Abstract
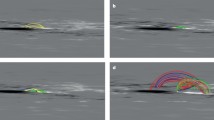
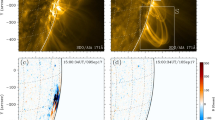
We study a filament eruption, two-ribbon flare, and coronal mass ejection (CME) that occurred in NOAA Active Region 10898 on 6 July 2006. The filament was located South of a strong sunspot that dominated the region. In the evolution leading up to the eruption, and for some time after it, a counter-clockwise rotation of the sunspot of about 30 degrees was observed. We suggest that the rotation triggered the eruption by progressively expanding the magnetic field above the filament. To test this scenario, we study the effect of twisting the initially potential field overlying a pre-existing flux-rope, using three-dimensional zero-β MHD simulations. We first consider a relatively simple and symmetric system, and then study a more complex and asymmetric magnetic configuration, whose photospheric-flux distribution and coronal structure are guided by the observations and a potential field extrapolation. In both cases, we find that the twisting leads to the expansion of the overlying field. As a consequence of the progressively reduced magnetic tension, the flux-rope quasi-statically adapts to the changed environmental field, rising slowly. Once the tension is sufficiently reduced, a distinct second phase of evolution occurs where the flux-rope enters an unstable regime characterised by a strong acceleration. Our simulations thus suggest a new mechanism for the triggering of eruptions in the vicinity of rotating sunspots.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amari, T., Luciani, J.F.: 1999, Astrophys. J. Lett. 515, L81. doi: 10.1086/311971 .
Amari, T., Luciani, J.F., Aly, J.J., Tagger, M.: 1996, Astrophys. J. Lett. 466, L39. doi: 10.1086/310158 .
Attrill, G.D.R., van Driel-Gesztelyi, L., Démoulin, P., Zhukov, A.N., Steed, K., Harra, L.K., Mandrini, C.H., Linker, J.: 2008, Solar Phys. 252, 349. doi: 10.1007/s11207-008-9255-z .
Aulanier, G., Démoulin, P., Grappin, R.: 2005, Astron. Astrophys. 430, 1067. doi: 10.1051/0004-6361:20041519 .
Aulanier, G., Pariat, E., Démoulin, P.: 2005, Astron. Astrophys. 444, 961. doi: 10.1051/0004-6361:20053600 .
Aulanier, G., Török, T., Démoulin, P., DeLuca, E.E.: 2010, Astrophys. J. 708, 314. doi: 10.1088/0004-637X/708/1/314 .
Barnes, C.W., Sturrock, P.A.: 1972, Astrophys. J. 174, 659. doi: 10.1086/151527 .
Bateman, G.: 1978, MHD Instabilities, MIT Press, Cambridge.
Baum, P.J., Bratenahl, A.: 1980, Solar Phys. 67, 245. doi: 10.1007/BF00149805 .
Bi, Y., Jiang, Y.C., Yang, L.H., Zheng, R.S.: 2011, New Astron. 16, 276. doi: 10.1016/j.newast.2010.11.009 .
Brown, D.S., Nightingale, R.W., Alexander, D., Schrijver, C.J., Metcalf, T.R., Shine, R.A., Title, A.M., Wolfson, C.J.: 2003, Solar Phys. 216, 79. doi: 10.1023/A:1026138413791 .
Canou, A., Amari, T.: 2010, Astrophys. J. 715, 1566. doi: 10.1088/0004-637X/715/2/1566 .
Chen, J.: 1989, Astrophys. J. 338, 453. doi: 10.1086/167211 .
Chifor, C., Tripathi, D., Mason, H.E., Dennis, B.R.: 2007, Astron. Astrophys. 472, 967. doi: 10.1051/0004-6361:20077771 .
Démoulin, P., Aulanier, G.: 2010, Astrophys. J. 718, 1388. doi: 10.1088/0004-637X/718/2/1388 .
Démoulin, P., Henoux, J.C., Priest, E.R., Mandrini, C.H.: 1996, Astron. Astrophys. 308, 643.
Evershed, J.: 1910, Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 70, 217.
Fan, Y.: 2009, Astrophys. J. 697, 1529. doi: 10.1088/0004-637X/697/2/1529 .
