Abstract
Objectives
This study was performed to assess the morphological appearance, incidence of bridging, and linear dimensions of the sella turcica (ST) in Bosnian and Iraqi subjects, and to identify associations of sex, age, and racial group with the size of the ST.
Methods
The digital standardised lateral cephalograms of 360 Bosnian and Iraqi patients (116 female, 64 male; age range 8–28 years) were retrospectively analysed. The following ST-related parameters were analysed on the lateral cephalograms: sella morphology, sella bridging, and sella size. The data were correlated with sex, age, and race.
Results
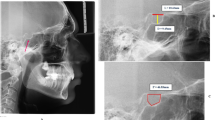
The ST exhibited a normal morphology in most subjects of both races (86.7%). The frequency of partial bridging was found in 38.9 and 37.2% of Bosnian and Iraqi subjects, respectively. A significant correlation was detected between the length of the ST and sex in both the Bosnian and Iraqi subjects (p < 0.05). A direct correlation was present between patient age and the size of the ST in both races at the 0.01 and 0.001 levels for depth, length, and diameter. When race was compared with sella size, a significant difference was found in the length and depth of the ST (p < 0.001).
Conclusions
Similarities were found between Bosnian and Iraqi subjects in the morphology, incidence of bridging, and linear dimensions of the ST. Length was the only parameter significantly associated with sex, age, and racial group. These findings could be used as reference standards for studying the ST in both races.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alkofide EA. The shape and size of the sella turcica in skeletal class I, class II, and class III Saudi subjects. Eur J Orthod. 2007;29(5):457–63.
Tekiner H, Acer N, Kelestimur F. Sella turcica: an anatomical, endocrinological, and historical perspective. Pituitary. 2015;18(4):575–8.
Neha SM, Shetty VS, Shetty S. Sella size and jaw bases—is there a correlation? Cont Clin Dent. 2016;7(1):61–6.
Marsan G, Oztas E. Incidence of bridging and dimensions of sella turcica in class I and III Turkish adult female patients. World J Orthod. 2009;10(2):99–103.
Norton N. Netter’s head and neck anatomy for dentistry. Philadelphia: Elsevier Saunders; 2011.
Iván E, Pérez I, Allison K, Chávez A, Ponce D. Frequency of sella turcica bridge and clinoid enlargement in lateral cephalometric plain film radiography from Peruvians. Int J Morphol. 2013;31(2):373–7.
Hasan HA, Alam MK, Abdullah YJ, Nakano J, Yusa T, Yusof A, et al. 3DCT morphometric analysis of sella turcica in Iraqi population. J Hard Tissue Biol. 2016;25(3):227–32.
Abdel-Kader HM. Sella turcica bridges in orthodontic and orthognathic surgery patients. A retrospective cephalometric study. Au Orthod J. 2007;23(1):30–5.
Keats T, Lusted L. Atlas of roentgenographic measurement. St. Louis: Mosby; 1990.
Friedland B, Meazzini MC. Incidental finding of an enlarged sella turcica on a lateral cephalogram. Am J Orthod Dentofac Orthop. 1996;110(5):508–12.
Peker T, Anil A, Gulekon N, Turgut HB, Pelin C, Karakose M. The incidence and types of sella and sphenopetrous bridges. Neuro Rev. 2006;29(3):219–23.
Becktor JP, Einersen S, Kjaer I. A sella turcica bridge in subjects with severe craniofacial deviations. Eur J Orthod. 2000;22(1):69–74.
Leonardi R, Barbato E, Vichi M, Caltabiano M. A sella turcica bridge in subjects with dental anomalies. Eur J Orthod. 2006;28(6):580–5.
Shah AM, Bashir U, Ilyas T. The shape and size of the sella turcica in skeletal class I, II and III in patients presenting at Islamic International Dental Hospital, Islamabad. Pakistan Oral Dent J. 2011;31(1):104–10.
Valizadeh S, Shahbeig S, Mohseni S, Azimi F, Bakhshandeh H. Correlation of shape and size of sella turcica with the type of facial skeletal class in an Iranian group. Iranian J Radiol. 2015;12(3):e16059.
Sathyanarayana H, Kailasam V, Chitharanjan A. The size and morphology of sella turcica in different skeletal patterns among South Indian population: a lateral cephalometric study. J In Orthod Soc. 2013;47(4):266–71.
Hussein S, Noori A. Prevalence of oral mucosal changes among 13 year old children in Sulaimani city, Iraq. Sulaimani Dent J. 2014;1:5–9.
Lakic B, Racic M, Vulic D. Retrospective analysis of the role and performance of family medicine versus emergency medical services in the pre-hospital management of patients with AMI in Banja Luka. Acta Med Acad. 2016;45(1):10–8.
