Abstract
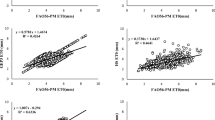
This study aimed to forecast the daily reference evapotranspiration (ETo) using a gene-expression programming (GEP) algorithm with limited public weather forecast information over Gaoyou station, located in Jiangsu province, China. To calibrate and validate the gene-expression code, important meteorological data and weather forecast information were collected from the local meteorological station and public weather media, respectively. The GEP algebraic formulation was successfully constructed based only on daily minimum and maximum air temperature using the true FAO56 Penman-Monteith (PM) set as reference values. The performance of the models was then assessed using the correlation coefficient (R), root mean squared error (RMSE), root relative squared error (RRSE) and mean absolute error (MAE). The study demonstrated that GEP is able to calibrate ETo (all errors ≤0.990 mm/day, R = 0.832–0.866) and forecast the daily ETo with good accuracy (RMSE = 1.207 mm/day, MAE = 0.902 mm/day, RRSE = 0.629 mm/day, R = 0.777). The model accuracies slightly decreased over a 7-day forecast lead-time. These results suggest that the GEP algorithm can be considered as a deployable tool for ETo forecast to anticipate decision on short-term irrigation schedule in the study zone.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arca B, Duce P, Snyder RL, Spano D, Fiori M (2004) Use of numerical weather forecast and time series models for predicting reference evapotranspiration. Acta Hortic 664:8
Arab Amiri M, Mesgari MS (2016) Spatial variability analysis of precipitation in northwest Iran. Arab J Geosci 9(11):1–10
Arab Amiri M, Amerian Y, Mesgari MS (2016) Spatial and temporal monthly precipitation forecasting using wavelet transform and neural networks, Qara-Qum catchment, Iran. J Geosci 2016(9):421
Allen RG, Pereira LS, Raes D, Smith M (1998) Crop evapotranspiration. Guidelines for computing crop water requirements. FAO Irrigation & Drainage Paper: 56. FAO, Rome 300(9):D05109. (http://www.fao.org/docrep/X0490E/X0490E00.htm#Contents)
Ballesteros R, Ortega JF, Moreno MA (2012) FORETo: new software for reference evapotranspiration forecasting, soil and water engineering. International conference of agricultural engineering-CIGR-AgEng 2012: agriculture and engineering for a healthier life, 8-12 July 2012, Valencia
Blaney HF, Criddle WD (1962) Determining consumptive use and irrigation water requirements, USDA technical bulletin 1275. US Department of Agriculture, Beltsville
de la Casa AC, Ovando GG (2016) Variation of reference evapotranspiration in the central region of Argentina between 1941 and 2010. Journal of Hydrology: Regional Studies 5:66–79
Cong ZT, Yang DW, Ni GH (2009) Does evaporation paradox exist in China? Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 13:357–366
Droogers P, Allen RG (2002) Estimating reference evapotranspiration under inaccurate data conditions. Irrig Drain Syst 16(1):33–45
Esmaeilzadeh B, Sattari MT (2015) Monthly evapotranspiration modeling using intelligent Systems in Tabriz. Iran Agric sci dev 4(3):35–40
Ferreira C (2001) Gene expression programming: a new adaptive algorithm for solving problems. Complex Syst 13(2):87–129
Guven A, Aytek A, Yuce MI, Aksoy H (2008) Genetic programming-based empirical model for daily reference evapotranspiration estimation. Soil Air Water CLEAN 36(10–11):905–912
Guven A, Kişi Ö (2010) Daily pan evaporation modeling using linear genetic programming technique. Irrig Sci 29(2):135–145
Hargreaves GH (1994) Defining and using reference evapotranspiration. J Irrig Drain Eng 120(6):1132–1139
Hargreaves GH, Samani ZA (1985) Reference crop evapotranspiration from temperature. Appl Engine Agric 1(2):96–99
Kassam A, Smith M (2001) FAO methodologies on crop water use and crop water productivity. PAPER NO CWP-M07 ROME, expert meeting on crop water productivity 3 to 5 December 2001
Khoob AR (2008a) Comparative study of Hargreaves’s and artificial neural network’s methodologies in estimating reference evapotranspiration in a semiarid environment. Irrig Sci 26(3):253–259
Khoob AR (2008b) Artificial neural network estimation of reference evapotranspiration from pan evaporation in a semi-arid environment. Irrig Sci 27(1):35–39
Kişi O (2006) Generalized regression neural networks for evapotranspiration modeling. Hydrol Sci J 51(6):1092–1105
Kisi O, Cengiz TM (2013) Fuzzy genetic approach for estimating reference evapotranspiration of Turkey: Mediterranean region. Water Resour Manag 27(10):3541–3553
