Abstract
Alterations in stream environments can alter fish food availability, but there is little research data related to the impacts of urbanization on fish diets in tropical streams. Thus, we sought to compare the diet of ten fish species in urbanized and non-urbanized streams reaches. Fish stomach contents were obtained for four urban and five non-urban stream reaches from two medium-sized cities. We verified the similarity of diet composition from urbanized/non-urbanized streams. In-stream features mainly related to the substrate highlighted a perturbation gradient: gravel, pebbles and cobbles were associated to the wider urban reaches while silt were representative in the narrow pools from non-urban streams. Fishes changed their diet in response to urban and non-urban treatments. Omnivorous fishes consumed more detritus and Chironomidae and less terrestrial adult insects in urban reaches, while invertivorous fish consumed more terrestrial adult insects and Trichoptera larvae in the non-urbanized stream reaches. Although the management of the physical structure of streams in Brazil has been basically focused on riparian reforestation, our results suggest that a restoration plan for urban streams cannot be limited to reforestation of its surroundings, but also need to consider the physical structure of the channel, especially the substrate, which contributes to promote in-stream variability.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abelha MCF, Agostinho AA, Goulart E (2001) Plasticidade trófica em peixes de água doce. Acta Sci 23:425–434
Abujanra F, Agostinho AA, Hahn NS (2009) Effects of the flood regime on the body condition of fish of different trophic guilds, in the upper Paraná River floodplain, Brazil. Braz J Biol 69(2):469–479
Allan JD (1995) Stream ecology: structure and function of running water. Chapman & Hall, New York
Araujo-Lima CARM, Agostinho AA, Fabré N (1995) Trophic aspects of fish communities in Brasilian rivers and reservoir. In: Tundisi JG, Tundisi TM (eds) Limnology in Brazil, pp 105–136
Barletta M, Jaureguizar AJ, Baigun C, Fontoura NF, Agostinho AA, Almeida-Val VMF, Val AL, Torres RA, Jimenes-Segura LF, Giarrizzo T, Fabré NN, Batista VS, Lasso C, Taphorn DC, Costa MF, Chaves PT, Vieira JP, Correa MFM (2010) Fish and aquatic habitat conservation in South America: a continental overview with emphasis on neotropical systems. J Fish Biol 76:2118–2176
Barros G, Zuanon J, Deus C (2016) Effects of species co-occurrence on the trophic-niche breadth of characids in Amazon forest streams. J Fish Biol 90:326–340. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfb.13183
Bojsen BH (2005) Diet and condition of three fish species (Characidae) of the Andean foothills in relation to deforestation. Environ Biol Fish 73:61–73
Bojsen BH, Barriga R (2002) Effects of deforestation on fish community structure in Ecuadorian Amazon streams. Freshw Biol 4:2246–2260
Bonato KO, Delariva RL, Silva JC (2012) Diet and trophic guilds of fish assemblages in two streams with different anthropic impacts in the northwest of Paraná, Brazil. Zoologia 29(1):27–38
Bordignon CR, Casatti L, Pérez-Mayorga MA, Teresa FB, Brejão GL (2015) Fish complementarity is associated to forests in Amazonian streams. Neotrop Ichthyol 13(3):579–590
Boulton AJ, Boyero L, Covich AP, Dobson M, Lake S, Pearson R (2008) Are tropical streams ecologically different from temperate streams? In: Dudgeon D (ed) Tropical stream ecology. Amsterdan, academic press, pp 257–284
Bowen SH (1983) Detritivory in neotropical fish communities. Environ Biol Fish 9:137–144
Braga FMS (1999) O grau de preferência alimentar: um método qualitativo e quantitativo para o estudo do conteúdo estomacal de peixes. Acta Sci 21(2):291–295
Callisto M, Moretti M, Goulart M (2001) Macroinvertebrados Bentônicos como Ferramenta para Avaliar a Saúde de Riachos. Rev Bras Rec Hídr 6(1):71–82
Casatti L, Langeani F, Ferreira CP (2006) Effects of physical habitat degradation on the stream fish assemblage structure in a pasture region. Environ Manag 38:974–982
Casatti L, Ferreira CP, Langeani F (2009a) Fish-based biotic integrity index for assessment of lowland streams in southeastern Brazil. Hydrobiologia 623:173–189
