Abstract
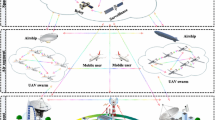
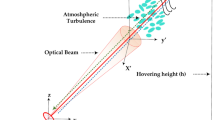
In order to share the global information and resources efficiently over a huge network topology, the Space-Air-Ground Integrated Network (SAGIN) system integrates a number of networks for optimal utilization. Nonetheless, the related communication units between the mobile platforms and air-to-ground links are constrained to a low-bit rate radio-based technology. In addition, the required services to be supported demand a high capacity link. This will ensure effective management of multiple information in parallel and in real-time. One of attractive systems with inherent features to support the network demands is the free-space optical (FSO) communication system. Nevertheless, drift support in the SAGIN could be challenging for the FSO system. This is due to the required line-of-sight link alignment between the receiver and transmitter modules. Besides, FSO system is susceptible to the atmospheric turbulence-induced fading. This can be addressed by operating unmanned aerial vehicles in the SAGIN system in swarm mode. Conversely, this can bring about channel correlation eventually resulting into system performance impairments. This paper considers the effect of correlated FSO channel on the SAGIN system outage performance. To accomplish this, we consider exponential model for modeling the correlations between the apertures. Moreover, to account for the spatial correlation for different diversity orders in the air-to-ground as well as air-to-air communications, we employ a multivariate Gamma–Gamma (\(\varGamma \varGamma\)) distribution. The results of the analysis appropriately quantify the effects of the atmospheric turbulence-induced fading as well as correlation on the system outage performance.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chlestil, C., Leitgeb, E., Schmitt, N. P., Muhammad, S. S., Zettl, K., & Rehm, W. (2006). Reliable optical wireless links within UAV swarms. In 2006 international conference on transparent optical networks, (vol 4. pp. 39–42). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICTON.2006.248491.
Wu, Z., Kumar, H., & Davari, A. (2005). Performance evaluation of OFDM transmission in UAV wireless communication. In Proceedings of the thirty-seventh southeastern symposium on system theory, 2005. SSST ’05., (pp. 6–10). https://doi.org/10.1109/SSST.2005.1460867.
Heng, K. H., Liu, N., He, Y., Zhong, W. D., & Cheng, T. H. (2008). Adaptive beam divergence for inter-UAV free space optical communications. In 2008 IEEE photonicsglobal@Singapore, (pp. 1–4). https://doi.org/10.1109/IPGC.2008.4781473.
Zhou, L., Last, M., Milanovic, V., Kahn, J. M., & Pister K. S. J. (2003). Two-axis scanning mirror for free-space optical communication between UAVs. In 2003 IEEE/LEOS international conference on optical MEMS (Cat. No.03EX682), (pp. 157–158). https://doi.org/10.1109/OMEMS.2003.1233514.
Alimi, I., Shahpari, A., Sousa, A., Ferreira, R., Monteiro, P., & Teixeira, A. (2017). Challenges and opportunities of optical wireless communication technologies. In P. Pinho (Ed.), Optical communication technology. Rijeka: InTech. https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.69113.
Alimi, I. A., Monteiro, P. P., & Teixeira, A. L. (2017). Analysis of multiuser mixed RF/FSO relay networks for performance improvements in cloud computing-based radio access networks (CC-RANs). Optics Communications, 402(Supplement C), 653–661. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optcom.2017.06.097.
Ghassemlooy, Z., Arnon, S., Uysal, M., Xu, Z., & Cheng, J. (2015). Emerging optical wireless communications-advances and challenges. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 33(9), 1738–1749. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSAC.2015.2458511.
Alimi, I. A., Shahpari, A., Monteiro, P. P., & Teixeira, A. L. (2017). Effects of diversity schemes and correlated channels on owc systems performance. Journal of Modern Optics, 64(21), 2298–2305. https://doi.org/10.1080/09500340.2017.1357851.
Alimi, I. A., Abdalla, A. M., Rodriguez, J., Monteiro, P. P., & Teixeira, A. L. (2017). Spatial interpolated lookup tables (LUTs) models for ergodic capacity of MIMO FSO systems. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 29(7), 583–586. https://doi.org/10.1109/LPT.2017.2669337.
Alimi, I., Shahpari, A., Ribeiro, V., Sousa, A., Monteiro, P., & Teixeira, A. (2017). Channel characterization and empirical model for ergodic capacity of free-space optical communication link. Optics Communications, 390, 123–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optcom.2017.01.001.
Chan, V. W. S. (2006). Free-space optical communications. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 24(12), 4750–4762. https://doi.org/10.1109/JLT.2006.885252.
