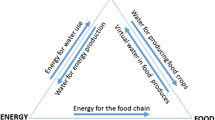
Abstract
With the increasing threat to water, energy, and food resources world-wide, it is highly imperative to manage these resources sustainably. This study develops an optimal crop area allocation model based on a novel nexus-sustainability index (NSI), integrating the water use, energy use (environmental dimension); land use, labour use (social dimension); yield return, and per capita food production (economic dimension) indicators in agricultural food production. This NSI-based model is evaluated in a reservoir-canal command for optimal water and energy uses and, subsequently, compared with the conventional models of Net-Economic Return (NER), Water-Food (W-F) nexus, and Energy-Food (E-F) nexus based approaches using multi-criteria decision making (MCDM) analysis. The comparative results revealed that the NSI-based model is the best that could save water, energy and labour resources by 36.82(±1.91)%, 23.72(±2.47)%, and 2.29(±0.16)% during the Kharif season; and 17.5(±0.59)%, 19.82(±1.52)%, and 2.02(±0.42)% during the Rabi season as compared to the existing condition, respectively, enhancing the net economic return by 56.53(±3.28)% and 79.96(±2.97)% during the corresponding seasons, respectively. Finally, it is advocated that the NSI-based approach could manage the water and energy resources sustainably ensuring security in the local water-energy-land-food (WELF) nexus.






Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
14 July 2020
The original version of this article unfortunately contains mistake in equation 9. The mistake and correction is described below.
References
Allen R. G, Pereira L. S, Raes D, and Smith M (1998) Guidelines for computing crop water requirements. Irrigation and drainage paper 56, food and agricultural Organization of the United Nations, Rome
Alluvione F, Moretti B, Sacco D, Grignani C (2011) EUE (energy use efficiency) of cropping systems for a sustainable agriculture. Energy 36(7):4468–4481. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2011.03.075
Cai X, Wallington K, Shafiee-Jood M, Marston L (2018) Understanding and managing the food-energy-water nexus–opportunities for water resources research. Advances Water Res 111:259–273. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advwatres.2017.11.014
Daher BT, Mohtar RH (2015) Water-energy-food (WEF) Nexus tool 2.0: guiding integrative resource planning and decision-making. Water Int 40(5–6):748–771. https://doi.org/10.1080/02508060.2015.1074148
Dargin J, Daher B, Mohtar RH (2018) Complexity versus simplicity in water energy food nexus (WEF) assessment tools. Sci Total Environ 650:1566–1575
Das B, Singh A, Panda SN, Yasuda H (2015) Optimal land and water resources allocation policies for sustainable irrigated agriculture. Land Use Policy 42:527–537. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landusepol.2014.09.012
Dastane N. G (1978) Effective rainfall in irrigated agriculture. Irrigation and drainage paper 25, food and agricultural Organization of the United Nations, Rome
Fawzy G (2009) The impact of optimizing the irrigation water use on the economics of agriculture production and water saving. Journal of Water Science 15(2):65–68
Garg NK, Dadhich SM (2014) Integrated non-linear model for optimal cropping pattern and irrigation scheduling under deficit irrigation. Agric Water Manag 140:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2014.03.008
Giampietro M, Aspinall R, Bukkens S, Benalcazar J, Diaz-Maurin F, Flammin A, Gomiero T, Kovacic Z, Madrid C, Ramos-Martin J, Serrano-Tovar T (2013) An innovative accounting framework for the Food-Energy-Water Nexus—Application of the MuSIASEM approach to three case studies. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO), Environment and Natural Resources Management Working Paper 56
Giampietro M, Aspinall R. J, Ramos-Martin J, and Bukkens S. G (2014) Resource accounting for sustainability assessment: the nexus between energy, food, water and land use. Routledge, London, U.K
Gomez-Limon JA, Arriaza M, Riesgo L (2003) An MCDM analysis of agricultural risk aversion. Eur J Oper Res 151:569–585. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0377-2217(02)00625-2
Gregory R, Failing L (2002) Using decision analysis to encourage sound deliberation: water use planning in British Columbia, Canada. Journal of Policy Analysis and Management 21:492–499. https://doi.org/10.1002/pam.10059
