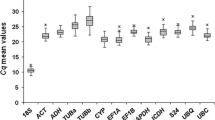
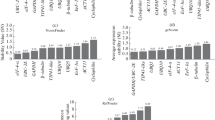
Abstract
The reliability of analyses using real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) depends on the selection of appropriate reference genes to correct for sample-to-sample and run-to-run variations. The aim of the present study was to select the most suitable reference genes for gene expression analyses in tissue samples from coffee, Coffea arabica L. (Arabica) grown under well-watered (WW) and water-deficit (WD) conditions and C. canephora Pierre ex A. Froehner (Robusta) grown under WW conditions. Expression profiles and stabilities were evaluated for 12 reference genes in different tissues from C. arabica and for 8 genes in tissues from C. canephora. The web-based RefFinder tool, which combines the geNorm, NormFinder, Bestkeeper, and Delta-Ct algorithms, was employed to assess the stability of the tested genes. The most stable reference genes identified for all tissues grouped (WW/WD) of C. arabica were clathrin adaptor protein medium subunit (AP47), ubiquitin (UBQ), 60S ribosomal protein L39 (RPL39), and elongation factor 1α (EF1α), while class III alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH2), β-actin (ACT), glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH), and ubiquitin (UBQ) genes were the most stable for all tissues grouped (WW) of C. canephora tissues. Validation by the expression level analysis of CaACO-like demonstrated that the use of the best and the worst set of reference genes produced different expression results. The results reinforce the general assumption that there is no universal reference gene and that it is essential to select the most appropriate gene for each individual experiment to apply adequate normalization procedures of RT-qPCR data.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achkor H, Díaz M, Fernández MR, Biosca JA, Parés X, Martínez MC (2003) Enhanced formaldehyde detoxification by overexpression of glutathione-dependent formaldehyde dehydrogenase from Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 132(4):2248–2255. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.103.022277
Andersen CL, Jensen JL, Ørntoft TF (2004) Normalization of real-time quantitative reverse transcription-PCR data: a model-based variance estimation approach to identify genes suited for normalization, applied to bladder and colon cancer data sets. Cancer Res 64(15):5245–5250. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-0496
Andersen GR, Nyborg J (2001) Structural studies of eukaryotic elongation factors. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol 66(0):425–438. https://doi.org/10.1101/sqb.2001.66.425
Arraes FB et al (2015) Implications of ethylene biosynthesis and signaling in soybean drought stress tolerance. BMC Plant Biol 15(1):213. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-015-0597-z
Ballesteros I, Domínguez T, Sauer M, Paredes P, Duprat A, Rojo E, Sanmartín M, Sánchez-Serrano JJ (2013) Specialized functions of the PP2A subfamily II catalytic subunits PP2A-C3 and PP2A-C4 in the distribution of auxin fluxes and development in Arabidopsis. Plant J 73(5):862–872. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.12078
Barbin DF, ALdSM F, Sun D-W, Nixdorf SL, Hirooka EY (2014) Application of infrared spectral techniques on quality and compositional attributes of coffee: an overview. Food Res Int 61:23–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2014.01.005
Barsalobres-Cavallari CF, Severino FE, Maluf MP, Maia IG (2009) Identification of suitable internal control genes for expression studies in Coffea arabica under different experimental conditions. BMC Mol Biol 10(1):1. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2199-10-1
Bonifacino JS (2014) Adaptor proteins involved in polarized sorting. J Cell Biol 204(1):7–17. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.201310021
Bustin SA, Benes V, Garson JA, Hellemans J, Huggett J, Kubista M, Mueller R, Nolan T, Pfaffl MW, Shipley GL, Vandesompele J, Wittwer CT (2009) The MIQE guidelines: minimum information for publication of quantitative real-time PCR experiments. Clin Chem 55(4):611–622. https://doi.org/10.1373/clinchem.2008.112797
Campos MD, Frederico AM, Nothnagel T, Arnholdt-Schmitt B, Cardoso H (2015) Selection of suitable reference genes for reverse transcription quantitative real-time PCR studies on different experimental systems from carrot (Daucus carota L.) Sci Horti-Amsterdam 186:115–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2014.12.038
