Abstract
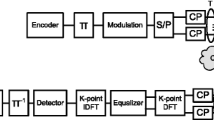
We consider performance comparison and application specific integrated circuit (ASIC) designs of linear minimum mean-square error (LMMSE) and K-best list sphere detector (LSD) algorithms for 4 × 4 and 8 × 8 multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) systems. Requirements for higher data rate and lower power consumption set new challenges for implementation. In order to minimize the power consumption, an optimal detector would be able to switch the detection algorithm to suit the channel conditions. The detectors are designed for three different modulation schemes using 28 nm complementary metal oxide semiconductor (CMOS) technology. The communications performance is evaluated in the Third Generation Partnership Project (3GPP) Long-Term Evolution (LTE) system. The impact of transmit precoding is considered. The ASIC designs aim at providing the hardware design aspects to the comparison of detectors. The designs are synthesized and complexity and power consumption results are found. Based on the ASIC synthesis and communications performance results, we show the performance–energy efficiency and performance–complexity comparison. We also present the most suitable scenarios for a low-power detector and show how the transmit precoding impacts the detector selection.





















Similar content being viewed by others
References
(2010). 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP); Technical Specification Group Radio Access Network, “Evolved universal terrestrial radio access E-UTRA; physical channels and modulation (release 10) TS 36.211 (version 10.0.0),” Tech. Rep.
Onggosanusi, E.N., Dabak, A.G., Hosur, S. (2006). Multimode detection. Patent U.S. 2006/0018410 A1.
Shen, H., Zhang, H., Zhao, C. (2011). An efficient adaptive receiver for MIMO? OFDM systems In Proceedings of the international conference on wireless communications and signal processing (pp. 1–5).
Chen, X., Minwegen, A., Hassan, Y., Kammler, D., Li, S., Kempf, T., Chattopadhyay, A., Ascheid, G. (2012). FLEXDET: Flexible, efficient multi-mode MIMO detection uding reconfigurable ASIP. In Proc. Int. Symb. on Field-progr. Custom Comp. machines, (Vol 3 pp. 69–76).
Chen, X., Minwegen, A., Hussain, S.B., Chattopadhyay, A., Ascheid, G., Leupers, R. (2015). Flexible, efficient multimode MIMO detection by using reconfigurable ASIP. IEEE Trans. VLSI, Syst., 23(10), 2173–2186.
Sheikh, F., Chen, C. -H., Yoon, D., Alexandrov, B., Bowman, K., Chun, A., Alavi, H., Zhang, Z. (2014). 3.2 Gbps channel-adaptive configurable MIMO detector for multi-mode wireless communication. In Proceedings of the IEEE Works. on Sign. Proc. Syst. (pp. 1–6). Northern Ireland: Belfast.
(2013). 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP); Technical Specification Group Radio Access Network,“Evolved universal terrestrial radio access E-UTRA; physical layer procedures (release 11) TS 36.213 (version 11.2.0),” Tech. Rep.
Yoshizawa, S., Miyazaki, N., Nakagawa, D., Miyanaga, Y. (2011). A low-power adaptive MIMO detector for MIMO–OFDM WLAN systems. In Proc. annual Conf. Asia-pacific signal and information processing association (pp. 2486–2489). Xi’an.
Suikkanen, E., & Juntti, M. (2014). Study of adaptive detection and channel estimation for MIMO–OFDM systems. In Springer Wireless Pers. Commun.
Suikkanen, E., Janhunen, J., Shahabuddin, S., Juntti, M. (2013). Study of adaptive detection for MIMO–OFDM systems. In Proc. Int. Symp. on System-on-Chip (pp. 1–4). Tampere.
Suikkanen, E., Ketonen, J., Juntti, M. (2014). Detection and channel estimation in 88 MIMO–OFDM. In Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. Cognitive Radio Oriented Wireless Networks and Communications (pp. 299–304). Oulu.
Suikkanen, E., & Juntti, M. (2015). ASIC implementation and performance comparison of adaptive detection for MIMO–OFDM system. In Proc. annual Asilomar Conf. signals, Syst., Comp. (pp. 1632–1636). Pacific Grove.
Artes, H., Seethaler, D., Hlawarsch, F. (2003). Efficient detection algotihms for MIMO channels: a geometrical approach to approximate ML detection. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 51(11), 2808–2820.
Wong, K., Tsui, C., Cheng, R.-K., Mow, W. (2002). A VLSI architecture of a K-best lattice decoding algorithm for MIMO channels. In Proc. IEEE Int. Symp. on Circuits and Systems, (Vol 3 pp. 273–276). Scottsdale.
Burg, A., Borgmann, M., Wenk, M., Zellweger, M., Fichtner, W., Bölcskei, H. (2005). VLSI implementation of MIMO detection using the sphere decoding algorithm. IEEE Journal Solid-State Circuits, 40(7), 1566–1577.
