0, User Guide. Illumina Inc., San Diego
Iovene M, Zhang T, Lou Q, Buell CR, Jiang J (2013) Copy number variation in potato—an asexually propagated autotetraploid species. Plant J 75(1):80–89. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.12200
Klagges C, Campoy JA, Quero-Garcia J, Guzman A, Mansur L, Gratacos E, Silva H, Rosyara UR, Iezzoni A, Meisel LA, Dirlewanger E (2013) Construction and comparative analyses of highly dense linkage maps of two sweet cherry intra-specific progenies of commercial cultivars. PLoS One 8(1):e54743. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0054743
NASS (2012) National Agricultural Statistics Service. http://www.nass.usda.org
Peace C, Bassil N, Main D, Ficklin S, Rosyara UR, Stegmeir T, Sebolt A, Gilmore B, Lawley C, Mockler TC, Bryant DW, Wilhelm L, Iezzoni A (2012) Development and evaluation of a genome-wide 6K SNP array for diploid sweet cherry and tetraploid sour cherry. PLoS One 7(12):e48305. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0048305
Pirona R, Eduardo I, Pacheco I, Da Silva Linge C, Miculan M, Verde I, Tartarini S, Dondini L, Pea G, Bassi D, Rossini L (2013) Fine mapping and identification of a candidate gene for a major locus controlling maturity date in peach. BMC Plant Biol 13(1):166. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2229-13-166
Quilot B, Wu BH, Kervella J, Genard M, Foulongne M, Moreau K (2004) QTL analysis of quality traits in an advanced backcross between Prunus persica cultivars and the wild relative species P. davidiana. Theor Appl Genet 109(4):884–897. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-004-1703-z
R Core Team (2015) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna URL http://www.R-project.org/
Rak K, Bethke PC, Palta JP (2017) QTL mapping of potato chip color and tuber traits within an autotetraploid family. Mol Breed 37(2):15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-017-0619-7
Sánchez-Pérez W, Howad F, Dicenta P, Arús, P, Martínez-Gómez P (2007) Mapping major genes and quantitative trait loci controlling agronomic traits in almond. Plant Breed 126(3):310–318. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1439-0523.2007.01329.x
Sánchez-Pérez R, Del Cueto J, Dicenta F, Martínez-Gómez P (2014) Recent advancements to study flowering time in almond and other Prunus species. Front Plant Sci 5:334
Schuster M, Wolfram B (2005) Sour cherry breeding at Dresden-Pillnitz. Acta Hortic (667):127–130. https://doi.org/10.17660/ActaHortic.2005.667.17
Stegmeir T, Sebolt A, Iezzoni A (2014a) Phenotyping protocol for sour cherry (Prunus cerasus L.) to enable a better understanding of trait inheritance. J Am Pomol Soc 68:40–47
Stegmeir T, Schuster M, Sebolt A, Rosyara U, Sundin GW, Iezzoni A (2014b) Cherry leaf spot resistance in cherry (Prunus) is associated with a quantitative trait locus on linkage group 4 inherited from P. canescens. Mol Breed 34(3):927–935. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-014-0086-3
Stegmeir T, Cai L, Basundari FRA, Sebolt AM, Iezzoni AF (2015) A DNA test for fruit color in tetraploid sour cherry (Prunus cerasus L.) Mol Breed 35(7):149. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-015-0337-y
Teo YY, Inouye M, Small KS, Gwilliam R, Deloukas P, Kwiatkowski DP, Clark TG (2007) A genotype calling algorithm for the Illumina Bead Array platform. Bioinformatics 23(20):2741–2746. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btm443
Verde I, Quarta R, Cedrola C, Dettori MT (2002) QTL analysis of agronomic traits in a BC1 peach population. Acta Hortic (592):291–297. https://doi.org/10.17660/ActaHortic.2002.592.41
Verde I, Jenkins J, Dondini L, Micali S, Pagliarani G, Vendramin E, Paris R, Aramini V, Gazza L, Rossini L, Bassi D, Troggio M, Shu S, Grimwood J, Tartarini S, Dettori MT, Schmutz J (2017) The Peach v2.0 release: high-resolution linkage mapping and deep resequencing improve chromosome-scale assembly and contiguity. BMC Genomics 18(1):225. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-017-3606-9
Wang D, Karle R, Iezzoni AF (2000) QTL analysis of flower and fruit traits in sour cherry. Theor Appl Genet 100(3-4):535–544. https://doi.org/10.1007/s001220050070
Zhang G, Sebolt A, Sooriyapathirana S, Wang D, Bink M, Olmstead J, Iezzoni A (2010) Fruit size QTL analysis of an F1 population derived from a cross between a domesticated sweet cherry cultivar and a wild forest sweet cherry. Tree Genet Genomes 6(1):25–36. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-009-0225-x
Zheng C, Voorrips RE, Jansen J, Hackett CA, Ho J, Bink MC (2016) Probabilistic multilocus haplotype reconstruction in outcrossing tetraploids. Genetics 203(1):119–131. https://doi.org/10.1534/genetics.115.185579
Acknowledgements
This project was supported in part by the USDA-NIFA-Specialty Crop Research Initiative project, RosBREED: Enabling marker-assisted breeding in Rosaceae (2009-51181-05808), and RosBREED 2: Combining disease resistance with horticultural quality in new rosaceous cultivars (2014-51181-22378).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Data Archiving Statement
The linkage map constructed and the QTL regions identified will be made available at the Genome Database for Rosaceae (www.rosaceae.org/publication_datasets) under accession number tfGDR 1033.
Additional information
Communicated by E. Dirlewanger
Electronic supplementary material
Supplementary Table S1
(DOCX 15 kb)
Supplementary Table S2
(DOCX 17 kb)
Supplementary Table S3
(DOCX 46 kb)
Supplementary Fig. S1
(DOCX 165 kb)
Supplementary Fig. S2
(DOCX 61 kb)
Supplementary Fig. S3
(XLSX 20 kb)
Supplementary Fig. S4
(XLSX 22 kb)
Supplementary Fig. S5
(XLSX 17 kb)
Supplementary Fig. S6
(XLSX 23 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cai, L., Stegmeir, T., Sebolt, A. et al. Identification of bloom date QTLs and haplotype analysis in tetraploid sour cherry (Prunus cerasus). Tree Genetics & Genomes 14, 22 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-018-1236-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-018-1236-2