Fan, Y., Gibson, S.E.: 2003, Astrophys. J. Lett. 589, L105. doi: 10.1086/375834 .
Fan, Y., Gibson, S.E.: 2007, Astrophys. J. 668, 1232. doi: 10.1086/521335 .
Forbes, T.: 2010, In: Schrijver, C.J., Siscoe, G.L. (eds.) Heliophysics: Space Storms and Radiation: Causes and Effects, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 159.
Forbes, T.G.: 2000, J. Geophys. Res. 105, 23153. doi: 10.1029/2000JA000005 .
Galsgaard, K., Nordlund, Å.: 1997, J. Geophys. Res. 102, 219. doi: 10.1029/96JA01462 .
Gerrard, C.L., Arber, T.D., Hood, A.W.: 2002, Astron. Astrophys. 387, 687. doi: 10.1051/0004-6361:20020491 .
Gerrard, C.L., Hood, A.W., Brown, D.S.: 2004, Solar Phys. 222, 79. doi: 10.1023/B:SOLA.0000036877.20077.42 .
Gerrard, C.L., Brown, D.S., Mellor, C., Arber, T.D., Hood, A.W.: 2003, Solar Phys. 213, 39. doi: 10.1023/A:1023281624037 .
Gibson, S.E., Fan, Y., Mandrini, C., Fisher, G., Demoulin, P.: 2004, Astrophys. J. 617, 600. doi: 10.1086/425294 .
Gombosi, T.I., Powell, K.G., de Zeeuw, D.L.: 1994, J. Geophys. Res. 99, 21525.
Gopalswamy, N., Yashiro, S., Kaiser, M.L., Howard, R.A., Bougeret, J.-L.: 2001, Astrophys. J. Lett. 548, L91. doi: 10.1086/318939 .
Green, L.M., Démoulin, P., Mandrini, C.H., Van Driel-Gesztelyi, L.: 2003, Solar Phys. 215, 307. doi: 10.1023/A:1025678917086 .
Green, L.M., Kliem, B., Török, T., van Driel-Gesztelyi, L., Attrill, G.D.R.: 2007, Solar Phys. 246, 365. doi: 10.1007/s11207-007-9061-z .
Guo, J., Liu, Y., Zhang, H., Deng, Y., Lin, J., Su, J.: 2010a, Astrophys. J. 711, 1057. doi: 10.1088/0004-637X/711/2/1057 .
Guo, Y., Schmieder, B., Démoulin, P., Wiegelmann, T., Aulanier, G., Török, T., Bommier, V.: 2010b, Astrophys. J. 714, 343. doi: 10.1088/0004-637X/714/1/343 .
Handy, B.N., Acton, L.W., Kankelborg, C.C., Wolfson, C.J., Akin, D.J., Bruner, M.E., Caravalho, R., Catura, R.C., Chevalier, R., Duncan, D.W., Edwards, C.G., Feinstein, C.N., Freeland, S.L., Friedlaender, F.M., Hoffmann, C.H., Hurlburt, N.E., Jurcevich, B.K., Katz, N.L., Kelly, G.A., Lemen, J.R., Levay, M., Lindgren, R.W., Mathur, D.P., Meyer, S.B., Morrison, S.J., Morrison, M.D., Nightingale, R.W., Pope, T.P., Rehse, R.A., Schrijver, C.J., Shine, R.A., Shing, L., Strong, K.T., Tarbell, T.D., Title, A.M., Torgerson, D.D., Golub, L., Bookbinder, J.A., Caldwell, D., Cheimets, P.N., Davis, W.N., Deluca, E.E., McMullen, R.A., Warren, H.P., Amato, D., Fisher, R., Maldonado, H., Parkinson, C.: 1999, Solar Phys. 187, 229. doi: 10.1023/A:1005166902804 .
Hiremath, K.M., Suryanarayana, G.S.: 2003, Astron. Astrophys. 411, L497. doi: 10.1051/0004-6361:20031618 .
Hiremath, K.M., Lovely, M.R., Kariyappa, R.: 2006, J. Astrophys. Astron. 27, 333. doi: 10.1007/BF02702538 .
Isenberg, P.A., Forbes, T.G.: 2007, Astrophys. J. 670, 1453. doi: 10.1086/522025 .
