Abstract
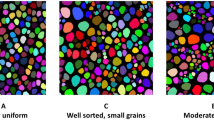
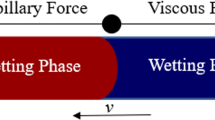
Imbibition is a commonly encountered multiphase problem in various fields, and exact prediction of imbibition processes is a key issue for better understanding capillary flow in heterogeneous porous media. In this work, a numerical framework for describing imbibition processes in porous media with material heterogeneity is proposed to track the moving wetting front with the help of a partially saturated region at the front vicinity. A new interface treatment, named the interface integral method, is developed here, combined with which the proposed numerical model provides a complete framework for imbibition problems. After validation of the current model with existing experimental results of one-dimensional imbibition, simulations on a series of two-dimensional cases are analysed with the presences of multiple porous phases. The simulations presented here not only demonstrate the suitability of the numerical framework on complex domains but also present its feasibility and potential for further engineering applications involving imbibition in heterogeneous media.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Maktoumi, A., Kacimov, A., Al-Ismaily, S., Al-Busaidi, H., Al-Saqri, S.: Infiltration into two-layered soil: the Green-Ampt and Averyanov models revisited. Transp. Porous Media 109(1), 169–193 (2015)
Alyafei, N., Blunt, M.J.: Estimation of relative permeability and capillary pressure from mass imbibition experiments. Adv. Water Resour. 115, 88–94 (2018)
Böttcher, C.J.F., van Belle, O.C., Bordewijk, P., Rip, A.: Theory of Electric Polarization. Elsevier, Amsterdam (1978)
Bal, K., Fan, J., Sarkar, M., Ye, L.: Differential spontaneous capillary flow through heterogeneous porous media. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 54(13–14), 3096–3099 (2011)
Bear, J.: Dynamics of Fluids in Porous Media. Courier Corporation, North Chelmsford (2013)
Block, R.J., Durrum, E.L., Zweig, G.: A Manual of Paper Chromatography and Paper Electrophoresis. Elsevier, Amsterdam (2016)
Brooks, R., Corey, T.: Hydraulic Properties of Porous Media, Hydrology Papers, p. 24. Colorado State University, Fort Collins (1964)
Cai, J., Perfect, E., Cheng, C.-L., Hu, X.: Generalized modeling of spontaneous imbibition based on Hagen–Poiseuille flow in tortuous capillaries with variably shaped apertures. Langmuir 30(18), 5142–5151 (2014)
Cai, J., You, L., Hu, X., Wang, J., Peng, R.: Prediction of effective permeability in porous media based on spontaneous imbibition effect. Int. J. Mod. Phys. C 23(07), 1250054 (2012)
Cai, J., Yu, B.: A discussion of the effect of tortuosity on the capillary imbibition in porous media. Transp. Porous Media 89(2), 251–263 (2011)
Conrath, M., Fries, N., Zhang, M., Dreyer, M.E.: Radial capillary transport from an infinite reservoir. Transp. Porous Media 84(1), 109–132 (2010)
Debbabi, Y., Jackson, M.D., Hampson, G.J., Fitch, P.J., Salinas, P.: Viscous crossflow in layered porous media. Transp. Porous Media 117(2), 281–309 (2017)
Di Donato, G., Lu, H., Tavassoli, Z., Blunt, M.J.: Multirate-transfer dual-porosity modeling of gravity drainage and imbibition. SPE J. 12(01), 77–88 (2007)
Durlofsky, L.J.: Numerical calculation of equivalent grid block permeability tensors for heterogeneous porous media. Water Resour. Res. 27(5), 699–708 (1991)
Elizalde, E., Urteaga, R., Berli, C.L.: Rational design of capillary-driven flows for paper-based microfluidics. Lab Chip 15(10), 2173–2180 (2015)
Ern, A., Mozolevski, I., Schuh, L.: Discontinuous Galerkin approximation of two-phase flows in heterogeneous porous media with discontinuous capillary pressures. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 199(23–24), 1491–1501 (2010)
Fries, N., Dreyer, M.: An analytic solution of capillary rise restrained by gravity. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 320(1), 259–263 (2008)
Fries, N., Odic, K., Conrath, M., Dreyer, M.: The effect of evaporation on the wicking of liquids into a metallic weave. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 321(1), 118–129 (2008)
Guerrero-Martínez, F.J., Younger, P.L., Karimi, N., Kyriakis, S.: Three-dimensional numerical simulations of free convection in a layered porous enclosure. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 106, 1005–1013 (2017)
Hall, C.: Barrier performance of concrete: a review of fluid transport theory. Mater. Struct. 27(5), 291–306 (1994)
Hanžič, L., Kosec, L., Anžel, I.: Capillary absorption in concrete and the Lucas–Washburn equation. Cement Concr. Compos. 32(1), 84–91 (2010)
Hashin, Z., Shtrikman, S.: A variational approach to the theory of the elastic behaviour of multiphase materials. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 11(2), 127–140 (1963)
Helmig, R., Weiss, A., Wohlmuth, B.I.: Dynamic capillary effects in heterogeneous porous media. Comput. Geosci. 11(3), 261–274 (2007)
Huinink, H.: Fluids in porous media: Transport and phase changes, pp. 1–116 (2016)