Chang ZC, Hu FC, Lai E, Yao CC, Chen MH, Chen YJ. Landmark identification errors on cone-beam computed tomography-derived cephalograms and conventional digital cephalograms. Am J Orthod Dentofac Orthoped. 2011;140(6):e289–e97.
Damstra J, Huddleston Slater JJ, Fourie Z, Ren Y. Reliability and the smallest detectable differences of lateral cephalometric measurements. Am J Orthod Dentofac Orthoped. 2010;138(5):546.e541–8 (discussion 546–7).
Silverman F. Roentgen standards for size of the pituitary fossa from infancy through adolescence. Am J Roentgenol. 1957;78(3):45–60.
Hasan H, Alam M, Yusof A, Mizushima H, Kida A, Osuga N. Size and morphology of sella turcica in Malay populations: a 3D CT study. J Hard Tissue Biol. 2016;25(3):313–20.
IPérez I, Chávez A, Ponce D. Frequency of sella turcica bridge and clinoid enlargement in lateral cephalometric plain film radiography from Peruvians. Int J Morphol. 2013;31(2):373–7.
Koo T, Li M. A guideline of selecting and reporting intraclass correlation coefficients for reliability research. J Chiropr Med. 2016;15(2):155–63.
Andredaki M, Koumantanou A, Dorotheou D, Halazonetis DJ. A cephalometric morphometric study of the sella turcica. Eur J Orthod. 2007;29(5):449–56.
Ruiz C, Wafae N, Wafae G. Sella turcica morphometry using computed tomography. Eur J Anat. 2008;12:47–50.
Axelsson S, Storhaug K, Kjaer I. Post-natal size and morphology of the sella turcica. Longitudinal cephalometric standards for Norwegians between 6 and 21 years of age. Eur J Orthod. 2004;26(6):597–604.
Cederberg RA, Benson BW, Nunn M, English JD. Calcification of the interclinoid and petroclinoid ligaments of sella turcica: a radiographic study of the prevalence. Orthod Craniofac Res. 2003;6(4):227–32.
Kantor ML, Norton LA. Normal radiographic anatomy and common anomalies seen in cephalometric films. Am J Orthod Dentofac Orthoped. 1987;91(5):414–26.
Meyer-Marcotty P, Weisschuh N, Dressler P, Hartmann J, Stellzig-Eisenhauer A. Morphology of the sella turcica in Axenfeld-Rieger syndrome with PITX2 mutation. J Oral Pathol Med. 2008;37(8):504–10.
Islam M, Alam M, Yusof A, Kato I, Honda Y, Kubo K, et al. 3D CT study of morphological shape and size of sella turcica in Bangladeshi population. J Hard Tissue Biol. 2017;26(1):1–6.
Axelsson S, Storhaug K, Kjaer I. Post-natal size and morphology of the sella turcica in Williams syndrome. Eur J Orthod. 2004;26(6):613–21.
Jones RM, Faqir A, Millett DT, Moos KF, McHugh S. Bridging and dimensions of sella turcica in subjects treated by surgical-orthodontic means or orthodontics only. Angle Orthod. 2005;75(5):714–8.
Olubunmi O, Yinka O, Oladele O, Adimchukwunaka G, Afees O. An assessment of the size of sella turcica among adult Nigerians resident in Lagos. Int J Med Imaging. 2016;4(3):12–6.
Osunwoke E, Mokwe C, Amah-Tariah F. Radiologic measurements of the sella turcica in an adult Nigerian population. Int J Pharm Sci Res. 2014;4:115–7.
Chavan S, Kathole M, Katti A, Herekar N. Radiological analysis of sella turcica. Int J Recent Trends Sci Technol. 2012;4(1):36–40.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Chinese Scholarship Council (CSC) under Grant number CSC-2016368012.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Fenik Kaml Muhammed, Adil O. Abdullah, Zhwan Jamal Rashid, Tamara Pusic, Mohammed F. Shbair, and Yi Liu declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Human rights statement
All procedures followed were in accordance with the ethical standards of the responsible committee (institutional and national) and with the Helsinki Declaration of 1964 and later versions. The study protocol was approved by the Local Research Ethics Committee of Stomatology of China Medical University (Shenyang, People’s Republic of China). This article does not contain any studies with animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
Informed consent was not needed in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Muhammed, F.K., Abdullah, A.O., Rashid, Z.J. et al. Morphology, incidence of bridging, and dimensions of sella turcica in different racial groups. Oral Radiol 35, 127–134 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11282-018-0328-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11282-018-0328-x