Gregory R, Wellman K (2001) Bringing stakeholder values into environmental policy choices. A community-based estuary case study. Ecol Econ 39:37–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0921-8009(01)00214-2
Hargreaves GH, Samani ZA (1985) Reference crop evapo-transpiration from temperature. Appl Eng Agric 1(2):96–99. https://doi.org/10.13031/2013.26773
Hoff H (2011) Understanding the nexus: background paper for the Bonn 2011 conference. The water, energy and food security Nexus, solutions for the green economy, Bonn Cof., environment Stockholm institute, Stockholm
Howells M, Hermann S, Welsch M, Bazilian M, Segerström R, Alfstad T, Wiberg D (2013) Integrated analysis of climate change, land-use, energy and water strategies. Nat Clim Chang 3(7):621–626
Kaur B, Sidhu RS, Vatta K (2010) Optimal crop plans for sustainable water use in Punjab. Agric Econ Res Rev 23(2):273–284
Kaushal MP, Khepar SD, Panda SN (1985) Saline groundwater management and optimal cropping pattern. Water Int 10(2):86–91. https://doi.org/10.1080/02508068508686316
Khan S, Hanjra MA (2009) Footprints of water and energy inputs in food production – global perspectives. Food Policy 34:130–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodpol.2008.09.001
Kurian M (2017) The water-energy-food nexus: trade-offs thresholds and transdisciplinary approaches to sustainable development. Environ Sci Pol 68:97–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsci.2016.11.006
Levy J, Hipel K, Kilgour DM (2000) Using environmental indicators to quantify the robustness of policy alternatives to uncertainty Ecol Model 130:79–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-3800(00)00226-X
Mariolakos I (2007) Water resources management in the framework of sustainable development. Desalination 213:147–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2006.05.062
Mayya S. G, Prasad R (1989) System analysis of tank irrigation: crop staggering. J of Irri and Drain Eng. https://ascelibrary.org/doi/abs/10.1061
Mazziotta M, Pareto A (2013) Methods for constructing composite indices: one for all or all for one. Rivista Italiana di Economia Demografia e Statistica 67(2):67–80
McDaniels TL (1995) Using judgment in resource management: a multiple objective analysis of a fisheries management decision. Oper Res 43:415–426. https://doi.org/10.1287/opre.43.3.415
Negm A, El-eshmawiy K, Elfatah H, El-shiraif L (2006) The optimal Egyptian indicative cropping pattern using nonlinear fractional programming. Journal of Applied Science Res 2(2):91–99
Nguyen DCH, Dandy GC, Maier HR, Ascough JC (2016) Improved ant colony optimization for optimal crop and irrigation water allocation by incorporating domain knowledge. J Water Resour Plan Manag 142:04016025. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)WR.1943-5452.0000662
Nijkamp P, Rietveld P, and Voogd H (1990). Multicriteria evaluation in physical planning. Amsterdam: North-Holland
Parnell GS, Frimpon M, Barnes J, Kloeber JM, Deckro RF, Jackson JA (2001) Safety risk analysis of an innovative environmental technology. Risk Anal 21:143–155
Paudyal G. N, Gupta A. D (1990) Irrigation planning by multilevel optimization. J of Irri and Drain Eng. https://ascelibrary.org/doi/10.1061, Irrigation Planning by Multilevel Optimization
Rasul G (2014) Food, water, and energy security in South Asia: a nexus perspective from the Hindu Kush Himalayan region. Environ Sci Pol 39:35–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsci.2014.01.010
Raul S. K (2012) Simulation-optimization modelling for integrated land and water resources management in the Hirakud canal command. Ph.D. Dissertation, Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur (India)
Raul SK, Panda SN, Hollander H, Billib M (2011) Integrated water resources management in a major canal command in eastern India. Hydrol Process 25:2551–2562. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.8028
Ringler C, Willenbockel D, Perez N, Rosegrant M, Zhu T, Matthews N (2016) Global linkages among energy, food and water: an economic assessment. J Environ Stud Sci 6(1):161–171. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13412-016-0386-5
Ruju KS, Kumar DN (1999) Multicriterion decision making in irrigation planning. Agric Syst 62(2):117–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0308-521X(99)00060-8
Sahoo B, Lohani AK, Sahu RK (2006) Fuzzy multi-objective and linear programming based management models for optimal land-water-crop system panning. Water Resources Manage 20(6):931–948. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-005-9015-x
