Abstract
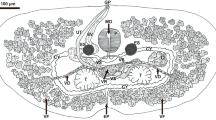
A species of Isospora Schneider, 1881 (Protozoa: Apicomplexa: Eimeriidae) considered as new to science is described and characterised molecularly from the eastern white-throated spadebill Platyrinchus mystaceus Vieillot in the Parque Nacional do Itatiaia, southeastern Brazil. Isospora lopesi n. sp. has oöcysts that are subspheroidal to ovoidal, 18–24 × 18–22 (20.6 × 19.7) µm, with smooth, bilayered wall, c.1.5 μm thick. Micropyle and oöcyst residuum are absent, but one polar granule is present. Sporocysts are ellipsoidal, 12–16 × 8–11 (14.4 × 8.6) µm. The Stieda body is flattened to half-moon-shaped and sub-Stieda body is rounded. Sporocyst residuum is present, consisting of numerous spherules of different sizes. Sporozoites are vermiform with anterior and posterior refractile bodies and nucleus. Molecular analysis was conducted at the mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit 1 (cox1) gene. This new isolate exhibited similarity greater than 98% with Isospora spp. isolates from spectacled warblers Sylvia conspicillata Temminck, 1820. This is the fourth isosporoid coccidian described from New World tyrannid birds, but is the first to have a complementary molecular characterisation.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berto, B. P., Flausino, W., Ferreira, I., & Lopes, C. W. G. (2008). Eimeria divinolimai sp. n. (Apicomplexa: Eimeriidae) in the Casiornis rufus Vieillot, 1816 (Passeriformes: Tyrannidae) in Brazil. Revista Brasileira de Parasitologia Veterinária, 17, 33–35.
Berto, B. P., Flausino, W., Luz, H. R., Ferreira, I., & Lopes, C. W. G. (2009a). Isospora mionectesi sp. nov. (Apicomplexa, Eimeriidae) from the grey-hooded flycatcher, Mionectes rufiventris in Brazil. Acta Parasitologica, 54, 301–304.
Berto, B. P., Flausino, W., McIntosh, D., Teixeira-Filho, W. L., & Lopes, C. W. G. (2011). Coccidia of New World passerine birds (Aves: Passeriformes): a review of Eimeria Schneider, 1875 and Isospora Schneider, 1881 (Apicomplexa: Eimeriidae). Systematic Parasitology, 80, 159–204.
Berto, B. P., & Lopes, C. W. G. (2013). Distribution and dispersion of coccidia in wild passerines of the Americas. In: Ruiz, L. & Iglesias, L. (Eds), Birds: evolution and behavior, breeding strategies, migration and spread of disease. New York: Nova Science Publishers, pp. 47–66.
Berto, B. P., Luz, H. R., Flausino, W., Ferreira, I., & Lopes, C. W. G. (2009b). New species of Eimeria Schneider, 1875 and Isospora Schneider, 1881 (Apicomplexa: Eimeriidae) from the short-crested flycatcher Myiarchus ferox (Gmelin) (Passeriformes: Tyrannidae) in South America. Systematic Parasitology, 74, 75–80.
Berto, B. P., McIntosh, D., & Lopes, C. W. G. (2014). Studies on coccidian oocysts (Apicomplexa: Eucoccidiorida). Revista Brasileira de Parasitologia Veterinária, 23, 1–15.
BirdLife International (2016). http://www.birdlife.org. Accessed 13 November 2017.
Boughton, D. C., Boughton, R. B., & Volk, J. (1938). Avian hosts of the genus Isospora (Coccidiida). Ohio Journal of Science, 38, 149–163.
Box, E. D. (1981). Isospora as an extraintestinal parasite of passerine birds. Journal of Protozoology, 28, 244–246.
Brands, S. J. (2017). Systema Naturae 2000, The Taxonomicon, Universal Taxonomic Services, Zwaag, The Netherlands. http://taxonomicon.taxonomy.nl. Accessed 13 November 2017.
CBRO. (2014). Listas das aves do Brasil. http://www.cbro.org.br. Accessed 13 November 2017.
del Hoyo, J., Collar, N. J., Christie, D. A., Elliott, A., Fishpool, L. D. C., Boesman, P., & Kirwan, G. M. (2016). HBW and BirdLife International Illustrated Checklist of the Birds of the World. Barcelona-Cambridge: Lynx Edicions and BirdLife International, 904 pp.
Dolnik, O. V., Palinauskas, V., & Bensch, S. (2009). Individual oocysts of Isospora (Apicomplexa: Coccidia) parasites from avian feces: from photo to sequence. Journal of Parasitology, 95, 169–174.