Jiang, Y., Yang, L., Li, K., Ren, D.: 2007, Astrophys. J. Lett. 662, L131. doi: 10.1086/519490 .
Kahler, S.W., Akiyama, S., Gopalswamy, N.: 2012, Astrophys. J. 754, 100. doi: 10.1088/0004-637X/754/2/100 .
Kahler, S.W., Moore, R.L., Kane, S.R., Zirin, H.: 1988, Astrophys. J. 328, 824. doi: 10.1086/166340 .
Kazachenko, M.D., Canfield, R.C., Longcope, D.W., Qiu, J., Des Jardins, A., Nightingale, R.W.: 2009, Astrophys. J. 704, 1146. doi: 10.1088/0004-637X/704/2/1146 .
Keppens, R., Nool, M., Tóth, G., Goedbloed, J.P.: 2003, Comput. Phys. Commun. 153, 317. doi: 10.1016/S0010-4655(03)00139-5 .
Kliem, B., Török, T.: 2006, Phys. Rev. Lett. 96(25), 255002. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.96.255002 .
Kliem, B., Titov, V.S., Török, T.: 2004, Astron. Astrophys. 413, L23. doi: 10.1051/0004-6361:20031690 .
Klimchuk, J.A., Antiochos, S.K., Norton, D.: 2000, Astrophys. J. 542, 504. doi: 10.1086/309527 .
Lau, Y.-T., Finn, J.M.: 1990, Astrophys. J. 350, 672. doi: 10.1086/168419 .
Li, L., Zhang, J.: 2009, Astrophys. J. Lett. 706, L17. doi: 10.1088/0004-637X/706/1/L17 .
Lionello, R., Mikić, Z., Linker, J.A., Amari, T.: 2002, Astrophys. J. 581, 718. doi: 10.1086/344222 .
Liu, R., Kliem, B., Török, T., Liu, C., Titov, V.S., Lionello, R., Linker, J.A., Wang, H.: 2012, Astrophys. J. 756, 59. doi: 10.1088/0004-637X/756/1/59 .
Longcope, D.W., Welsch, B.T.: 2000, Astrophys. J. 545, 1089. doi: 10.1086/317846 .
Lugaz, N., Manchester, W.B. IV, Gombosi, T.I.: 2005, Astrophys. J. 634, 651. doi: 10.1086/491782 .
Maričić, D., Vršnak, B., Roša, D.: 2009, Solar Phys. 260, 177. doi: 10.1007/s11207-009-9421-y .
Maričić, D., Vršnak, B., Stanger, A.L., Veronig, A.: 2004, Solar Phys. 225, 337. doi: 10.1007/s11207-004-3748-1 .
Maričić, D., Vršnak, B., Stanger, A.L., Veronig, A.M., Temmer, M., Roša, D.: 2007, Solar Phys. 241, 99. doi: 10.1007/s11207-007-0291-x .
Masson, S., Pariat, E., Aulanier, G., Schrijver, C.J.: 2009, Astrophys. J. 700, 559. doi: 10.1088/0004-637X/700/1/559 .
McIntosh, S.W., Leamon, R.J., Davey, A.R., Wills-Davey, M.J.: 2007, Astrophys. J. 660, 1653. doi: 10.1086/512665 .
Mikic, Z., Schnack, D.D., van Hoven, G.: 1990, Astrophys. J. 361, 690. doi: 10.1086/169232 .
Miklenic, C.H., Veronig, A.M., Vršnak, B.: 2009, Astron. Astrophys. 499, 893. doi: 10.1051/0004-6361/200810947 .
Min, S., Chae, J.: 2009, Solar Phys. 258, 203. doi: 10.1007/s11207-009-9425-7 .
Moore, R.L., Sterling, A.C., Hudson, H.S., Lemen, J.R.: 2001, Astrophys. J. 552, 833. doi: 10.1086/320559 .
Nindos, A., Andrews, M.D.: 2004, Astrophys. J. Lett. 616, L175. doi: 10.1086/426861 .
Panasenco, O., Martin, S., Joshi, A.D., Srivastava, N.: 2011, J. Atmos. Solar-Terr. Phys. 73, 1129. doi: 10.1016/j.jastp.2010.09.010 .