Sahoo B, Walling I, Deka BC, Bhatt BP (2012) Standardization of reference evapotranspiration models for a sub-humid valley rangeland in the Eastern Himalayas. J Irrig Drain Eng 138(10):880–895. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)IR.1943-4774.0000476
Sahoo S, Sahoo B, Panda SN (2018) Hillslope-storage Boussinesq model for simulating subsurface water storage dynamics in scantily-gauged catchments. Adv Water Res 121:219–234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advwatres.2018.08.016
Saxton K. E(2009) Soil-plant-atmosphere-water. https://hrsl.ba.ars.usda.gov/SPAW/Index.html accessed 25th April 2018
Sethi LN, Kumar D, Panda SN, Mal B (2002) Optimal crop planning and conjunctive use of water resources in a coastal river basin. Water Resour Manag 16:145–169. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016137726131
Sethi LN, Panda SN, Nayak AMK (2006) Optimal crop planning and water resources allocation in a coastal groundwater basin, Orissa, India. Agric Water Manag 83(3):209–220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2005.11.009
Shiklomanov IA (2000) Appraisal and assessment of world water resources. Water Int 25:11–32. https://doi.org/10.1080/02508060008686794
Singh A (2012) Optimal allocation of resources for the maximization of net agricultural return. J Irrig Drain Eng 138:830–836. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)IR.1943-4774.0000474
Singh A (2014) Optimizing the use of land and water resources for maximizing farm income by mitigating the hydrological imbalances. J Hydrol Eng 19:1447–1451. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)HE.1943-5584.0000924
Singh DK, Jaiswal CS, Reddy KS, Singh RM, Bhandarkar DM (2001) Optimal cropping pattern in a canal command area. Agric Water Manag 50(1):1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-3774(01)00104-4
SMOS-Barcelona Expert Centre (SMOS-BEC) (2007–2020) Land variables, Level 2 soil moisture user data product. http://bec.icm.csic.es/land-datasets (updated regularly). Accessed 10 Mar 2018
Store R, Kangas J (2001) Integrating spatial multi-criteria evaluation and expert knowledge for GIS-based habitat suitability modeling. Landscape Urban Plann 55:79–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0169-2046(01)00120-7
Swain R, Sahoo B (2015) Variable parameter McCarthy-Muskingum flow transport model for compound channels accounting for distributed nonuniform lateral flow. J Hydrol 530:698–715. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2015.10.030
United Nations (2014). United Nations, Introduction and proposed goals and targets on sustainable development for the post-2015 development agenda. https://sustainabledevelopment.un.org/content/documents/4528zerodraft12OWG.pdf Accessed 16th May 2018
US NIC (United States National Intelligence Council) (2012). Global trends 2030: alternative worlds. US NIC, Washington DC, USA
USDOE (2014). The water-energy Nexus: challenges and opportunities. U. S. Department of Energy, DOE/EPSA-0002
Van Genuchten M. T, Leij F. J, Yates S. R (1991) The RETC code for quantifying the hydraulic functions of unsaturated soils. U. S. Environ. Prot. Agency, Ada, Oklahoma
White DJ, Hubacek K, Feng K, Sun L, Meng B (2018) The water-energy-food Nexus in East Asia: a tele-connected value chain analysis using inter-regional input-output analysis. Appl Energy 210:550–567. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2017.05.159
World Bank (1992). World development report 1992: development and the environment. Oxford University Press, U.K
Zhou Y, Zhang B, Wang H, Bi J (2013) Drops of energy: conserving urban water to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Environ Sci Technol 47:10753–10761. https://doi.org/10.1021/es304816h
Acknowledgments
We thank the government organizations (duly cited in the text) for providing relevant data required for the study. We also thank the Ministry of Human Resources Development, Government of India, for providing the fellowship to the first author during the research tenure. We would like to extend our special thanks to the editors and anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments in greatly improving the quality of this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Das, A., Sahoo, B. & Panda, S.N. Evaluation of Nexus-Sustainability and Conventional Approaches for Optimal Water-Energy-Land-Crop Planning in an Irrigated Canal Command. Water Resour Manage 34, 2329–2351 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-020-02547-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-020-02547-y