Abstract
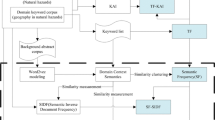
As an increasing number of scientific literature dataset are open access, more attention has gravitated to keyword analysis in many scientific fields. Traditional keyword analyses include the frequency based and the network based methods, both providing efficient mining techniques for identifying the representative keywords. The semantic meanings behind the keywords are important for understanding the research content. However, traditional keyword analysis methods pay scant attention to semantic meanings; the network based or frequency based methods as traditionally used, present limited semantic associations among the keywords. Moreover, the ways in which the semantic meanings behind the keywords are associated to the citations are not clear. Thus, we use the Google Word2Vec model to build word vectors and reduce them to a two-dimensional plane in a Voronoi diagram using the t-SNE algorithm, to link meanings with citations. The distance between semantic meanings of keywords in two-dimensional plane are similar to distances in geographical space, thus we introduce a geographic metaphor, “Ghost City” to describe the relationship between semantics and citations for hot topics that have recently become not so hot. Along with “Ghost City” zones, “Always Hot”, “Newly Emerging Hot”, and “Always Silent” areas are classified and mapped, describing the spatial heterogeneity and homogeneity of the semantic distribution of keywords cited in a domain database. Using a collection of “geographical natural hazard” literature datasets, we demonstrate that the proposed method and classification scheme can efficiently provide a unique viewpoint for interpreting the interaction between semantics and the citations, as “Ghost City”, “Always Hot”, “Newly Emerging Hot”, and “Always Silent” areas.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Borgatti, S. P., & Everett, M. G. (2006). A graph-theoretic perspective on centrality. Social Networks, 28(4), 466–484.
Callon, M., Courtial, J.-P., Turner, W. A., & Bauin, S. (1983). From translations to problematic networks: An introduction to co-word analysis. Information (International Social Science Council), 22(2), 191–235.
Chen, C. (1999). Visualising semantic spaces and author co-citation networks in digital libraries. Information Processing and Management, 35(3), 401–420. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0306-4573(98)00068-5.
Chen, C. (2006). CiteSpace II: Detecting and visualizing emerging trends and transient patterns in scientific literature. Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology, 57(3), 359–377.
Garfield, E. (2009). From the science of science to Scientometrics visualizing the history of science with HistCite software. Journal of Informetrics, 3(3), 173–179.
He, Q., Chen, B., Pei, J., Qiu, B., Mitra, P., & Giles, C. L. (2009). Detecting topic evolution in scientific literature: How can citations help? In Conference on information and knowledge management, 2009 (pp. 957–966).
Hu, K., Qi, K., Guan, Q., Wu, C., Yu, J., Qing, Y., et al. (2017). A scientometric visualization analysis for night-time light remote sensing research from 1991 to 2016. Remote Sensing, 9(8), 802.
Kang, C., & Qin, K. (2016). Understanding operation behaviors of taxicabs in cities by matrix factorization. Computers, Environment and Urban Systems, 60, 79–88.
Ke, Q., Ferrara, E., Radicchi, F., & Flammini, A. (2015). Defining and identifying Sleeping Beauties in science. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 112(24), 7426–7431.
Kessler, M. M. (1963). Bibliographic coupling between scientific papers. American Documentation, 14(1), 10–25.
Kleinberg, J. (2003). Bursty and hierarchical structure in streams. Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery, 7(4), 373–397.
Mane, K. K., & Borner, K. (2004). Mapping topics and topic bursts in PNAS. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 101, 5287–5290.
Mikolov, T., Sutskever, I., Chen, K., Corrado, G., & Dean, J. (2013). Distributed representations of words and phrases and their compositionality. In Neural information processing systems, 2013 (pp. 3111–3119).
Newman, M. E., & Girvan, M. (2004). Finding and evaluating community structure in networks. Physical Review E, 69(2), 026113.
Skupin, A. (2004). The world of geography: Visualizing a knowledge domain with cartographic means. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 101, 5274–5278.
Small, H. (1973). Co-citation in the scientific literature: A new measure of the relationship between two documents. Journal of the American Society for Information Science, 24(4), 265–269.
Song, M., Heo, G. E., & Kim, S. Y. (2014). Analyzing topic evolution in bioinformatics: Investigation of dynamics of the field with conference data in DBLP. Scientometrics, 101(1), 397–428. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-014-1246-2.
Teixeira, A. A. C., Vieira, P. C., & Abreu, A. P. (2016). Sleeping Beauties and their princes in innovation studies. Scientometrics. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-016-2186-9.
Uzzi, B., Mukherjee, S., Stringer, M., & Jones, B. (2013). Atypical combinations and scientific impact. Science, 342(6157), 468–472.
van der Maaten, L., & Hinton, G. (2008). Visualizing data using t-SNE. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 9, 2579–2605.
van Eck, N., & Waltman, L. (2009). Software survey: VOSviewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping. Scientometrics, 84(2), 523–538.
Wu, Q., Zhang, C., Hong, Q., & Chen, L. (2014). Topic evolution based on LDA and HMM and its application in stem cell research. Journal of Information Science, 40(5), 611–620.
Xie, P. (2015). Study of international anticancer research trends via co-word and document co-citation visualization analysis. Scientometrics, 105(1), 611–622.
Yan, E. (2014). Research dynamics: Measuring the continuity and popularity of research topics. Journal of Informetrics, 8(1), 98–110.
Yan, E., Ding, Y., Milojević, S., & Sugimoto, C. R. (2012). Topics in dynamic research communities: An exploratory study for the field of information retrieval. Journal of Informetrics, 6(1), 140–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joi.2011.10.001.
Yang, S., Han, R., Wolfram, D., & Zhao, Y. (2016). Visualizing the intellectual structure of information science (2006–2015): Introducing author keyword coupling analysis. Journal of Informetrics, 10(1), 132–150.
Zhang, F., Zhu, X., Guo, W., Ye, X., Hu, T., & Huang, L. (2016). Analyzing urban human mobility patterns through a thematic model at a finer scale. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 5(6), 78.
Zheng, J., Gong, J., Li, R., Hu, K., Wu, H., & Yang, S. (2017). Community evolution analysis based on co-author network: A case study of academic communities of the journal of “Annals of the Association of American Geographers”. Scientometrics. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-017-2515-7.
Zhou, D., Ji, X., Zha, H., & Giles, C. L. (2006). Topic evolution and social interactions: How authors effect research. In Conference on information and knowledge management, 2006 (pp. 248–257).
Acknowledgements
This research is supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 41371370) and National Science Foundation for Young Scientists of China (Grant Nos. 41601298, 41501443).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, K., Qi, K., Yang, S. et al. Identifying the “Ghost City” of domain topics in a keyword semantic space combining citations. Scientometrics 114, 1141–1157 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-017-2604-7
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-017-2604-7