Abstract
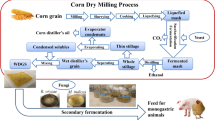
Solid-state fermentation (SSF) with Agaricus brasiliensis and Agaricus bisporus on corn was carried out. The results showed that SSF with the two fungi made up the deficiency of tryptophan in corn and improved the protein nutritional value of corn. The conjugated polyphenols contents in fermented corn decreased and free polyphenols (FPP) contents increased. FPP contents in corn fermented with the two fungi reached respectively 25 and 88 times of control, total polyohenols contents reached respectively 1.4 and 3.3 times of control. The antioxidant properties (i.e. 1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl radical scavenging capacity, reducing power, ferrous ion chelating ability and superoxide anion radical scavenging ability) of fermented corn were improved significantly. SSF with A. bisporus was more favorable to the enhancement in protein nutritional value and antioxidant properties of corn than that of A. brasiliensis. The results indicated that SSF with the two fungi could upgrade the protein nutritional value, FPP content and antioxidant properties of corn.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arranz S, Calixto FS (2010) Analysis of polyphenols in cereals may be improved performing acidic hydrolysis: A study in wheat flour and wheat bran and cereals of the diet. J Cereal Sci 51:313–318
Astorga-España MS, Rodríguez-Galdón B, Rodríguez-Rodríguez EM, Díaz-Romero C (2016) Amino acid content in seaweeds from the Magellan Straits (Chile). J Food Compos Anal 53:77–84
Bano ZRS (1982) Pleurotus mushroom as a nutritious food in the tropical mushrooms biological nature and cultivation methods. The Chinese University Press, Hong Kong
Blandino A, Al-Aseeri ME, Pandiella SS, Cantero D, Webb C (2003) Cereal-based fermented foods and beverages. Food Res Int 36:527–543
Bosch L, Alegría A, Farré R (2006) Application of the 6-aminoquinolyl-N-hydroxysccinimidyl carbamate (AQC) reagent to the RP-HPLC determination of amino acids in infant foods. J Chromatogr B 831:176–183
Camelini CM, Gomes A, Cardozo FTGS., Simões CMO, Rossi MJ, Giachini AJ, Petrus JCC, de Mendonça MM (2013) Production of polysaccharide from Agaricus subrufescens Peck on solid-sate fermentation. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97:123–133
Chen JH, Li J, Zhang DM, Zhang TP, Zhu WH (2008) Biochemistry experiment. Science Press, Beijing
Chethan S, Malleshi NG (2007) Finger millet polyphenols: Optimization of extraction and the effect of pH on their stability. Food Chem 105:862–870
Cremades O, Diaz-Herrero MM, Carbonero-Aguilar P, Gutierrez-Gil JF, Fontiveros E, Rodríguez-Morgado B, Parrado J, Bautista J (2012) Preparation and characterisation of selenium-enriched mushroom aqueous enzymatic extracts (MAEE) obtained from the white button mushroom (Agaricus bisporus). Food Chem 133:1538–1543
Crisan EV, Sands A (1978) Nutritional value: the biology and cultivation of edible mushrooms. Academic Press, New York
Gil-Ramírez A, Pavo-Caballero C, Baeza E, Baenas N, Garcia-Viguera C, Marín FR, Soler-Rivas C (2016) Mushrooms do not contain flavonoids. J Funct Foods 25:1–13
Han JR (2003) Solid-state fermentation of cornmeal with the basidiomycete Hericium erinaceum for degrading starch and upgrading nutritional value. Int J Food Microbiol 80:61–66
Han JR, An CH, Yuan JM (2005) Solid-state fermentation of cornmeal with the basidiomycete Ganoderma lucidum for degrading starch and upgrading nutritional value. J Appl Microbiol 99:910–915
Huang WK (1989) Examination and Analysis of Food. China Light Industry Press, Beijing
Jayakumar T, Thomas PA, Sheu JR, Geraldine P (2011) In-vitro and in-vivo antioxidant effects of the oyster mushroom Pleurotus ostreatus. Food Res Int 44:851–861
Kandil A, Li J, Vasanthan T, Bressler DC (2012) Phenolic acids in some cereal grains and their inhibitory effect on starch liquefaction and saccharification. J Agric Food Chem 60:8444–8449
Kumari D, Achal V (2008) Effect of different substrates on the production and non-enzymatic antioxidant activity of Pleurotus ostreatus (Oyster mushroom). Life Sci J 5:73–76
Lin SY, Yeh CC, Liang CH, Mau JL (2012) Preparation of Chaga medicinal mushroom, Inonotus obliquus-fermented rice using solid-state fermentation and its taste quality and antioxidant property. Int J Med Mushrooms 14:581–592
McDonald S, Prenzler PD, Autolovich M, Robards K (2001) Phenolic content and antioxidant activity of olive extracts. Food Chem 73:73–84
Mizuno T (2002) Medicinal properties and clinical effects of culinary-medicinal mushroom Agaricus blazei Murrill (Agaricommycetidae). Int J Med Mushrooms 4:299–312
Postemsky P, Curvetto N (2014) Enhancement of wheat grain antioxidant activity by solid state fermentation with Grifola spp. J Med Food 17:543–549
Ray AA (1985) SAS user’s guide: statistics. SAS Institute, Cary
Sanchez JE, Royse DJ (2009) Scytalidium thermophilum-colonized grain, corncobs and chopped wheat straw substrates for the production of Agaricus bisporus. Bioresour Technol 100:1670–1674
Sedmak JJ, Grossberg ES (1977) A rapid, sensitive, and versatile assay for protein using Coomassie Brilliant Blue G250. Anal Biochem 79:544–552
Sun CH (2011) Nutrition and food hygiene. People’s Medical Publishing House, Beijing
Wu WM, Chen YY (1985) Applied fuzzy set methods. Beijing Teachers University Press, Beijing
Zhai FH, Wang Q, Han JR (2015) Nutritional components and antioxidant properties of seven kinds of cereals fermented by the basidiomycete Agaricus blazei. J Cereal Sci 65:202–208
Acknowledgements
Support for this research by the Shanxi Province Coal Fund (Grant No. FT2014-03) is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhai, FH., Liu, HY. & Han, JR. Protein nutritional value, polyphenols and antioxidant properties of corn fermented with Agaricus brasiliensis and Agaricus bisporus. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 34, 36 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-017-2399-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-017-2399-y