Jin, Y., Li, X., Zhao, M., Liu, X., Li, H.: A mathematical model of fluid flow in tight porous media based on fractal assumptions. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 108, 1078–1088 (2017)
Kun-Can, Z., Tong, W., Hai-Cheng, L., Zhi-Jun, G., Wen-Fei, W.: Fractal analysis of flow resistance in random porous media based on the staggered pore-throat model. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 115, 225–231 (2017)
Lewandowska, J., Szymkiewicz, A., Auriault, J.-L.: Upscaling of Richards’ equation for soils containing highly conductive inclusions. Adv. Water Resour. 28(11), 1159–1170 (2005)
Liu, M., Wu, J., Gan, Y., Hanaor, D.A., Chen, C.: Evaporation limited radial capillary penetration in porous media. Langmuir 32(38), 9899–9904 (2016)
Liu, M., Wu, J., Gan, Y., Hanaor, D.A., Chen, C.: Tuning capillary penetration in porous media: combining geometrical and evaporation effects. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 123, 239–250 (2018)
Liu, Z., Hu, J., Zhao, Y., Qu, Z., Xu, F.: Experimental and numerical studies on liquid wicking into filter papers for paper-based diagnostics. Appl. Therm. Eng. 88, 280–287 (2015)
Lucas, R.: Ueber das Zeitgesetz des kapillaren Aufstiegs von Flüssigkeiten. Kolloid-Zeitschrift 23(1), 15–22 (1918)
Mendez, S., Fenton, E.M., Gallegos, G.R., Petsev, D.N., Sibbett, S.S., Stone, H.A., Zhang, Y., López, G.P.: Imbibition in porous membranes of complex shape: quasi-stationary flow in thin rectangular segments. Langmuir 26(2), 1380–1385 (2009)
Meng, Q., Liu, H., Wang, J.: A critical review on fundamental mechanisms of spontaneous imbibition and the impact of boundary condition, fluid viscosity and wettability. Adv. Geo-energy Res. 1, 1–17 (2017)
Morrow, N.R., Mason, G.: Recovery of oil by spontaneous imbibition. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 6(4), 321–337 (2001)
Navarro, V., Yustres, A., Cea, L., Candel, M., Juncosa, R., Delgado, J.: Characterization of the water flow through concrete based on parameter estimation from infiltration tests. Cem. Concr. Res. 36(9), 1575–1582 (2006)
Nguyen, T.H., Fraiwan, A., Choi, S.: Based batteries: a review. Biosens. Bioelectron. 54, 640–649 (2014)
Patel, H.S., Meher, R.: Modelling of imbibition phenomena in fluid flow through heterogeneous inclined porous media with different porous materials. Nonlinear Eng. 6(4), 263–275 (2017)
Perez-Cruz, A., Stiharu, I., Dominguez-Gonzalez, A.: Two-dimensional model of imbibition into paper-based networks using Richards’ equation. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 21(5), 98 (2017)
Pettersen, Ø.: Simulation of two-phase flow in porous rocks on a laboratory scale: diffusion operator splitting and consistency. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 65(3), 229–252 (1987)
Quéré, D.: Inertial capillarity. EPL (Europhys. Lett.) 39(5), 533 (1997)
Reyssat, M., Sangne, L., Van Nierop, E., Stone, H.: Imbibition in layered systems of packed beads. EPL (Europhys. Lett.) 86(5), 56002 (2009)
Rokhforouz, M., Akhlaghi Amiri, H.: Phase-field simulation of counter-current spontaneous imbibition in a fractured heterogeneous porous medium. Phys. Fluids 29(6), 062104 (2017)
Schneider, M., Köppl, T., Helmig, R., Steinle, R., Hilfer, R.: Stable propagation of saturation overshoots for two-phase flow in porous media. Transp. Porous Media 121(3), 621–641 (2018)
Spaid, M.A., Phelan Jr., F.R.: Modeling void formation dynamics in fibrous porous media with the lattice Boltzmann method. Compos. A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 29(7), 749–755 (1998)
Tang, R., Yang, H., Gong, Y., Liu, Z., Li, X., Wen, T., Qu, Z., Zhang, S., Mei, Q., Xu, F.: Improved analytical sensitivity of lateral flow assay using sponge for HBV nucleic acid detection. Sci. Rep. 7(1), 1360 (2017)
Warren, J., Price, H.: Flow in heterogeneous porous media. Soc. Pet. Eng. J. 1(03), 153–169 (1961)
Washburn, E.W.: The dynamics of capillary flow. Phys. Rev. 17(3), 273 (1921)
Xiao, J., Cai, J., Xu, J.: Saturated imbibition under the influence of gravity and geometry. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 521, 226–231 (2018)
Xiao, J., Stone, H.A., Attinger, D.: Source-like solution for radial imbibition into a homogeneous semi-infinite porous medium. Langmuir 28(9), 4208–4212 (2012)
Zhuang, L., Hassanizadeh, S.M., Kleingeld, P.J., van Genuchten, M.T.: Revisiting the horizontal redistribution of water in soils: Experiments and numerical modeling. Water Resour. Res. 53(9), 7576–7589 (2017)
Zienkiewicz, O.C., Taylor, R.L., Zienkiewicz, O.C., Taylor, R.L.: The Finite Element Method. McGraw-hill, London (1977)
Zimmerman, R.W.: Thermal conductivity of fluid-saturated rocks. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 3(3), 219–227 (1989)
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by Australian Research Council (Projects DP170102886) and The University of Sydney SOAR Fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Suo, S., Liu, M. & Gan, Y. Modelling Imbibition Processes in Heterogeneous Porous Media. Transp Porous Med 126, 615–631 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-018-1146-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-018-1146-7