Abstract
Purpose
This study aimed to estimate the validity and applicability of Vela laser enucleation of the prostate (VoLEP) in the management of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH).
Methods
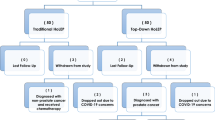
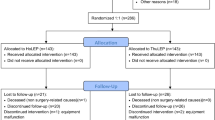
A retrospective chart review of 112 patients with BPH who underwent VoLEP (n = 60) or holmium laser enucleation of the prostate (HoLEP) (n = 56) was conducted at our institution from January 2015 to June 2015. The general and perioperative characteristics of the patients were collected. The 12-month follow-up data, including the lower urinary tract symptom (LUTS) indexes (International Prostate Symptom Score [I-PSS], quality-of-life [QoL] score and maximum flow rate [Qmax]), as well as rates of perioperative and late complications, were analyzed.
Results
No significant differences were observed in pre- and perioperative parameters, including operation time (58.05 ± 10.14 vs. 60.14 ± 12.30 min, P = 0.44), serum sodium decrease (3.49 ± 0.83 vs. 3.48 ± 0.84 mmol/L, P = 0.97), hemoglobin decrease (1.28 ± 0.38 vs. 1.24 ± 0.77 g/dL, P = 0.71), catheterization time (3.63 ± 1.10 vs. 3.89 ± 1.11 days, P = 0.21) and hospital stay (4.57 ± 1.25 vs. 4.68 ± 1.18 days, P = 0.63) between the two groups of patients. Compared with the HoLEP group, the noise during operation was lower in VoLEP group (47.22 ± 10.31 vs. 59.45 ± 9.65 db, P < 0.05). During 1, 6 and 12 months of follow-up visits, the LUTS indexes (I-PSS, QoL score and Qmax) were remarkably improved in both groups when comparing with the baseline values. Furthermore, LUTS indexes were comparable in both groups (P > 0.05).
Conclusion
Similarly as the holmium laser, the Vela laser is a potent, safe, efficient durable and surgical treatment option for minimally invasive surgery in patients with BPH-induced LUTS.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Madersbacher S, Marberger M (1999) Is transurethral resection of the prostate still justified? BJU Int 83(3):227–237
Ahyai SA, Gilling P, Kaplan SA, Kuntz RM, Madersbacher S, Montorsi F, Speakman MJ, Stief CG (2010) Meta-analysis of functional outcomes and complications following transurethral procedures for lower urinary tract symptoms resulting from benign prostatic enlargement. Eur Urol 58(3):384–397. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2010.06.005
Elzayat EA, Habib EI, Elhilali MM (2005) Holmium laser enucleation of the prostate: a size-independent new “gold standard”. Urology 66(5 Suppl):108–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.urology.2005.06.006
Sun N, Fu Y, Tian T, Gao J, Wang Y, Wang S, An W (2014) Holmium laser enucleation of the prostate versus transurethral resection of the prostate: a randomized clinical trial. Int Urol Nephrol 46(7):1277–1282
Elshal AM, El-Assmy A, Mekkawy R, Taha D-E, El-Nahas AR, Laymon M, El-Kappany H, Ibrahiem E-H (2017) Prospective controlled assessment of men’s sexual function changes following Holmium laser enucleation of the prostate for treatment of benign prostate hyperplasia. Int Urol Nephrol 49(10):1741–1749
Kwon T, Park S, Park S, Moon KH (2017) Metabolic syndrome is predictive of lower urinary tract symptom improvement after holmium laser enucleation of the prostate for benign prostatic obstruction. Int Urol Nephrol 49(7):1105–1110
Tan AH, Gilling PJ (2003) Holmium laser prostatectomy. BJU Int 92(6):527–530
Chen YB, Chen Q, Wang Z, Peng YB, Ma LM, Zheng DC, Cai ZK, Li WJ, Ma LH (2013) A prospective, randomized clinical trial comparing plasmakinetic resection of the prostate with holmium laser enucleation of the prostate based on a 2-year followup. J Urol 189(1):217–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.juro.2012.08.087
Michalak J, Tzou D, Funk J (2015) HoLEP: the gold standard for the surgical management of BPH in the 21(st) Century. Am J Clin Exp Urol 3(1):36–42