Duszynski, D. W., & Wilber, P. G. (1997). A guideline for the preparation of species descriptions in the Eimeriidae. Journal of Parasitology, 83, 333–336.
Hafeez, M. A., Stasiak, I., Delnatte, P., El-Sherry, S., Smith, D. A., & Barta, J. R. (2014). Description of two new Isospora species causing visceral coccidiosis in captive superb glossy starlings, Lamprotornis superbus (Aves: Sturnidae). Parasitology Research, 113, 3287–3297.
ICZN. (2012). International Commission on Zoological Nomenclature: Amendment of articles 8, 9, 10, 21 and 78 of the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature to expand and refine methods of publication. Bulletin of Zoological Nomenclature, 69, 161–169.
Illera, J. C., Fernández-Álvarez, Á., Hernández-Flores, C. N., & Foronda, P. (2015). Unforeseen biogeographical patterns in a multiple parasite system in Macaronesia. Journal of Biogeography, 42, 1858–1870.
Kawazoe, U., Gouvea, H., Jorge, P., Caputo, C. M. E., & Perdigão, J. C. (1989). A survey of intestinal coccidiosis from wild birds from the Itatiaia National Park, Minas Gerais, Brazil. Journal of Protozoology, 36, 11A.
Ogedengbe, J. D., Hanner, R. H., & Barta, J. R. (2011). DNA barcoding identifies Eimeria species and contributes to the phylogenetics of coccidian parasites (Eimeriorina, Apicomplexa, Alveolata). International Journal for Parasitology, 41, 843–850.
Rodrigues, M. B., Silva, L. M., Lopes, B. D. B., Berto, B. P., Luz, H. R., Ferreira, I., & Lopes, C. W. G. (2015). A new species of Isospora Schneider, 1881 (Apicomplexa: Eimeriidae) from the grey-hooded attila Attila rufus Vieillot, 1819 (Passeriformes: Tyrannidae) on the Marambaia Island, Brazil. Zootaxa, 4034, 193–196.
Sick, H. (1997). Ornitologia Brasileira. Rio de Janeiro: Nova Fronteira, 862 pp.
Silva, L. M., Rodrigues, M. B., Lopes, B. D. B., Berto, B. P., Luz, H. R., Ferreira, I., & Lopes, C. W. G. (2016). A new coccidian, Isospora parnaitatiaiensis n. sp. (Apicomplexa, Eimeriidae), from the white-shouldered fire-eye Pyriglena leucoptera (Passeriformes, Thamnophilidae) from South America. Parasitology Research, 115, 745–749.
Tamura, K., Dudley, J., Nei, M., & Kumar, S. (2007). MEGA4: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 24, 1596–1599.
Tokiwa, T., Kojima, A., Sasaki, S., Kubota, R., & Ike, K. (2017). Isospora lunaris n. sp. (Apicomplexa: Eimeriidae) from the domestic Java sparrow in Japan. Parasitology International, 66, 100–105.
Yang, R., Brice, B., Elliot, A., & Ryan, U. (2015). Isospora serinuse n. sp. (Apicomplexa: Eimeriidae) from a domestic canary (Serinus canaria forma domestica) (Passeriformes: Fringillidae) in Western Australia. Experimental Parasitology, 159, 59–66.
Yang, R., Brice, B., Jian, F., & Ryan, U. (2016). Morphological and molecular characterization of Isospora manorinae n. sp. in a yellow-throated miner (Manorina flavigula wayensis) (Gould, 1840). Experimental Parasitology, 163, 16–23.
Acknowledgements
We are thankful to the staff at the Parque Nacional do Itatiaia, mainly to the research coordinator Dr Léo Nascimento.
Funding
This study was supported by grants from the Fundação Carlos Chagas Filho de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado do Rio de Janeiro (FAPERJ), Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq) and Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
Field collecting permits were issued to BPB by SISBIO/ICMBio (license No. 49605–1) and CEUA/ICBS/UFRRJ (protocol No. 008/2015). All applicable institutional, national and international guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed.
Additional information
This article was registered in the Official Register of Zoological Nomenclature (ZooBank) as A03A911C-95B2-404A-A8D4-D3BDFF598468. This article was published as an Online First article on the online publication date shown on this page. The article should be cited by using the doi number. This is the Version of Record.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
da Silva-Carvalho, L.M., Pastura, D.G.N., Gomes, J.V. et al. Isospora lopesi n. sp. (Apicomplexa: Eimeriidae) from the eastern white-throated spadebill Platyrinchus mystaceus Vieillot (Passeriformes: Tyranni: Tyrannidae) in South America. Syst Parasitol 95, 455–463 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11230-018-9795-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11230-018-9795-z