Cassol D, Cruz FP, Espindola K, Mangeon A, Müller C, Loureiro ME, Corrêa RL, Sachetto-Martins G (2016) Identification of reference genes for quantitative RT-PCR analysis of microRNAs and mRNAs in castor bean (Ricinus communis L.) under drought stress. Plant Physiol Bioch 106:101–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2016.02.024
Chen L, H-y Z, Kuang J-f, J-g L, Lu W-j, J-y C (2011) Validation of reference genes for RT-qPCR studies of gene expression in banana fruit under different experimental conditions. Planta 234(2):377–390. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-011-1410-3
Cheng D, Zhang Z, He X, Liang G (2013) Validation of reference genes in Solenopsis invicta in different developmental stages, castes and tissues. PLoS One 8(2):e57718. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0057718
Cruz F, Kalaoun S, Nobile P, Colombo C, Almeida J, Barros LMG, Romano E, Grossi-de-Sá MF, Vaslin M, Alves-Ferreira M (2009) Evaluation of coffee reference genes for relative expression studies by quantitative real-time RT-PCR. Mol Breeding 23(4):607–616. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-009-9259-x
Davis AP, Tosh J, Ruch N, Fay MF (2011) Growing coffee: Psilanthus (Rubiaceae) subsumed on the basis of molecular and morphological data; implications for the size, morphology, distribution and evolutionary history of Coffea. Bot J Linn Soc 167(4):357–377. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1095-8339.2011.01177.x
de Carvalho K, Bespalhok Filho JC, Dos Santos TB, de Souza SGH, Vieira LGE, Pereira LFP, Domingues DS (2013) Nitrogen starvation, salt and heat stress in coffee (Coffea arabica L.): identification and validation of new genes for qPCR normalization. Mol Biotechnol 53(3):315–325. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-012-9529-4
de la Cruz J, Karbstein K, Woolford Jr JL (2015) Functions of ribosomal proteins in assembly of eukaryotic ribosomes in vivo. Annu Rev Biochem 84(1):93–129. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-biochem-060614-033917
De Santis C, Smith-Keune C, Jerry DR (2011) Normalizing RT-qPCR data: are we getting the right answers? An appraisal of normalization approaches and internal reference genes from a case study in the finfish Lates calcarifer. Mar Biotechnol 13(2):170–180. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10126-010-9277-z
Fall R, Benson AA (1996) Leaf methanol—the simplest natural product from plants. Trends Plant Sci 1(9):296–301. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1360-1385(96)88175-0
Ferradás Y, Rey L, Martínez Ó, Rey M, González MV (2016) Identification and validation of reference genes for accurate normalization of real-time quantitative PCR data in kiwifruit. Plant Physiol Bioch 102:27–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2016.02.011
Figueiredo A, Loureiro A, Batista D, Monteiro F, Várzea V, Pais M, Gichuru EK, Silva M (2013) Validation of reference genes for normalization of qPCR gene expression data from Coffea spp. hypocotyls inoculated with Colletotrichum kahawae. BMC Res Notes 6(1):388. https://doi.org/10.1186/1756-0500-6-388
Freitas NC, Barreto HG, Fernandes-Brum CN, Moreira RO, Chalfun-Junior A, Paiva LV (2016) Validation of reference genes for qPCR analysis of Coffea arabica L. somatic embryogenesis-related tissues. Plant Cell Tiss Org Culture 128(3):663–678. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-016-1147-6
Goulao LF, Fortunato AS, Ramalho JC (2012) Selection of reference genes for normalizing quantitative real-time PCR gene expression data with multiple variables in Coffea spp. Plant Mol Biol Rep 30(3):741–759. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11105-011-0382-6
Gu C-S, Liu L-Q, Deng Y-M, Zhu X-D, Lu X-Q, Huang S-Z (2014) Validation of reference genes for RT-qPCR normalization in Iris. lactea var. chinensis leaves under different experimental conditions. Sci Hortic-Amsterdam 175:144–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2014.06.011
Guerreiro-Filho O, Mendes ANG, Carvalho GR, Silvarolla MB, Botelho CE, Fazuoli LC (2008) Origem e Classificação Botânica do Cafeeiro. In: de Carvalho CHS (ed) Cultivares de Café: Origem, características e recomendações. Embrapa Café, Brasília
Hicke L, Dunn R (2003) Regulation of membrane protein transport by ubiquitin and ubiquitin-binding proteins. Annu Rev Cell Dev Bi 19(1):141–172. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.cellbio.19.110701.154617