Casatti L, Ferreira CP, Carvalho FR (2009b) Grass-dominated stream sites exhibit low fish species diversity and dominance by guppies: an assessment of two tropical pasture river basins. Hydrobiologia 632:273–283
Casatti L, Teresa FB, Gonçalves-Souza T, Bessa E, Manzotti AR, Gonçalves CS, Zeni JO (2012) From forests to cattail: how does the riparian zone influence stream fish? Neotrop Ichthyol 10(1):205–214
Casatti L, Teresa FB, Zeni JO, Ribeiro MD, Brejão GL, Ceneviva-Bastos M (2015) More of the same: high functional redundancy in stream fish assemblages from tropical Agroecosystems. Environ Manag 55(6):1300–1314
Cavaca HS, Carvalho MAG, Srbek-Araujo AC (2014) Riqueza e abundância de macroinvertebrados bentônicos em riachos associados a diferentes fitofisionomias sobre a formação Barreiras. Natureza on line 12(5):224–229
Ceneviva-Bastos M, Montana CG, Schalk CM, Camargo PB, Casatti L (2017) Responses of aquatic food webs to the addition of structural complexity and basal resource diversity in degraded Neotropical streams. Austral Ecology
Cetra M, Rondineli GR, Souza UP (2011) Compartilhamento de recursos por duas espécies de peixes nectobentônicas de riachos na bacia do rio Cachoeira (BA). Biota Neotrop 11:1–9
Collier KJ (1995) Environmental factors affecting the taxonomic composition of aquatic macroinvertebrate communities in lowland waterways of northland, New Zealand. New Zeal J Mar Fresh 29(4):453–465
Collier KJ (2014) Wood decay rates and macroinvertebrate community structure along contrasting human pressure gradients (Waikato, New Zealand). New Zeal J Mar Fresh 48(1):97–111
Cottenie K (2005) Integrating environmental and spatial processes in ecological community dynamics. Ecol Lett 8:1175–1182
Cruz BB, Miranda LE, Cetra M (2013) Links between riparian landcover, instream environment and fish assemblages in headwater streams of South-Eastern Brazil. Ecol Freshw Fish 22:607–616
Cunico AM, Agostinho AA, Latini JD (2006) Influência da urbanização sobre as assembléias de peixes em três córregos de Maringá, Paraná. Rev Bras Zool 23(4):1101–1110
Cunico AM, Ferreira EA, Agostinho AA, Beaumord AC, Fernandes R (2012) The effects of local and regional environmental factors on the structure of fish assemblages in the Pirapó Basin, Southern Brazil. Landsc Urban Plan 105:336–344
Daruich J, Tripole S, Gil MA, Vallania A (2013) Algal and Cyanobacterial communities in two rivers of the province of San Luis (Argentina) subjected to anthropogenic influence. Acta Limnol Bras 25(1):79–90
Dudgeon D, Arthington AH, Gessner MO, Kawabata ZI, Knowler DJ, Lévêque C, Naiman RJ, Prieur-Richard AH, Soto D, Stiassny MLJ, Sullivan CA (2006) Freshwater biodiversity: importance, threats, status and conservation challenges. Biol Rev 81:163182
Esselman PC, Allan JD (2010) Relative influences of catchment- and reach-scale abiotic factors on freshwater fish communities in rivers of northeastern Mesoamerica. Ecol of. Freshw Fish 9:439–454
Ferreira CP, Casatti L (2006) Influência da estrutura do hábitat sobre a ictiofauna de um riacho em uma micro-bacia de pastagem, São Paulo, Brasil. Rev Bras Zool 23(3):642–651
Ferreira A, Paula F, Ferraz SFDEB, Gerhard P, Kashiwaqui EAL, Cyrino JEP, Martinelli LA (2012) Riparian coverage affects diets of characids in neotropical streams. Ecol Freshw Fish 21:12–22
Ferreira FC, Silva AT, Gonçalves CS, Petrere Jr M (2014) Disentangling the influences of habitat structure and limnological predictors on stream fish communities of a coastal basin, southeastern Brazil. Neotrop Ichthyol 12(1):177–186
Francis RA (2012) Positioning urban rivers within urban ecology. Urban Ecosyst 15:285–291
Fryirs K, Brierley G (2013) Geomorphic analysis of river systems: an approach to reading the landscape. Wiley-Blackwell, Oxford, p 360
Fundação SEADE (2013) Fundação sistema estadual de análise de dados. http://www.seade.gov.br/produtos/imp/index.php?page=consulta&action=var_list&busca=Taxa+de+Urbaniza%E7%E3o. Accessed 22 July 2013
Gonçalves CS, Braga FMS (2012) Changes in ichthyofauna composition along a gradient from clearwaters to blackwaters in coastal streams of Atlantic forest (southeastern Brazil) in relation to environmental variables. Neotrop Ichthyol 10(3):675–684
Hammer O, Harper DAT, Ryan PD (2011) PAST: paleontological statistics software package for education and data analysis. Palaeontol Electron 4(1):9
