Abstract
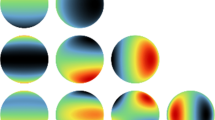
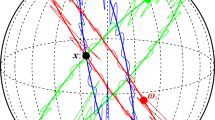
We provide a method for fast and exact simulation of Gaussian random fields on the sphere having isotropic covariance functions. The method proposed is then extended to Gaussian random fields defined over the sphere cross time and having covariance functions that depend on geodesic distance in space and on temporal separation. The crux of the method is in the use of block circulant matrices obtained working on regular grids defined over longitude and latitude.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chiles, J.P., Delfiner, P.: Geostatistics: Modelling Spatial Uncertainty. Wiley, New York (1999)
Clarke, J., Alegría, A., Porcu, E.: Regularity properties and simulations of Gaussian random fields on the sphere cross time. Electron. J. Stat. 12, 399–426 (2018)
Coxeter, H.S.M.: Regular Polytopes. Methuen, London (1973)
Creasey, P.E., Lang, A.: Fast generation of isotropic Gaussian random fields on the sphere. Monte Carlo Methods Appl. 24(1), 1–11 (2018)
Davies, T.M., Bryant, D., et al.: On circulant embedding for Gaussian random fields in R. J. Stat. Softw. 55(9), 1–21 (2013)
Davis, P.J.: Circulant Matrices. Wiley, New York (1979)
Dietrich, C., Newsam, G.: A fast and exact method for multidimensional Gaussian stochastic simulations: extension to realizations conditioned on direct and indirect measurements. Water Resour. Res. 32(6), 1643–1652 (1996)
Dietrich, C., Newsam, G.N.: Fast and exact simulation of stationary Gaussian processes through circulant embedding of the covariance matrix. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 18, 1088–1107 (1997)
Emery, X., Arroyo, D., Porcu, E.: An improved spectral turning-bands algorithm for simulating stationary vector Gaussian random fields. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 30(7), 1863–1873 (2016)
Gneiting, T.: Strictly and non-strictly positive definite functions on spheres. Bernoulli 19, 1327–1349 (2013)
Gneiting, T., Ševčíková, H., Percival, D.B., Schlather, M., Jiang, Y.: Fast and exact simulation of large Gaussian lattice systems in \({\mathbb{R}}^2\): exploring the limits. J. Comput. Graph. Stat. 15(3), 483–501 (2006)
Huang, C., Zhang, H., Robeson, S.M.: On the validity of commonly used covariance and variogram functions on the sphere. Math. Geosci. 43, 721–733 (2011)
Huang, C., Zhang, H., Robeson, S.M.: A simplified representation of the covariance structure of axially symmetric processes on the sphere. Stat. Probab. Lett. 82(7), 1346–1351 (2012)
Jun, M., Stein, M.L.: Nonstationary covariance models for global data. Ann. Appl. Stat. 2, 1271–1289 (2008)
Lang, A., Schwab, C.: Isotropic Gaussian random fields on the sphere: regularity, fast simulation and stochastic partial differential equations. Ann. Appl. Probab. 25, 3047–3094 (2015)
Møller, J., Syversveen, A.R., Waagepetersen, R.P.: Log Gaussian Cox processes. Scand. J. Stat. 25, 451–482 (1998)
Møller, J., Nielsen, M., Porcu, E., Rubak, E.: Determinantal point process models on the sphere. Bernoulli 24, 1171–1201 (2015)
Myllymäki, M., Mrkvička, T., Grabarnik, P., Seijo, H., Hahn, U.: Global envelope tests for spatial processes. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B (Stat. Methodol.) 79(2), 381–404 (2017)
Park, M.H., Tretyakov, M.: A block circulant embedding method for simulation of stationary Gaussian random fields on block-regular grids. Int. J. Uncertain. Quantif. 5, 527544 (2015)
Porcu, E., Bevilacqua, M., Genton, M.G.: Spatio-temporal covariance and cross-covariance functions of the great circle distance on a sphere. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 111(514), 888–898 (2016)
Stein, M.L.: Interpolation of Spatial Data: Some Theory for Kriging. Springer, Berlin (2012)
Wood, A.T., Chan, G.: Simulation of stationary Gaussian processes in [0,1]\(^d\). J. Comput. Graph. Stat. 3, 409–432 (1994)
Zhihao, C.: A note on symmetric block circulant matrix. J. Math. Res. Expo. 10, 469–473 (1990)
Acknowledgements
The first author was supported by The Danish Council for Independent Research—Natural Sciences, Grant DFF 7014-00074 “Statistics for point processes in space and beyond,” and by the “Centre for Stochastic Geometry and Advanced Bioimaging,” funded by Grant 8721 from the Villum Foundation. Third author was supported by FONDECYT Number 1170290.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cuevas, F., Allard, D. & Porcu, E. Fast and exact simulation of Gaussian random fields defined on the sphere cross time. Stat Comput 30, 187–194 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11222-019-09873-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11222-019-09873-1