Hirschburger D, Müller M, Voegele RT, Link T (2015) Reference genes in the pathosystem Phakopsora pachyrhizi/soybean suitable for normalization in transcript profiling. Int J Mol Sci 16(9):23057–23075. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160923057
Hu R, Fan C, Li H, Zhang Q, Y-F F (2009) Evaluation of putative reference genes for gene expression normalization in soybean by quantitative real-time RT-PCR. BMC Mol Biol 10(1):93. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2199-10-93
Huang L, Yan H, Jiang X, Yin G, Zhang X, Qi X, Zhang Y, Yan Y, Ma X, Peng Y (2014) Identification of candidate reference genes in perennial ryegrass for quantitative RT-PCR under various abiotic stress conditions. PLoS One 9(4):e93724. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0093724
ICO (2016a) Historical Data on the Global Coffee Trade—Total exports by all exporting countries. http://www.ico.org/new_historical.asp. Accessed 02/05/2017 2016
ICO (2016b) Historical Data on the Global Coffee Trade—Total production by all exporting countries. http://www.ico.org/new_historical.asp. Accessed 02/05/2017 2016
Imai T, Ubi BE, Saito T, Moriguchi T (2014) Evaluation of reference genes for accurate normalization of gene expression for real time-quantitative PCR in Pyrus pyrifolia using different tissue samples and seasonal conditions. PLoS One 9(1):e86492. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0086492
Kumar V, Madhava Naidu M, Ravishankar GA (2006) Developments in coffee biotechnology—in vitro plant propagation and crop improvement. Plant Cell Tiss Org 87(1):49–65. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-006-9134-y
Larrainzar E et al (2014) Drought stress provokes the down-regulation of methionine and ethylene biosynthesis pathways in Medicago truncatula roots and nodules. Plant Cell Environ 37(9):2051–2063. https://doi.org/10.1111/pce.12285
Lashermes P, Combes MC, Robert J, Trouslot P, D'Hont A, Anthony F, Charrier A (1999) Molecular characterisation and origin of the Coffea arabica L. genome. Mol Gen Genet MGG 261(2):259–266. https://doi.org/10.1007/s004380050965
Lin L, Han X, Chen Y, Wu Q, Wang Y (2013) Identification of appropriate reference genes for normalizing transcript expression by quantitative real-time PCR in Litsea cubeba. Mol Gen Genomics 288(12):727–737. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-013-0785-1
Ling H, Wu Q, Guo J, Xu L, Que Y (2014) Comprehensive selection of reference genes for gene expression normalization in sugarcane by real time quantitative RT-PCR. PLoS One 9(5):e97469. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0097469
Luo H, Chen S, Wan H, Chen F, Gu C, Liu Z (2010) Candidate reference genes for gene expression studies in water lily. Anal Biochem 404(1):100–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ab.2010.05.002
Martins MQ, Fortunato AS, Rodrigues WP, Partelli FL, Campostrini E, Lidon FC, DaMatta FM, Ramalho JC, Ribeiro-Barros AI (2017) Selection and validation of reference genes for accurate RT-qPCR data normalization in Coffea spp. under a climate changes context of interacting elevated [CO2] and temperature. Front Plant Sci 8. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.00307
Moorhead GB, De Wever V, Templeton G, Kerk D (2009) Evolution of protein phosphatases in plants and animals. Biochem J 417(2):401–409. https://doi.org/10.1042/BJ20081986
Nicot N, Hausman JF, Hoffmann L, Evers D (2005) Housekeeping gene selection for real-time RT-PCR normalization in potato during biotic and abiotic stress. J Exp Bot 56(421):2907–2914. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/eri285
Pfaffl MW (2001) A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res 29(9):e45–445. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/29.9.e45
Pfaffl MW, Tichopad A, Prgomet C, Neuvians TP (2004) Determination of stable housekeeping genes, differentially regulated target genes and sample integrity: BestKeeper—excel-based tool using pair-wise correlations. Biotechnol Lett 26(6):509–515. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:BILE.0000019559.84305.47
Rodrigues TB et al (2014) Validation of reference housekeeping genes for gene expression studies in western corn rootworm (Diabrotica virgifera virgifera). PLoS One 9(10):e109825. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0109825