Chen Q, Chen YB, Wang Z, Peng YB, Zheng DC, Cai ZK, Li WJ, Zhou J (2012) An improved morcellation procedure for holmium laser enucleation of the prostate. J Endourol 26(12):1625–1628. https://doi.org/10.1089/end.2012.0265
Oelke M, Bachmann A, Descazeaud A, Emberton M, Gravas S, Michel MC, N’Dow J, Nordling J, de la Rosette JJ, European Association of U (2013) EAU guidelines on the treatment and follow-up of non-neurogenic male lower urinary tract symptoms including benign prostatic obstruction. Eur Urol 64(1):118–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2013.03.004
Berry SJ, Coffey DS, Walsh PC, Ewing LL (1984) The development of human benign prostatic hyperplasia with age. J Urol 132(3):474–479
Geavlete B, Stanescu F, Iacoboaie C, Geavlete P (2013) Bipolar plasma enucleation of the prostate vs open prostatectomy in large benign prostatic hyperplasia cases—a medium term, prospective, randomized comparison. BJU Int 111(5):793–803. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1464-410X.2012.11730.x
Gratzke C, Schlenker B, Seitz M, Karl A, Hermanek P, Lack N, Stief CG, Reich O (2007) Complications and early postoperative outcome after open prostatectomy in patients with benign prostatic enlargement: results of a prospective multicenter study. J Urol 177(4):1419–1422. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.juro.2006.11.062
Kuntz RM, Lehrich K, Ahyai SA (2008) Holmium laser enucleation of the prostate versus open prostatectomy for prostates greater than 100 grams: 5-year follow-up results of a randomised clinical trial. Eur Urol 53(1):160–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2007.08.036
Lee NG, Xue H, Lerner LB (2012) Trends and attitudes in surgical management of benign prostatic hyperplasia. Can J Urol 19(2):6170–6175
Naspro R, Suardi N, Salonia A, Scattoni V, Guazzoni G, Colombo R, Cestari A, Briganti A, Mazzoccoli B, Rigatti P, Montorsi F (2006) Holmium laser enucleation of the prostate versus open prostatectomy for prostates > 70 g: 24-month follow-up. Eur Urol 50(3):563–568. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2006.04.003
Kuntz RM, Lehrich K (2002) Transurethral holmium laser enucleation versus transvesical open enucleation for prostate adenoma greater than 100 gm: a randomized prospective trial of 120 patients. J Urol 168(4):1465–1469. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.ju.0000027901.47718.fc
Ginsberg SH, Pantin E, Kraidin J, Solina A, Panjwani S, Yang G (2013) Noise levels in modern operating rooms during surgery. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth 27(3):528–530. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.jvca.2012.09.001
Shapiro RA, Berland T (1972) Noise in the operating room. N Engl J Med 287(24):1236–1238. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJM197212142872407
Engelmann CR, Neis JP, Kirschbaum C, Grote G, Ure BM (2014) A noise-reduction program in a pediatric operation theatre is associated with surgeon’s benefits and a reduced rate of complications: a prospective controlled clinical trial. Ann Surg 259(5):1025–1033. https://doi.org/10.1097/SLA.0000000000000253
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by grants from the Key Disciplines Group Construction Project of the Pudong Health Bureau of Shanghai (Grant No. PWZxq2014-11) and project of Shanghai Committee of Science and Technology (Grant No. 15DZ1941503).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gu, M., Liu, C., Chen, Yb. et al. Comparison of Vela and holmium laser enucleation of the prostate: a retrospective clinical trial with a 12-month follow-up. Int Urol Nephrol 50, 819–823 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-018-1840-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-018-1840-y