Pariat, E., Antiochos, S.K., DeVore, C.R.: 2009, Astrophys. J. 691, 61. doi: 10.1088/0004-637X/691/1/61 .
Priest, E.R., Forbes, T.G.: 1992, J. Geophys. Res. 97, 1521. doi: 10.1029/91JA02435 .
Régnier, S., Canfield, R.C.: 2006, Astron. Astrophys. 451, 319. doi: 10.1051/0004-6361:20054171 .
Robbrecht, E., Patsourakos, S., Vourlidas, A.: 2009, Astrophys. J. 701, 283. doi: 10.1088/0004-637X/701/1/283 .
Romano, P., Contarino, L., Zuccarello, F.: 2005, Astron. Astrophys. 433, 683. doi: 10.1051/0004-6361:20041807 .
Roussev, I.I., Forbes, T.G., Gombosi, T.I., Sokolov, I.V., DeZeeuw, D.L., Birn, J.: 2003, Astrophys. J. Lett. 588, L45. doi: 10.1086/375442 .
Santos, J.C., Büchner, J., Otto, A.: 2011, Astron. Astrophys. 535, A111. doi: 10.1051/0004-6361/201116792 .
Sato, T., Hayashi, T.: 1979, Phys. Fluids 22, 1189. doi: 10.1063/1.862721 .
Schatten, K.H., Wilcox, J.M., Ness, N.F.: 1969, Solar Phys. 6, 442. doi: 10.1007/BF00146478 .
Scherrer, P.H., Bogart, R.S., Bush, R.I., Hoeksema, J.T., Kosovichev, A.G., Schou, J., Rosenberg, W., Springer, L., Tarbell, T.D., Title, A., Wolfson, C.J., Zayer, I., MDI Engineering Team: 1995, Solar Phys. 162, 129. doi: 10.1007/BF00733429 .
Schrijver, C.J., Elmore, C., Kliem, B., Török, T., Title, A.M.: 2008, Astrophys. J. 674, 586. doi: 10.1086/524294 .
Stenflo, J.O.: 1969, Solar Phys. 8, 115. doi: 10.1007/BF00150662 .
Suryanarayana, G.S.: 2010, New Astron. 15, 313. doi: 10.1016/j.newast.2009.09.004 .
Temmer, M., Veronig, A.M., Vršnak, B., Rybák, J., Gömöry, P., Stoiser, S., Maričić, D.: 2008, Astrophys. J. Lett. 673, L95. doi: 10.1086/527414 .
Tian, L., Alexander, D.: 2006, Solar Phys. 233, 29. doi: 10.1007/s11207-006-2505-z .
Tian, L., Alexander, D., Nightingale, R.: 2008, Astrophys. J. 684, 747. doi: 10.1086/589492 .
Titov, V.S., Démoulin, P.: 1999, Astron. Astrophys. 351, 707.
Török, T., Kliem, B.: 2003, Astron. Astrophys. 406, 1043. doi: 10.1051/0004-6361:20030692 .
Török, T., Kliem, B.: 2005, Astrophys. J. Lett. 630, L97. doi: 10.1086/462412 .
Török, T., Kliem, B.: 2007, Astron. Nachr. 328, 743. doi: 10.1002/asna.200710795 .
Török, T., Kliem, B., Titov, V.S.: 2004, Astron. Astrophys. 413, L27. doi: 10.1051/0004-6361:20031691 .
Török, T., Aulanier, G., Schmieder, B., Reeves, K.K., Golub, L.: 2009, Astrophys. J. 704, 485. doi: 10.1088/0004-637X/704/1/485 .
Török, T., Panasenco, O., Titov, V.S., Mikić, Z., Reeves, K.K., Velli, M., Linker, J.A., De Toma, G.: 2011, Astrophys. J. Lett. 739, L63. doi: 10.1088/2041-8205/739/2/L63 .
Valori, G., Kliem, B., Török, T., Titov, V.S.: 2010, Astron. Astrophys. 519, A44. doi: 10.1051/0004-6361/201014416 .
van Ballegooijen, A.A.: 2004, Astrophys. J. 612, 519. doi: 10.1086/422512 .
