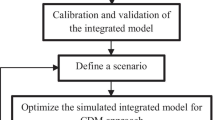
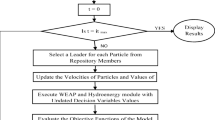
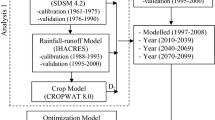
Abstract
The assessment of climate change and its impacts on hydropower generation is a complex issue. This paper evaluates the application of representative concentration pathways (RCPs, 2.6, 4.5, and 8.5) with the change factor (CF) method and the statistical downscaling method (SDSM) to generate six climatic scenarios of monthly temperature and rainfall over the period 2020–2049 in the Karkheh basin, Iran. The identification of unit hydrographs and component flows from rainfall, evaporation and streamflow data (IHACRES) model was employed to simulate runoff for the purpose of designing a run-of-river hydropower plant in the Karkheh basin. The non-dominated sorting genetic algorithm (NSGA)-II was employed to maximize yearly energy generation and the plant factor, simultaneously. Results indicate the runoff scenarios associated with the SDSM lead to higher run-of-river hydropower generation in 2020–2049 compared to the CF results.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adhikary P, Roy PK, Mazumdar A (2012) Safe and efficient control of hydro power plant by fuzzy logic. Int J Eng Sci Adv Technol 2(5):1270–1277
Anagnostopoulos JS, Papantonis D (2007) Optimal sizing of a run-of-river hydropower plant. Energy Convers Manag 48(10):2663–2670
Ashofteh PS, Bozorg-Haddad O, Mariño MA (2013) Scenario assessment of streamflow simulation and transition probability in future periods under climate change. J Water Resour Manag 27:255–274
Bozorg-Haddad O, Farhangi M, Fallah-Mehdipour E, Mariño MA (2014) Effects of inflow uncertainty on the performance of multireservoir systems. J Irrig Drain 140(11)
Croke BFW, Jakeman AJ (2008) Hydrological modeling in arid and semi-arid areas. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Deb K (1999) Multi-objective genetic algorithms: problem difficulties and construction of test problem. Evol Comput 7(3):205–230
Deb K, Goyal M (1996) A combined genetic adaptive search (GeneAS) for engineering design. J Comput Sci Info 26(4):30–45
Ghorbani KH, Sohrabian E, Salarijazi M, Abdolhosseini M (2016) Prediction of climate change impact on monthly river discharge trend using IHACRES hydrological model (case study: Galikesh watershed). J Soil Water Resou Convers 5(4):19–34
Jager HI, Bevelhimer MS (2007) How run-of-river operation affects hydropower generation and value. Environ Manag 40(6):1004–1015
Jung L, Moradkhani H, Chang H (2012) Uncertainty assessment of climate change impacts for hydrologically distinct river basins. J Hydrol 466-467:73–87
Littlewood IAN (2001) Practical aspects of calibrating and selecting unit hydrograph-based models for continuous river flow simulation. Hydrol Sci J 46(5):795–811
Motevalli M, Zadbar A, Elyasi E, Jalaal M (2015) Using Monte-Carlo approach for analysis of quantitative and qualitative operation of reservoirs systems with regard to the inflow unceratinty. J Afr Earth Sci 105:1–16
Rojanamon P, Chaisomphob T, Bureekul T (2009) Application of geographical information system to site selection of small run-of-river hydropower project by considering engineeringleconomics/environmental criteria and social impact. Renew Sust Energ Rev 13(9):2336–2348
Sammartano V, Aricò C, Sinagra M, Tucciarelli T (2015) Cross-flow turbine design for energy production and discharge regulation. J Hydraul Eng, 141(3)
Sammartano V, Filianoti P, Morreale G, Sinagra M, Tucciarelli T (2016) Banki-Michell micro-turbines for energy production in water distribution networks. Proceedings of the 4th European congress of the International Association of Hydroenvironment Engineering and Research, IAHR 2016, 966–972
Sammartano V, Filianoti P, Sinagra M, Tucciarelli T, Scelba G, Morreale G (2017) Coupled hydraulic and electronic regulation of cross-flow turbines in hydraulic plants. J Hydraul Eng, 143(1)
Sarzaeim P, Bozorg-Haddad O, Fallah-Mehdipour E, Loáiciga HA (2017) Environmental water demand assessment under climate change conditions. Environ Monit Asses, 189(7)
Tan ML, Ficklin DL, Ibrahim AL, Yusop Z (2014) Impacts and uncertainties of climate change on streamflow of the Johor river basin, Malaysia using a CMIP5 general circulation model ensemble. J Water Climate Chang 5(4):676–695
Vicuna S, Edwin PM, Joyce B, Dracup JA, Purkey D (2007) The sensitivity of California water resources to climate change scenarios. J Am Water Resour Assoc 43(2):482–498
Wilby RL, Harris I (2006) A framework for assessing uncertainties in climate change impacts: low-flow scenarios for the river Thames, UK. Water Resour Res, 42(2)
Wilby RL, Dawson CW, Barrow EM (2002) SDSM-a decision support tool for the assessment of regional climate change impacts. J Environ Model Softw 17(2):145–157
Zhang Y, You Q, Chen C, Ge J (2016) Impacts of climate change on streamflow under RCP scenarios: a case study in Xin river basin, China. Atmos Res 178-179:512–534
Acknowledgements
Authors thank Iran’s National Elites Foundation for financial support of this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interests
None.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sarzaeim, P., Bozorg-Haddad, O., Zolghadr-Asli, B. et al. Optimization of Run-of-River Hydropower Plant Design under Climate Change Conditions. Water Resour Manage 32, 3919–3934 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-018-2027-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-018-2027-0