Barbero, L.G., & Thompson, J.S. (2006). FPGA design considerations in the implementation of a fixed-throughput sphere decoder for MIMO systems. In Int. Conf. on field programmable logic and applications (pp. 1–6). Sydney.
Wu, B., & Masera, G. (2012). Efficient VLSI implementation of soft-input soft-output fixed-complexity sphere decoder. IET Communications, 6(9), 1111–1118.
Myllylä, M., Juntti, M., Cavallaro, J. (2010). Implementation aspects of list sphere decoder algorithms for MIMO–OFDM systems. Signal Processing, Elsevier, 90(10), 2863–2876.
Wübben, D., Böhnke, R., Kühn, V., Kammeyer, K. (2003). MMSE extension of v-BLAST based on sorted QR decomposition. In Proceedings of IEEE Veh. Technol. Conf., (Vol. 1 pp. 508–512). Orlando.
Ozdemir, M.K., & Arslan, H. (2007). Channel estimation for wireless OFDM systems. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 9(2), 18–48.
Meidlinger, M., & Wang, Q. (2012). Performance evaluation of LTE advanced downlink channel estimation. In Proc. Int. Conf. on Syst., Sign. and image Proc., (Vol. 252–255), Vienna.
Lin, S., Costello, D.J. Jr, Miller, M.J. (1984). Automatic-repeat-request error-control scheme. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 22(12), 5–17.
Chase, D. (1985). Code combining – a maximum-likelihood decoding approach for combining an arbitrary number of noisy packets. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 33(5), 385–393.
ZTE. (2009). R1-091716 DL codebook design for 8 Tx MIMO in LTE-A. 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP) TSG RAN WG1 Meeting 57, San Francisco, USA, Tech. Rep.
(2002). 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP); Technical Specification Group Radio Access Network. Radio transmission and reception (3G TS 45.005 version 5.4.0 (release 5)). 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP), Tech. Rep.
Cadence Design Systems Datasheet. (2016). Cadence Cto-silicon compiler. [Online]. Available: http://www.cadence.com/products/sd/siliconcompiler/pages/default.aspx, accessed: Mar. 17, 2016.
Synopsys Design Compiler Datasheet. (2016). Synopsys design compiler 2010. [Online]. Available:http://www.synopsys.com/Tools/Implementation/RTLSynthesis/Pages/default.aspx, accessed: Mar. 17, 2016.
Ketonen, J., Juntti, M., Cavallaro, J.R. (2010). Performance-complexity comparison of receivers for a LTE MIMO–OFDM system. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 58(6), 3360–3372.
Gestner, B., & Anderson, D.V. (2008). Single Newton-Raphson iteration for integer-rounded divider for lattice reduction algorithms. In IEEE 51st Midwest Symp. on Circ. and Syst. (Vol. 2), Knoxville.
Golub, G.H., & Van Loan, C.F. (1996). Matrix Computations, 3rd edn. Baltimore: The Johns Hopkins University Press.
Damen, M.O., El gamal, H., Caire, G. (2003). On maximum–likelihood detection and the search for the closest lattice point. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 49(10), 2389–2402.
Myllylä, M., Antikainen, J., Juntti, M., Cavallaro, J.R. (2007). The effect of LLR clipping to the complexity of list sphere detector algorithms. In Proc. Annual Asilomar Conf. signals, Syst., Comp. (pp. 1559–1563). Pacific Grove.
El-Amawy, A., & Dharmarajan, K.R. (1989). Parallel VLSI algorithm for stable inversion of dense matrices. Computers and Digital Techniques, IEE Proceedings E, 136(6), 575–580.
Collings, I., Butler, M.R.G., McKay, M. (2004). Low complexity receiver design for MIMO bit-interleaved coded modulation. In Proc. IEEE Int. Symp. spread spectrum techniques and applications (pp. 1993–1997). Sydney.
Suikkanen, E., Ketonen, J., Juntti, M. (Aug. 2012). Transmission adaptation. International PCT Patent Application No PCT/EP2012/066573.
Maurer, J., Matz, G., Seethaler, D. (2007). Low-complexity and full-diversity MIMO detection based on condition number thresholding. In Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. Acoust., speech, signal processing, (Vol. 3, pp. 61–64). Honolulu.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This research was financially supported in part by Tekes, the Finnish Funding Agency for Innovation, Academy of Finland, Nokia Solutions and Networks, Broadcom Communications Finland and Xilinx.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Suikkanen, E., Juntti, M. Performance and ASIC Designs of the K-best LSD and LMMSE Detectors for LTE Downlink. J Sign Process Syst 91, 1291–1304 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11265-019-1441-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11265-019-1441-8