Abstract
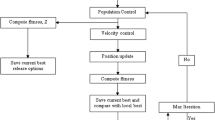
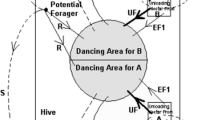
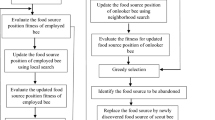
In this study, the Artificial Bee Colony (ABC) algorithm was developed to solve the Chenderoh Reservoir operation optimisation problem which located in the state of Perak, Malaysia. The proposed algorithm aimed to minimise the water deficit in the operating system and examine its performance impact based on monthly and weekly data input. Due to its capability to identify different possible events occurring in the reservoir, the ABC algorithm provides promising and comparable solutions for optimum release curves. The optimal release curves were then used to stimulate the reservoir release under different operating times under different inflow scenarios. To investigate the performance of both the monthly and weekly ABC optimisation employed in the reservoir, the well-known reliability, resilience and vulnerability indices were used for performance assessment. The indices tests revealed that weekly ABC optimisation outperformed in terms of reliability and vulnerability leading to the development of a better release policy for optimal operation.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adeyemo JA (2011) Reservoir operation using multi-objective evolutionary algorithms - a review. Asian Journal of Scientist Research
Asfaw TD, Hashim AM (2011) Reservoir Operation Analysis Aimed to Optimize the Capacity Factor of Hydroelectirc Power Generation. Paper presented at the 2011 International Conference on Environment and Industrial Innovation
Asfaw TD, Yusof KW, Hashim AM (2013) Competence-oriented decision model for optimizing the operation of a cascading hydroelectric power reservoir. [article]. Res J Appl Sci Eng Technol 6(10):1895–1901
Baltar AM, Fontane DG (2008) Use of multiobjective particle swarm optimization in water resources management. [article]. J Water Resour Plan Manag 134(3):257–265
Choong SM, El-Shafie A (2014) State-of-the-art for Modelling reservoir inflows and management optimization. [review]. Water Resour Manag 29(4):1267–1282
Diwold K, Beekman M, Middendorf M (2011) Honeybee optimisation – an overview and a new bee inspired optimisation scheme. In: Panigrahi BK, Shi Y, Lim M-H (eds) Handbook of swarm intelligence: concepts, principles and applications. Springer Berlin Heidelberg, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp 295–327
Eiben AE, J. E. S (2003) Introduction to evolutionary computing. Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg
Hossain MS, El-shafie A (2013) Performance analysis of artificial bee colony (ABC) algorithm in optimizing release policy of Aswan high dam. Neural Comput & Applic:1–8
Janga Reddy M, Nagesh Kumar D (2007) Multi-objective particle swarm optimization for generating optimal trade-offs in reservoir operation. [article]. Hydrol Process 21(21):2897–2909
Jothiprakash V, Arunkumar R (2014) Multi-reservoir optimization for hydropower production using NLP technique. KSCE J Civ Eng 18(1):344–354
Karaboga D (2005) An idea beased on honey bee swarm for numerical optimization: Erciyes University, engineering faculty, Computer Engineering department
Kennedy J, Eberhart R (1995) Particle swarm optimization. Paper presented at the Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Neural Networks
Liao X, Zhou J, Ouyang S, Zhang R, Zhang Y (2013) An adaptive chaotic artificial bee colony algorithm for short-term hydrothermal generation scheduling. Int J Electr Power Energy Syst 53:34–42
Montalvo I, Izquierdo J, Pérez-García R, Herrera M (2010) Improved performance of PSO with self-adaptive parameters for computing the optimal design of water supply systems. Eng Appl Artif Intell 23(5):727–735
Moy WS, Cohon JL, ReVelle CS (1986) A programming model for analysis of the reliability, resilience, and vulnerability of a water supply reservoir. [article]. Water Resour Res 22(4):489–498
Savic AD, Walters GA, Atkinson RM, Smith MR (1999) Genetic algorithm optimization of large water distribution system expansion. Measurement and Control 32(4):104–109
Shrestha S, Khatiwada M, Babel MS, Parajuli K (2014) Impact of climate change on river flow and hydropower production in Kulekhani hydropower project of Nepal. Environmental Processes 1(3):231–250
Zhou J, Liao X, Ouyang S, Zhang R, Zhang Y (2014) Multi-objective artificial bee colony algorithm for long-term scheduling of hydropower system: a case study of China. Water Utility Journal 7:13–23
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to express their sincere appreciation to the Generation Department of Tenaga Nasional Berhad (TNB) for providing the relevant data and their kind cooperation in this research. This research was partially supported by Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia, under the research grant for the second author DIP-2015-012 and for the third author DIP-2015-006.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choong, SM., El-Shafie, A. & Wan Mohtar, W.H.M. Optimisation of Multiple Hydropower Reservoir Operation Using Artificial Bee Colony Algorithm. Water Resour Manage 31, 1397–1411 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-017-1585-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-017-1585-x