Rojo E, Titarenko E, Leon J, Berger S, Vancanneyt G, Sánchez-Serrano JJ (1998) Reversible protein phosphorylation regulates jasmonic acid-dependent and-independent wound signal transduction pathways in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 13(2):153–165. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-313X.1998.00020.x
Shi Y (2009) Serine/threonine phosphatases: mechanism through structure. Cell 139(3):468–484. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2009.10.006
Silver N, Best S, Jiang J, Thein SL (2006) Selection of housekeeping genes for gene expression studies in human reticulocytes using real-time PCR. BMC Mol Biol 7(1):33. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2199-7-33
Steibel JP, Poletto R, Coussens PM, Rosa GJ (2009) A powerful and flexible linear mixed model framework for the analysis of relative quantification RT-PCR data. Genomics 94(2):146–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygeno.2009.04.008
Vandesompele J, De Preter K, Pattyn F, Poppe B, Van Roy N, De Paepe A, Speleman F (2002) Accurate normalization of real-time quantitative RT-PCR data by geometric averaging of multiple internal control genes. Genome Biol 3:research0034. 0031
Vandesompele J, Kubista M, Pfaffl MW (2009) Reference gene validation software for improved normalization real-time PCR: current technology and applications. Horizon Scientific Press
Vieira A, Talhinhas P, Loureiro A, Duplessis S, Fernandez D, Silva MC, Paulo OS, Azinheira HG (2011) Validation of RT-qPCR reference genes for in planta expression studies in Hemileia vastatrix, the causal agent of coffee leaf rust. Fungal Biol-UK 115(9):891–901. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.funbio.2011.07.002
Vieira LGE, Andrade AC, Colombo CA, Moraes AHA, Metha Â, Oliveira AC, Labate CA, Marino CL, Monteiro-Vitorello CB, Monte DC, Giglioti É, Kimura ET, Romano E, Kuramae EE, Lemos EGM, Almeida ERP, Jorge ÉC, Albuquerque ÉVS, Silva FR, Vinecky F, Sawazaki HE, Dorry HFA, Carrer H, Abreu IN, Batista JAN, Teixeira JB, Kitajima JP, Xavier KG, Lima LM, Camargo LEA, Pereira LFP, Coutinho LL, Lemos MVF, Romano MR, Machado MA, Costa MMC, Sá MFG, Goldman MHS, Ferro MIT, Tinoco MLP, Oliveira MC, van Sluys MA, Shimizu MM, Maluf MP, Eira MTS, Guerreiro Filho O, Arruda P, Mazzafera P, Mariani PDSC, Oliveira RLBC, Harakava R, Balbao SF, Tsai SM, Mauro SMZ, Santos SN, Siqueira WJ, Costa GGL, Formighieri EF, Carazzolle MF, Pereira GAG (2006) Brazilian coffee genome project: an EST-based genomic resource. Braz J Plant Physiol 18(1):95–108. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1677-04202006000100008
Wan H, Zhao Z, Qian C, Sui Y, Malik AA, Chen J (2010) Selection of appropriate reference genes for gene expression studies by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction in cucumber. Anal Biochem 399(2):257–261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ab.2009.12.008
Williams TD, Gensberg K, Minchin SD, Chipman JK (2003) A DNA expression array to detect toxic stress response in European flounder (Platichthys flesus). Aquat Toxicol 65(2):141–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0166-445X(03)00119-X
Xia W, Mason AS, Xiao Y, Liu Z, Yang Y, Lei X, Wu X, Ma Z, Peng M (2014) Analysis of multiple transcriptomes of the African oil palm (Elaeis guineensis) to identify reference genes for RT-qPCR. J Biotechnol 184:63–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2014.05.008
Xie F, Xiao P, Chen D, Xu L, Zhang B (2012) miRDeepFinder: a miRNA analysis tool for deep sequencing of plant small RNAs. Plant Mol Biol 80(1):75–84. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-012-9885-2
Yang SF, Hoffman NE (1984) Ethylene biosynthesis and its regulation in higher plants. Annu Rev Plant Phys 35(1):155–189. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.pp.35.060184.001103
Zeng S, Liu Y, Wu M, Liu X, Shen X, Liu C, Wang Y (2014) Identification and validation of reference genes for quantitative real-time PCR normalization and its applications in lycium. PLoS One 9(5):e97039. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0097039
Zhang C, Zhang L, Zhang S, Zhu S, Wu P, Chen Y, Li M, Jiang H, Wu G (2015) Global analysis of gene expression profiles in physic nut (Jatropha curcas L.) seedlings exposed to drought stress. BMC Plant Biol 15(1):17. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-014-0397-x
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the members of the Laboratory of Plant Molecular Physiology at the Universidade Federal de Lavras for their collaboration to this work and the Fundação Procafé for providing plant material to this study.