Landeras G, Ortiz-Barredo A, López JJ (2008) Comparison of artificial neural network models and empirical and semi-empirical equations for daily reference evapotranspiration estimation in the Basque Country (northern Spain). Agric Water Manag 95(5):553–565
López-Urrea R, Olalla FMDS, Fabeiro C, Moratalla A (2006) An evaluation of two hourly reference evapotranspiration equations for semiarid conditions. Agric Water Manag 86(3):277–282
Luo Y, Chang X, Peng S, Khan S, Wang W, Zheng Q, Cai X (2014) Short-term forecasting of daily reference evapotranspiration using the Hargreaves–Samani model and temperature forecasts. Agric Water Manag 136(2):42–51
Luo Y, Traore S, Lyu X, Wang W, Wang Y, Xie Y, Jiao X, Fipps G (2015) Medium range daily reference evapotranspiration forecasting by using ANN and Public weather forecasts. Water Resour Manag 29:3863–3876
McVicar TR, Roderick ML, Donohue RJ (2012) Global review and synthesis of trends in observed terrestrial near-surface wind speeds: implications for evaporation. J Hydrol 416–417:182–205
Osborne HD, Palmer CK, Kronedavis P, Melton FS, Hobbins M (2013) National Weather Service Forecast Reference Evapotranspiration. American Geophysical Union, Fall Meeting 2013, abstract #H21A-1012
Perera KC, Western AW, Nawarathna B, George B (2013) Forecasting daily reference evapotranspiration for Shepparton, Victoria, Australia using numerical weather prediction outputs. 20th international congress on Modelling and simulation, Adelaide, Australia, 1–6 December 2013 www.mssanz.org.au/modsim2013
Tabari H, Talaee PH, Some’e BS (2013) Spatial modelling of reference evapotranspiration using adjusted Blaney-Criddle equation in an arid environment. Hydrol Sci J 58(2):408–420
Thornthwaite CW (1948) An approach towards a rational classification of climate. Geogr. Rev 38:55–94
Trajkovic S (2005) Temperature-based approaches for estimating reference evapotranspiration. J Irrig Drain Eng 131(4):316–323
Traore S, Guven A (2011) New algebraic formulations of evapotranspiration extracted from gene-expression programming in the tropical seasonally dry regions of West Africa. Irrig Sci. doi:10.1007/s00271-011-0288-y
Traore S, Guven A (2012) Regional-specific numerical models of evapotranspiration using gene-expression programming Interface in Sahel. Water Resour Manag 26:4367
Traore S, Luo Y (2016) Fipps G (2016) deployment of artificial neural network for short-term forecasting of evapotranspiration using public weather forecast restricted messages. Agric Water Manag 163:363–379
Wang YM, Traore S, Kerh T (2009) Computational performance of reference evapotranspiration in semiarid zone of Africa. Sci Res Essays 4(6):577–583
Wang YM, Traore S, Kerh T, Leu JM (2010) Modelling reference evapotranspiration using feed forward Backpropagation algorithm in arid regions of Africa. Irrig Drain 60(3):404–417
Wang Z, Xie P, Lai C, Chen X, Wu X, Zeng Z, Li J (2017) Spatiotemporal variability of reference evapotranspiration and contributing climatic factors in China during 1961–2013. Journal of Hydrology, Volume 544:97–108
Yang Y, Cui Y, Lu Y, Lyu X, Traore S, Khane S, Wang W (2016) Short-term forecasting of daily reference evapotranspiration using the penman-Monteith model and public weather forecasts. Agric Water Manag 177:329–339
Zheng H, Liu X, Liu C, Dai X, Zhu R (2009) Assessing contributions to pan evaporation trends in Haihe River Basin, China. J Geophys Res 114:D24105. https://doi.org/10.1029/2009JD012203
Zhao LL, Xia J, Sobkowiak L, Li ZL (2014) Climatic characteristics of reference evapotranspiration in the Hai River basin and their attribution. Water 6:1482–1499
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the Ministry of Science and Technology of China under the National Key Research & Development (R&D) Plan (2016YFC0400101) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (91647204). The observed meteorological data obtained from the China Meteorological Data Sharing Service System (http://cdc.cma.gov.cn) and weather forecast data from Weather China (http://www.weather.com.cn) are gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Traore, S., Luo, Y. & Fipps, G. Gene-Expression Programming for Short-Term Forecasting of Daily Reference Evapotranspiration Using Public Weather Forecast Information. Water Resour Manage 31, 4891–4908 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-017-1784-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-017-1784-5