Veronig, A.M., Rybak, J., Gömöry, P., Berkebile-Stoiser, S., Temmer, M., Otruba, W., Vrsnak, B., Pötzi, W., Baumgartner, D.: 2010, Astrophys. J. 719, 655. doi: 10.1088/0004-637X/719/1/655 .
Vršnak, B.: 1990, Solar Phys. 129, 295. doi: 10.1007/BF00159042 .
Vršnak, B., Sudar, D., Ruždjak, D., Žic, T.: 2007, Astron. Astrophys. 469, 339. doi: 10.1051/0004-6361:20077175 .
Williams, D.R., Török, T., Démoulin, P., van Driel-Gesztelyi, L., Kliem, B.: 2005, Astrophys. J. Lett. 628, L163. doi: 10.1086/432910 .
Yan, X.L., Qu, Z.Q.: 2007, Astron. Astrophys. 468, 1083. doi: 10.1051/0004-6361:20077064 .
Yan, X.L., Qu, Z.Q., Kong, D.F.: 2008, Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 391, 1887. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2966.2008.14002.x .
Yan, X.L., Qu, Z.Q., Xu, C.L., Xue, Z.K., Kong, D.F.: 2009, Res. Astron. Astrophys. 9, 596. doi: 10.1088/1674-4527/9/5/010 .
Yan, X.L., Qu, Z.Q., Kong, D.-F., Xu, C.L.: 2012, Astrophys. J. 754, 16. doi: 10.1088/0004-637X/754/1/16 .
Yang, J., Jiang, Y., Yang, B., Zheng, R., Yang, D., Hong, J., Li, H., Bi, Y.: 2012, Solar Phys. 279, 115. doi: 10.1007/s11207-012-0002-0 .
Zhang, J., Li, L., Song, Q.: 2007, Astrophys. J. Lett. 662, L35. doi: 10.1086/519280 .
Zhang, J., Dere, K.P., Howard, R.A., Kundu, M.R., White, S.M.: 2001, Astrophys. J. 559, 452. doi: 10.1086/322405 .
Zhang, Y., Liu, J., Zhang, H.: 2008, Solar Phys. 247, 39. doi: 10.1007/s11207-007-9089-0 .
Zhu, C., Alexander, D., Tian, L.: 2012, Solar Phys. 278, 121. doi: 10.1007/s11207-011-9923-2 .
Zirin, H.: 1998, The Astrophysics of the Sun, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
Zuccarello, F.P., Bemporad, A., Jacobs, C., Mierla, M., Poedts, S., Zuccarello, F.: 2012, Astrophys. J. 744, 66. doi: 10.1088/0004-637X/744/1/66 .
Acknowledgements
We thank the anonymous referee for constructive comments that helped to improve the content of the article. We acknowledge the use of data provided by the SOHO/MDI consortium. SOHO/EIT was funded by CNES, NASA, and the Belgian SPPS. The SOHO/LASCO data used here are produced by a consortium of the Naval Research Laboratory(USA), Max–Planck–Institut für Aeronomie (Germany), Laboratoire d’Astrophysique de Marseille (France), and the University of Birmingham (UK). SOHO is a mission of international cooperation between ESA and NASA. The Transition Region and Coronal Explorer (TRACE) is a mission of the Stanford–Lockheed Institute for Space Research, and part of the NASA Small Explorer program. Hα data were provided by the Kanzelhöhe Observatory, University of Graz, Austria, and by the Hvar Observatory, University of Zagreb, Croatia. The research leading to these results has received funding from the European Commission’s Seventh Framework Programme (FP7/2007 – 2013) under the grant agreements No. 218816 (SOTERIA project, www.soteria-space.eu ) and No. 284461 (eHEROES, http://soteria-space.eu/eheroes/html ). TT was partially supported by NASA’s HTP, LWS, and SR&T programs. LvDG acknowledges funding through the Hungarian Science Foundation grant OTKA K81421.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below are the links to the electronic supplementary material.
(MOV 5.2 MB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Török, T., Temmer, M., Valori, G. et al. Initiation of Coronal Mass Ejections by Sunspot Rotation. Sol Phys 286, 453–477 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-013-0269-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-013-0269-9