Harding J, Clapcott J, Quinn J, Hayes J, Joy M, Storey R, Greig H, Hay J, James T, Beech M, Ozane R, Meredith A, Boothroyd I (2009) Stream habitat assessment protocols for wadeable rivers and streams of New Zeland. School of biological sciences, Canterbury educational printing services, New Zeland. Pp. 133
Helms BS, Feminella JW, Pan S (2005) Detection of biotic responses to urbanization using fish assemblages from small streams of western Georgia, USA. Urban Ecosyst 8:39–57
Herder F, Freyhoff J (2006) Resource particional in a tropical fish assemblage. J Fish Biol 69:571–589
Hlúbiková D, Novais MH, Dohet A, Hoffmann L, Ector L (2014) Effect of riparian vegetation on diatom assemblages in headwater streams under different land uses. Sci Total Environ 475:234–247
Jacobsen D, Cressa C, Mathooko JM, Dudgeon D (2008) Macroinvertebrates: composition, life histories and production. In: Dudgeon D (ed) Tropical stream ecology. Amsterdan, Academic Press, pp 65–106
Karpova GA, Klepets YV (2014) Influence of urban landscapes on the structural indices of Macrophytes in the Vorskla River. Hydrobiol J 50(6):3–16
Krause JR, Bertrand KN, Kafle A, Troelstrup NH Jr (2013) A fish index of biotic integrity for South Dakota’s Northern Glaciated Plains Ecoregion. Ecol Indic 34:313–322
Lammert M, Allan JD (1999) Assessing biotic integrity of streams: effects of scale in measuring the influence of land use/cover and habitat structure on fish and Macroinvertebrates. Environ Manag 23(2):257–270
Lorion CM, Kennedy BP (2009) Riparian forest buffers mitigate the effects of deforestation on fish assemblages in tropical headwater streams. Ecol Appl 19:468–479
Lowe-McConnell RH (1999) Estudos ecológicos de comunidades de peixes tropicais. Editora da Universidade de São Paulo, São Paulo
Lucinda PHF (2008) Systematics and biogeography of the genus Phalloceros Eigenmann, 1907 (Cyprinodontiformes: Poeciliidae: Poeciliinae), with the description of twenty-one new species. Neotrop Ichthyol 6(2):113–158
Luiz EA, Agostinho AA, Gomes LC, Hahn NS (1998) Ecologia trófica de peixes em dois riachos da Bacia do Rio Paraná. Braz J Biol 58:273–285
Luz-Agostinho KD, Agostinho AA, Gomes LC, HF J-J, Fugi R (2009) Effects of flooding regime on the feeding activity and body condition of piscivorous fish in the upper Paraná River floodplain. Braz J Biol 69(2):481–490
Maroneze DM, Tupinambás TH, Alves CBM, Vieira F, Pompeu PS, Callisto M (2011) Fish as ecological tools to complement biodiversity inventories of benthic macroinvertebrates. Hydrobiologia 673(1):29–40
Moore JC, Berlow EL, Coleman DC, de RPC, Dong Q, Hastings A, Johnson NC, McCann KS, Melville K, Morin PJ, Nadelhoffer K, Rosemond AD, Post DM, Sabo JL, Scow KM, Vanni MJ, Wall DH (2004) Detritus, trophic dynamics and biodiversity. Ecol Lett 7:584–600
Morgan RP, Cushman SF (2005) Urbanization effects on stream fish assemblages in Maryland, USA. J North Am Benthol Soc 24(3):643–655
Nerbonne BA, Vondracek B (2001) Effects of local land use on physical habitat, benthic macroinvertebrates, and fish in the Whitewater river, Minnesota, USA. Environ Manag 28(1):87–99
Noel DS, Martin CW, Federer CA (1986) Effects of forest clearcutting in New England on stream macroinvertebrates and periphyton. Environ Manag 10(5):661–670
Oksanen J, Blanchet FG, Friendly M, Kindt R, Legendre P, McGlinn D, Minchin PR, O'Hara RB, Simpson GL, Solymos P, Stevens MHH, Szoecs E, Wagner H (2017) Vegan: community ecology package. R package version 2:4–3 https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=vegan
Oliveira DC, Bennemann ST (2005) Ictiofauna, recursos alimentares e relações com as interferências antrópicas em um riacho urbano no sul do brasil. Biota Neotrop 5(1):95–107
Paul MJ, Meyer JL (2001) Streams in the urban landscape. Annu Rev Ecol Syst 32:333–365
Pease AA, Gonzalez-Diaz AA, Rodiles-Hernandez R, Winemiller KO (2012) Functional diversity and trait–environment relationships of stream fish assemblages in a large tropical catchment. Freshwat Biol 57:1060–1075. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2427.2012.02768.x
Pedersen ER, Perkins MA (1986) The use of benthic invertebrate data for evaluating impacts of urban runoff. Hydrobiologia 139:13–22
Peres-Neto PR, Jackson DA (2001) How well do multivariate data sets match? The advantages of a procrustean superimposition approach over the mantel test. Oecologia 129:169–178
