Abstract
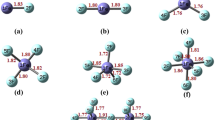
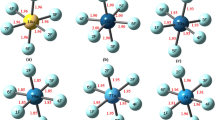
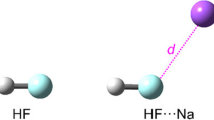
Theoretical studies on Lewis acid-base behavior of hypervalent halogen fluorides, F3X and F5X (X = Cl, Br, I) have been instrumental in guiding this work. We have also examined whether the hole-lump concept explains the formation of the F5X∙∙∙CO complexes. Calculations of proton affinities (PA) and gas-phase basicity (GB) on hypervalent halogen fluorides show that F3X and F5X molecules can act as Lewis bases in gas phase. Moreover, theoretical calculations indicate that F3X and F5X molecules can act as Lewis acids forming stable complexes with a Lewis base as CO. The quantum theory of atoms in molecules (QTAIM) shows that the electrostatic interaction between the lone pair of the Lewis base (CO) and nucleus of the hypervalent halogen atom (X) plays a key role in stabilizing and determining the optimal geometry of the F5X∙∙∙CO complexes, as in conventional XBs. The localized molecular orbital energy decomposition analysis (LMOEDA) reveals that electrostatic component plays an important role in the stability of the FnX···CO complexes.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hara S, Atta-ur-Rahman (ed) (2006) Advances in organic synthesis: modern organofluorine chemistry-synthetic aspects. Bentham Science Publisher Ltd.
Zhdankin VV, Stang PJ (2008) Chemistry of polyvalent iodine. Chem Rev 108:5299–5358
Akiba K (1998) Chemistry of hypervalent compounds. VCH Publishers, New York
Catalano L, Cavallo G, Metrangolo P, Resnati G, Terraneo G (2016) Halogen bonding in hypervalent iodine compounds. Top Curr Chem 373:289–309
Nakamoto K, Margoshes M, Rundle RE (1995) Stretching frequencies as a function of distances in hydrogen bonds. J Am Chem Soc 77:6480–6486
Schleyer PVR, West R (1959) Comparison of covalently bonded electronegative atoms as proton acceptor groups in hydrogen bonding. J Am Chem Soc 81:3164–3165
Duarte DJR, Sosa GL, Peruchena NM, Alkorta I (2016) Halogen bonding. The role of the polarizability of the electron-pair donor. Phys Chem Chem Phys 18:7300–7309
Nelyubina YV, Antipin MY, Dunin DS, Kotov VY, Lyssenko K (2010) Unexpected “amphoteric” character of the halogen bond: the charge density study of the co-crystal of N-methylpyrazine iodide with I2. Chem Commun 46:5325–5327
Politzer P, Lane P, Concha MC, Ma Y, Murray JS (2007) An overview of halogen bonding. J Mol Model 13:305–311
Politzer P, Murray JS, Clark T (2010) Halogen bonding: an electrostatically-driven highly directional noncovalent interaction. Phys Chem Chem Phys 12:7748–7757
Politzer P, Murray JS, Clark T (2013) Halogen bonding and other σ-hole interactions: a perspective. Phys Chem Chem Phys 15:11178–11189
Landrum GA, Goldberg N, Hoffman R, Myniaev RM (1998) Intermolecular interactions between hypervalent molecules: Ph2IX and XF3 (X = Cl , Br , I) dimers. New J Chem 22:883–890
Wang W (2011) Halogen bond involving hypervalent halogen: CSD search and theoretical study. J Phys Chem A 115:9294–9299
Grabowski SJ (2014) Halogen bond with the multivalent halogen acting as the Lewis acid center. Chem Phys Lett 605–606:131–136
Bader RFW, Johnson S, Tang TH, Popelier PL (1996) The electron pair. J Phys Chem 100:15398–15415
Fradera X, Austen MA, Bader RFW (1999) The Lewis model and beyond. J Phys Chem A 103:304–314
Gillespie RJ (2008) Fifty years of the VSEPR model. Coord Chem Rev 252:1315–1327
Clark T (2013) σ-Holes. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Comput Mol Sci 3:13–20
Eskandari K, Zariny H (2010) Halogen bonding: a lump-hole interaction. Chem Phys Lett 492:9–13
Duarte DJR, Sosa GL, Peruchena NM (2013) Nature of halogen bonding. A study based on the topological analysis of the Laplacian of the electron charge density and an energy decomposition analysis. J Mol Model 19:2035–2041