Funding
We also thank the National Institute of Science and Technology of Coffee (INCT-Café) for providing funding and the National Council for Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq), the Minas Gerais Research Foundation (FAPEMIG), and the Coordination of Improvement of Higher Education (CAPES) for grants.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by C. Chen
Electronic supplementary material
Online Resource 1
The RNA Integrity Number (RIN) Electrophoresis File Run Summary (Chip Summary) of the biological triplicates of RNA samples from WD Roots, WD Stems, WD Leaves and WW Roots of Coffea arabica. (PDF 256 kb)
Online Resource 2
The RNA Integrity Number (RIN) Electrophoresis File Run Summary (Chip Summary) of the biological triplicates of RNA samples from WW Stems, WW Leaves, WW Flowers and WW Fruits of Coffea arabica. (PDF 255 kb)
Online Resource 3
The RNA Integrity Number (RIN) Electrophoresis File Run Summary (Chip Summary) of the biological triplicates of RNA samples from WW Roots, WW Stems, WW Leaves and WD Flowers of Coffea canephora. (PDF 257 kb)
Online Resource 4
The RNA Integrity Number (RIN) Electrophoresis File Run Summary (Chip Summary) of the biological triplicates of RNA samples from WW Fruits of Coffea canephora. (PDF 254 kb)
Online Resource 5
Panel of the dissociation curves (Melt curves) of the primers of the candidate genes tested in Coffea arabica samples. The panels are named after the respective gene. The unique peaks show specificity of the primers. (GIF 3804 kb)
Online Resource 6
Panel of the dissociation curves (Melt curves) of the primers of the candidate genes tested in Coffea canephora samples. The panels are named after the respective gene. The unique peaks show specificity of the primers. (GIF 2213 kb)
Online Resource 7
Pairwise variation (V) of the candidate reference genes calculated by GeNorm. Vn/Vn + 1 values were used for decision of the optimal number of reference genes for all tissues grouped of C. arabica (GIF 30 kb)
Online Resource 8
Pairwise variation (V) of the candidate reference genes calculated by GeNorm. Vn/Vn + 1 values were used for decision of the optimal number of reference genes for root of C. arabica under WW and WD conditions (GIF 30 kb)
Online Resource 9
Pairwise variation (V) of the candidate reference genes calculated by GeNorm. Vn/Vn + 1 values were used for decision of the optimal number of reference genes for stem of C. arabica under WW and WD conditions (GIF 27 kb)
Online Resource 10
Pairwise variation (V) of the candidate reference genes calculated by GeNorm. Vn/Vn + 1 values were used for decision of the optimal number of reference genes for leaf of C. arabica under WW and WD conditions (GIF 28 kb)
Online Resource 11
Pairwise variation (V) of the candidate reference genes calculated by GeNorm. Vn/Vn + 1 values were used for decision of the optimal number of reference genes for leaf and root of C. arabica under WW and WD conditions (GIF 30 kb)
Online Resource 12
Pairwise variation (V) of the candidate reference genes calculated by GeNorm. Vn/Vn + 1 values were used for decision of the optimal number of reference genes for all tissues grouped of C. arabica under WD conditions (GIF 28 kb)
Online Resource 13
Pairwise variation (V) of the candidate reference genes calculated by GeNorm. Vn/Vn + 1 values were used for decision of the optimal number of reference genes for root of C. arabica under WD conditions (GIF 27 kb)
Online Resource 14
Pairwise variation (V) of the candidate reference genes calculated by GeNorm. Vn/Vn + 1 values were used for decision of the optimal number of reference genes for stem of C. arabica under WD conditions (GIF 25 kb)
Online Resource 15