Leitgeb, E., Zettl, K., Muhammad, S. S., Schmitt, N., & Rehm, W. (2007). Investigation in free space optical communication links between unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs). In 2007 9th International conference on transparent optical networks, (vol 3. pp. 152–155). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICTON.2007.4296268.
Muhammad, S. S., Plank, T., Leitgeb, E., Friedl, A., Zettl, K., Javornik, T., & Schmitt, N. (2008). Challenges in establishing free space optical communications between flying vehicles. In 2008 6th international symposium on communication systems, networks and digital signal processing, (pp. 82–86). https://doi.org/10.1109/CSNDSP.2008.4610721.
Qi, W., Hou, W., Song, Q., Guo, L., & Jamalipour, A. (2016). Topology control and routing based on adaptive RF/FSO switching in space-air integrated networks. In 2016 IEEE global communications conference (GLOBECOM), (pp. 1–6). https://doi.org/10.1109/GLOCOM.2016.7842334.
Alimi, I. A., Mufutau, A. O., Teixeira, A. L., & Monteiro, P. P. (2018). Performance analysis of space-air-ground integrated network (sagin) over an arbitrarily correlated multivariate fso channel. Wireless Personal Communications, 100(1), 47–66. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-018-5620-x.
Liu, H., Zhang, J., & Cheng, L. L. (2010). Application examples of the network fixed point theory for space-air-ground integrated communication network. International congress on ultra modern telecommunications and control systems (pp. 989–993). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICUMT.2010.5676493.
Liu, X., Qiu, M., Wang, X., Liu, W., & Cai, K. (2017). Energy efficiency optimization for communication of air-based information network with guaranteed timing constraints. Journal of Signal Processing Systems, 86(2), 299–312. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11265-016-1125-6.
Zhang, N., Zhang, S., Yang, P., Alhussein, O., Zhuang, W., & Shen, X. S. (2017). Software defined space-air-ground integrated vehicular networks: Challenges and solutions. IEEE Communications Magazine, 55(7), 101–109. https://doi.org/10.1109/MCOM.2017.1601156.
Baister, G., & Gatenby, P. V. (1994). Pointing, acquisition and tracking for optical space communications. Electronics Communication Engineering Journal, 6(6), 271–280. https://doi.org/10.1049/ecej:19940605.
Toyoshima, M. (2005). Trends in satellite communications and the role of optical free-space communications. Journal of Optical Networking, 4(6), 300–311. https://doi.org/10.1364/JON.4.000300.
Kaushal, H., & Kaddoum, G. (2017). Optical communication in space: Challenges and mitigation techniques. IEEE Communications Surveys Tutorials, 19(1), 57–96. https://doi.org/10.1109/COMST.2016.2603518.
Vishnevskii, V. M., Semenova, O. V., & Sharov, S. Y. (2013). Modeling and analysis of a hybrid communication channel based on free-space optical and radio-frequency technologies. Automation and Remote Control, 74(3), 521–528. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0005117913030144.
Alimi, I. A., Monteiro, P. P., & Teixeira, A. L. (2017). Outage probability of multiuser mixed RF/FSO relay schemes for heterogeneous cloud radio access networks (H-CRANs). Wireless Personal Communications, 95(1), 27–41. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-017-4413-y.
Yang, G., Khalighi, M. A., Bourennane, S., & Ghassemlooy, Z. (2012). Approximation to the sum of two correlated Gamma-Gamma variates and its applications in free-space optical communications. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 1(6), 621–624. https://doi.org/10.1109/WCL.2012.091312.120469.
Aboderin, O., & Alimi, I. A. (2015). Modeling land mobile satellite channel and mitigation of signal fading. American Journal of Mobile Systems, Applications and Services, 1(1), 46–53.
Yang, G., Khalighi, M. A., Ghassemlooy, Z., & Bourennane, S. (2013). Performance evaluation of correlated-fading space-diversity FSO links. In 2013 2nd International workshop on optical wireless communications (IWOW), (pp. 71–73). https://doi.org/10.1109/IWOW.2013.6777780.
Zhang, J., Matthaiou, M., Karagiannidis, G. K., & Dai, L. (2016). On the multivariate Gamma-Gamma distribution with arbitrary correlation and applications in wireless communications. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 65(5), 3834–3840. https://doi.org/10.1109/TVT.2015.2438192.
Alimi, I. A., Teixeira, A. L., & Monteiro, P. P. (2018). Toward an efficient C-RAN optical fronthaul for the future networks: A tutorial on technologies, requirements, challenges, and solutions. IEEE Communications Surveys Tutorials, 20(1), 708–769. https://doi.org/10.1109/COMST.2017.2773462.