Peressin A, Cetra M (2014) Responses of the ichthyofauna to urbanization in two urban areas in Southeast Brazil. Urban Ecosyst 17(3):675–690
Pinto BCT, Araujo FG, Hughes RM (2006) Effects of landscape and riparian condition on a fish index of biotic integrity in a large southeastern Brazil river. Hydrobiologia 556:69–83
Pringle CM, Hamazaki T (1998) The role of omnivory in a neotropical stream: separating diurnal and nocturnal effects. Ecology 79(1):269–280
Pusey BJ, Arthington AH (2003) Importance of the riparian zone to the conservation and management of freshwater fish: a review. Mar Freshw Res 54:1–16
R Core Team (2013) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. In: R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. URL https://www.R-project.org/
Ramírez A, Pringle CM, Wantzen KM (2008) Tropical stream conservation. In: Dudgeon D (ed) Tropical stream ecology. Academic, Amsterdan, pp 285–300
Rezende CF, Lobón-Cerviá J, Caramaschi EP, Mazzoni R (2013) Trophic ecology of two benthivorous fishes in relation to drift and benthos composition in a pristine Serra do mar stream (Rio de Janeiro, Brazil). Fundam Appl Limnol 183(2):163–175
Roy AH, Freeman MC, Freeman BJ, Wenger SJ, Meyer JL, Ensign WE (2006) Importance of riparian forests in urban catchments contingent on sediment and hydrologic regimes. Environ Manag 37(4):523–539
Sato Y, Godinho HP (1999) Peixes do rio São Francisco. In: Lowe-Mcconnell RH (ed) Estudos ecológicos de comunidades de peixes tropicais. Editora da Universidade de São Paulo, São Paulo 535pp
Silva JC, Delariva RL, Bonato KO (2012) Food-resource partitioning among fish species from a first-order stream in northwestern Paraná, Brazil. Neotrop Ichthyol 10(2):389–399
Smith WS, Biagioni RC, Halcsik L (2013) Fish fauna of Floresta Nacional de Ipanema, São Paulo State, Brazil. Biota Neotrop 13(2). http://www.biotaneotropica.org.br/v13n2/en/abstract?inventory+bn01713022013
Suren AM (2000) Effects of urbanization. In: Collier KJ, Winterbourn MJ (eds) New Zealand stream invertebrates: ecology and implications for management. New Zeland Limnological Society, Hamilton, pp 260–288
Teresa FB, Casatti L (2012) Influence of forest cover and mesohabitat types on functional and taxonomic diversity of fish communities in Neotropical lowland streams. Ecol Freshw Fish 21:433–442
Tófoli RM, Alves GHZ, Higuti J, Cunico AM, Hahn NS (2013) Diet and feeding selectivity of a benthivorous fish in streams: responses to the effects of urbanization. J Fish Biol 83:39–51
Uieda VS, Pinto TLF (2011) Feeding selectivity of ichthyofauna in a tropical stream: space-time variations in trophic plasticity. Community Ecol 12:31–39
Vermonden K, Leuven RSEW, van der Velde G, van Katwijk MM, Roelofs JGM, Hendriks AJ (2009) Urban drainage systems: an undervalued habitat for aquatic macroinvertebrates. Biol Conserv 142:1105–1115
Wantzen KM, Yule CM, Mathooko JM, Pringle CM (2008) Organic matter processing in tropical streams. In: Dudgeon D (ed) Tropical stream ecology. Amsterdan, Academic Press, pp 43–64
Zeni JO, Casatti L (2014) The influence of habitat homogenization on the trophic structure of fish fauna in tropical streams. Hydrobiologia 726:259–270
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to people from the UFSCar during data collection, including Bruna Botti Cruz, Bruno Mello, Fernanda Ayumi Teshima and Rodrigo Almeida da Silva. We are also grateful to Dr. Francisco Langeani Neto (UNESP/São José do Rio Preto) for species identification and Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo (FAPESP) for financial support (Proc. 2009/53056-8) and scholarship granted to the first author (2010/13758-0). Two anonymous reviewers provided helpful comments on earlier drafts of the manuscript.
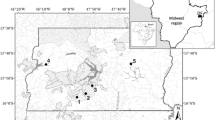
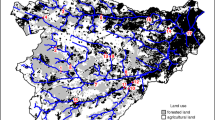
We also would like to thanks Fabio M. Suzuki, for very useful help with figure 1.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peressin, A., da Silva Gonçalves, C. & Cetra, M. Ichthyofauna diet changes in response to urbanization: the case of upper Paranapanema River basin (Brazil). Urban Ecosyst 21, 795–803 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11252-018-0755-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11252-018-0755-9