Eskandari K, Lesani M (2015) Does fluorine participate in halogen bonding? Chem Eur J 21:4739–4746
Duarte DJR, Peruchena NM, Alkorta I (2015) Double hole–lump interaction between halogen atoms. J Phys Chem A 119:3746–3752
Duarte DJR, Angelina EL, Peruchena NM (2012) On the strength of the halogen bonds: mutual penetration, atomic quadrupole moment and Laplacian distribution of the charge density analyses. Comput Theor Chem 998:164–172
Frisch MJ, Trucks GW, Schlegel HB, Scuseria GE, Robb MA, Cheeseman JR, Montgomery Jr JA, Vreven T, Kudin KN, Burant JC, Millam JM, Iyengar SS, Tomasi J, Barone V, Mennucci B, Cossi M, Scalmani G, Rega N, Petersson GA, Nakatsuji H, Hada M, Ehara M, Toyota K, Fukuda R, Hasegawa J, Ishida M, Nak-ajima T, Honda Y, Kitao O, Nakai H, Klene M, Li X, Knox JE, Hratchian HP, Cross JB, Bakken V, Adamo C, Jaramillo J, Gomperts R, Stratmann RE, Yazyev O, Austin AJ, Cammi R, Pomelli C, Ochterski JW, Ayala PY, Morokuma K, Voth GA, Salvador P, Dannenberg JJ, Zakrzewski VG, Dapprich S, Daniels AD, Strain MC, Farkas O, Malick DK, Rabuck AD, Raghava-chari K, Foresman JB, Ortiz JV, Cui Q, Baboul AG, Clifford S, Cioslowski J, Stefanov BB, Liu G, Liashenko A, Piskorz P, Komaromi I, Martin RL, Fox DJ, Keith T, Al-Laham MA, Peng CY, Nanayakkara A, Challacombe M, PMW G, Johnson B, Chen W, Wong MW, Gonzalez C, Pople JA (2004) Gaussian 09, Revision A.01. Gaussian, Inc, Wallingford
Curtiss LA, Redfern PC, Raghavachari K (2007) Gaussian-4 theory. J Chem Phys 126:084108-1–084108-12
Boys SF, Bernardi F (1970) The calculation of small molecular interactions by the differences of separate total energies. Some procedures with reduced errors. Mol Phys 19:553–566
Keith TA (2011) AIMAll (Version 11.12.19); TK Gristmill Software, Overland Park KS, aim.tkgristmill.com
Su P, Li H (2009) Energy decomposition analysis of covalent bonds and intermolecular interactions. J Chem Phys 131:014102
Schmidt MW, Baldridge KK, Boatz JA, Elbert ST, Gordon MS, Jensen JH, Koseki S, Matsunaga N, Nguyen KA, Su S, et al (1993) General atomic and molecular electronic structure system. J Comput Chem 14:1347–1363
Bader RFW (1990) Atoms in molecules. A Quantum Theory; Clarendon, Oxford
Popelier P (ed) (2000) Atoms in molecules: an introduction. Prentice-Hall, Harlow
Cacace F, De Petris G, Pepi F, Rossi M, Sgamellotti A (1998) Elemental chlorine and chlorine fluoride: theoretical and experimental proton affinity and the gas phase Chemistry of Cl2H+ and FClH+ ions. J Phys Chem A 102:10560–10567
Hunter EPL, Lias SG (1998) Evaluated gas phase basicities and proton affinities of molecules: an update. J Phys Chem Ref Data 27:413–656
Matta CF, Boyd RJ (2007) The quantum theory of atoms in molecules: from solid state to DNA and drug design. Weinheim, Wiley-VCH
Bondi A (1964) Van der Waals Volumes and Radii. J Phys Chem 68:441–451
Duarte DJR, Vallejos MM, Peruchena NM (2010) Topological analysis of aromatic halogen/hydrogen bonds by electron charge density and electrostatic potentials. J Mol Model 16:737–748
Riley KE, Hobza P (2008) Investigations into the nature of halogen bonding including symmetry adapted perturbation theory analyses. J Chem Theory Comput 4:232–242
Eskandari K, Mahmoodabadi N (2013) Pnicogen bonds: a theoretical study based on the Laplacian of electron density. J Phys Chem A 117:13018–13024
Acknowledgements
G.J. Buralli, D.J.R. Duarte and N.M. Peruchena acknowledge SEGCYT UNNE and CONICET for the financial support. NMP is a career research of CONICET, Argentina.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 1691 kb).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Buralli, G.J., Duarte, D.J.R., Sosa, G.L. et al. Lewis acid-base behavior of hypervalent halogen fluorides in gas phase. Struct Chem 28, 1823–1830 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11224-017-0966-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11224-017-0966-3