Abstract
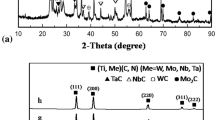
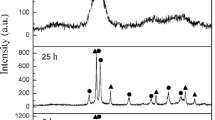
The development of new binder matrices and a fine hard phase have been studied in order to improve the properties of cermet material because TiC has a low stiffness and toughness at high temperature in spite of its high melting point, high hardness, oxidation and corrosion resistance, good thermal stability, and thermal shock resistance. Ni3Al intermetallics are great candidate binder matrices for some structural applications, especially those at the high temperature instead of Co or Ni. This permanently ordered compound up to its melting point has attracted wide interest since it is the prototype of one constituent phase of Ni-base superalloys strengthened by γ’phase precipitation. This research focused on the fabrication of Ni3Al–Al2O3/TiC composite materials by spark plasma sintering. Raw powders of Ni, Al, TiH2 and activated carbon were milled in a planetary mill to fabricate Ni3Al–Al2O3/TiC cermet. These mixtured powders were consolidated by spark plasma sintering up to 1,350°C in vacuum atmosphere under 10−3 Torr. Ni3Al–Al2O3/TiC composite was directly synthesized by dehydrogenation and carburization reaction during sintering process. In situ sintered Ni3Al–Al2O3/TiC composite materials were formed by spark plasma sintering above 1,100°C with 10-h milled powders. In the case of spark plasma sintering for 5 min at 1,350°C, it indicated a hardness value of 71 HRC and a relative density of 94.6% through the influence of rapid densification and fine TiC particle reinforced Ni3Al-base composites materials.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. Kitakawa, Mach. Tool. 33, 27 (1989)
H.S. Kalish, Met. Prog. 124, 21 (1983)
B.H. Lohse, A. Calka, D. Wexler, J. Alloy. Compd. 394, 148 (2005)
K. Nishigaki, Y. Oosawa, H. Doi, J. Japan Soc. Powder Powder Met. 26, 169 (1979)
D. Chen, M. Lu, D. Lin, T.L. Chen, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 167, 251 (1993)
T. Licko, V. Figusch, J. Puchyona, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 9, 219 (1992)
R. Koc, J.S. Folmer, J. Mater. Sci. 32, 3101 (1997)
D. Setoyama, J. Matsunaga, H. Muta, M. Uno, S. Yamanaka, J. Alloy. Compound. 381, 215 (2004)
T.K. Sung, I.S. Ahn, S.Y. Bae, W.H. Jeong, D.K. Park, J. Korean Powder Metallurgy Inst. 12, 174–178 (2005)
I.S. Ahn, T.K. Sung, S.Y. Bae, H.J. Cho, D.K. Park, J. Metal. Mater. Int. 12, 366 (2006)
I. Barin, Thermochemical Data of Pure Substances (VCH, Weinheim, Federal Republic of Germany, 1989)
K. Thorne, J. Ting, J. Chu, D. Mackenzie, D. Getman, F. Hawthorne, J. Mater. Sci. 27, 4406 (1992)
D.-W. Kim, S.-H. Choi, K.-R. Do, S.-G. Lim, I.-S. Ahn, The 3rd International Symposium on Functional Materials, 6, 342 (2009)
I. Barin, Thermochemical Data of Pure Substances, Part 1. (VCH, Weinheim, Federal Republic of Germany,1989), pp. 49–50
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by ReCAPT at Gyeong Sang National University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, DW., Choi, SH., Do, KR. et al. The Ni3Al–Al2O3/TiC cermet formation behavior with TiH2 base ball-milled powders with Ni, Al, and C during spark plasma sintering. Res Chem Intermed 36, 785–793 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11164-010-0182-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11164-010-0182-x