Alimi, I., Shahpari, A., Ribeiro, V., Kumar, N., Monteiro, P., & Teixeira, A. (2016). Optical wireless communication for future broadband access networks. In 2016 21st European conference on networks and optical communications (NOC), (pp. 124–128). https://doi.org/10.1109/NOC.2016.7506998.
Al Naboulsi, M., Sizun, H., & de Fornel, F. (2004). Fog attenuation prediction for optical and infrared waves. Optical Engineering, 43(2), 319–329. https://doi.org/10.1117/1.1637611.
Farid, A. A., & Hranilovic, S. (2007). Outage capacity optimization for free-space optical links with pointing errors. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 25(7), 1702–1710. https://doi.org/10.1109/JLT.2007.899174.
Sandalidis, H. G., Tsiftsis, T. A., & Karagiannidis, G. K. (2009). Optical wireless communications with heterodyne detection over turbulence channels with pointing errors. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 27(20), 4440–4445. https://doi.org/10.1109/JLT.2009.2024169.
Andrews, L., & Phillips, R. (2005). Laser beam propagation through random media. Bellingham: Press Monographs, SPIE Press.
Kiasaleh, K. (2005). Performance of APD-based, PPM free-space optical communication systems in atmospheric turbulence. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 53(9), 1455–1461. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCOMM.2005.855009.
Ghassemlooy, Z., Popoola, W., & Rajbhandari, S. (2012). Optical wireless communications: System and channel modelling with MATLAB®. Milton Park: Taylor & Francis.
Yang, Y.-Q., Chi, X.-F., Shi, J.-L., & Zhao, L.-L. (2015). Analysis of effective capacity for free-space optical communication systems over gamma-gamma turbulence channels with pointing errors. Optoelectronics Letters, 11(3), 213–216. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11801-015-5038-6.
Aggarwal, M., Garg, P., & Puri, P. (2015). Ergodic capacity of SIM-based DF relayed optical wireless communication systems. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 27(10), 1104–1107. https://doi.org/10.1109/LPT.2015.2407897.
Choi, J., & Love, D. J. (2014). Bounds on eigenvalues of a spatial correlation matrix. IEEE Communications Letters, 18(8), 1391–1394. https://doi.org/10.1109/LCOMM.2014.2332993.
Lim, H., Jang, Y., & Yoon, D. (2017). Bounds for eigenvalues of spatial correlation matrices with the exponential model in MIMO systems. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 16(2), 1196–1204. https://doi.org/10.1109/TWC.2016.2641419.
Loyka, S. L. (2001). Channel capacity of MIMO architecture using the exponential correlation matrix. IEEE Communications Letters, 5(9), 369–371. https://doi.org/10.1109/4234.951380.
Navidpour, S. M., Uysal, M., & Kavehrad, M. (2007). BER performance of free-space optical transmission with spatial diversity. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 6, 2813–2819. https://doi.org/10.1109/TWC.2007.06109.
Djordjevic, G. T., Petkovic, M. I., Anastasov, J. A., Ivanis, P. N., & Marjanovic, Z. M. (2016). On the effects of correlation on outage performance of fso-unbalanced multibranch sc receiver. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 28(12), 1348–1351. https://doi.org/10.1109/LPT.2016.2543002.
Reig, J. (2009). Multivariate nakagami-m distribution with constant correlation model. AEU - International Journal of Electronics and Communications, 63(1), 46–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aeue.2007.10.009.
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the European Regional Development Fund (FEDER), through the Regional Operational Programme of Lisbon (POR LISBOA 2020) and the Competitiveness and Internationalization Operational Programme (COMPETE 2020) of the Portugal 2020 framework, Project 5G (POCI-01-0247-FEDER-024539), ORCIP (CENTRO-01-0145-FEDER-022141) and SOCA (CENTRO-01-0145-FEDER-000010). It is also funded by Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia (FCT) through national funds under the project COMPRESS - PTDC/EEI-TEL/7163/2014 and by FEDER, through the Regional Operational Program of Centre (CENTRO 2020) of the Portugal 2020 framework [Project HeatIT with Nr. 017942 (CENTRO-01-0247-FEDER-017942)] and [Project Virtual Fiber Box with Nr. 033910 (POCI-01-0247-FEDER-033910)].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alimi, I.A., Teixeira, A.L. & Monteiro, P.P. Effects of Correlated Multivariate FSO Channel on Outage Performance of Space-Air-Ground Integrated Network (SAGIN). Wireless Pers Commun 106, 7–25 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-019-06271-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-019-06271-8