Pairwise variation (V) of the candidate reference genes calculated by GeNorm. Vn/Vn + 1 values were used for decision of the optimal number of reference genes for leaf of C. arabica under WD conditions (GIF 24 kb)
Online Resource 16
Pairwise variation (V) of the candidate reference genes calculated by GeNorm. Vn/Vn + 1 values were used for decision of the optimal number of reference genes for all tissues grouped of C. arabica under WW conditions (GIF 28 kb)
Online Resource 17
Pairwise variation (V) of the candidate reference genes calculated by GeNorm. Vn/Vn + 1 values were used for decision of the optimal number of reference genes for root of C. arabica under WW conditions (GIF 25 kb)
Online Resource 18
Pairwise variation (V) of the candidate reference genes calculated by GeNorm. Vn/Vn + 1 values were used for decision of the optimal number of reference genes for stem of C. arabica under WW conditions (GIF 26 kb)
Online Resource 19
Pairwise variation (V) of the candidate reference genes calculated by GeNorm. Vn/Vn + 1 values were used for decision of the optimal number of reference genes for leaf of C. arabica under WW conditions (GIF 25 kb)
Online Resource 20
Pairwise variation (V) of the candidate reference genes calculated by GeNorm. Vn/Vn + 1 values were used for decision of the optimal number of reference genes for flower of C. arabica under WW conditions (GIF 23 kb)
Online Resource 21
Pairwise variation (V) of the candidate reference genes calculated by GeNorm. Vn/Vn + 1 values were used for decision of the optimal number of reference genes for fruit of C. arabica under WW conditions (GIF 25 kb)
Online Resource 22
Pairwise variation (V) of the candidate reference genes calculated by GeNorm. Vn/Vn + 1 values were used for decision of the optimal number of reference genes for all tissues grouped of C. canephora under WW conditions (GIF 27 kb)
Online Resource 23
Pairwise variation (V) of the candidate reference genes calculated by GeNorm. Vn/Vn + 1 values were used for decision of the optimal number of reference genes for root of C. canephora under WW conditions (GIF 24 kb)
Online Resource 24
Pairwise variation (V) of the candidate reference genes calculated by GeNorm. Vn/Vn + 1 values were used for decision of the optimal number of reference genes for stem of C. canephora under WW conditions (GIF 23 kb)
Online Resource 25
Pairwise variation (V) of the candidate reference genes calculated by GeNorm. Vn/Vn + 1 values were used for decision of the optimal number of reference genes for leaf of C. canephora under WW conditions. (GIF 21 kb)
Online Resource 26
Pairwise variation (V) of the candidate reference genes calculated by GeNorm. Vn/Vn + 1 values were used for decision of the optimal number of reference genes for flower of C. canephora under WW conditions (GIF 21 kb)
Online Resource 27
Pairwise variation (V) of the candidate reference genes calculated by GeNorm. Vn/Vn + 1 values were used for decision of the optimal number of reference genes for fruit of C. canephora under WW conditions (GIF 21 kb)
Online Resource 28
RefFinder ranking for all conditions and combinations tested in C. arabica tissues. (XLSX 1211 kb)
Online Resource 29
RefFinder ranking for all conditions and combinations tested in C. canephora tissues. (XLSX 734 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fernandes-Brum, C.N., Garcia, B.d.O., Moreira, R.O. et al. A panel of the most suitable reference genes for RT-qPCR expression studies of coffee: screening their stability under different conditions. Tree Genetics & Genomes 13, 131 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-017-1213-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-017-1213-1