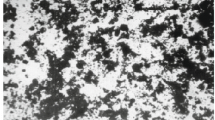
It is established that the addition of high-alumina petrochemical waste products to ceramic compounds leads to a reduction in the content of “dangerous” pores in acid-resistant materials that have been roasted in the temperature range 1280 – 1300°C from 88 to 54%. Moreover, this step does not tend to produce uniform porosity in the samples.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
V. Z. Abdrakhimov, Studies of Iron-containing Traditional Natural and Man-made Raw Materials in Sintering of Ceramic Materials. Influence of the Ions Fe 2+ and Fe 3+ on the Formation of Low-temperature Mullite [in Russian], Samara State Architecture and Construction University, Samara (2009), 427 pp.
P. P. Budnikov, V. L. Balkevich and A. S. Berezhnoi, et al., Chemical Engineering of Ceramics and Refractories [in Russian], Stroiizdat, Moscow (1972), 588 pp.
M. K. Gal’perin and L. V. Erokhina, On the porosity structure of ceramic articles, Tr. NIIstroikeramiki: Studies on Production Technology and Expansion of the Product Range of Ceramic Articles [in Russian], (1981), pp. 58 – 61.
A. V. Lykov, The Phenomenon of Transport in Capillary Bodies [in Russian], Gosteorizdat, Moscow (1964), 214 pp.
A. I. Avgustinik, Ceramic [in Russian], Leninzdat, Leningrad (1975), 588 pp.
S. Zh. Saibulatov, S. T. Suleimenov, and A. V. Ralko, Ash Ceramic Wall Materials [in Russian], Nauka, Alma-Ata (1982), 292 pp.
K. K. Strelov, Structure and Properties of Refractory Materials [in Russian], Metallurgiya, Moscow (1972), 168 pp.
A. F. Chizhskii, Mechanism and conditions for the appearance of fractures in the course of drying of ceramics, Steklo i Keramika, No. 10, 15 (1949).
M. K. Gal’perina and A. V. Erokhina, Kinetics and variations in the porosity structure in the course of roasting of clays of different mineral compositions, Tr. NIIstroikeramiki, vyp. 45, 3 – 18 (1981).
V. Z. Abdrakhimov, Ecological and practical aspects in the use of high-alumina petrochemical waste products in the production of acid-resistant materials, Novye Ogneupory, No. 1, 40 – 43 (2010); Refractories and Industrial Ceramics, 51, No. 1, 52 – 55 (2010).
V. F. Pavlov, Physico-chemical Foundations of Roasting of Construction Ceramics Articles [in Russian], Stroiizdat, Moscow (1977), 272 pp.
A. Ginier, x-ray Diffraction Analysis of Crystals [Russian translation], Fizmatgiz, Moscow (1961), 604 pp.
E. S. Abdrakhimova and V. Z. Abdrakhimov, Kinetics in variation of the porosity structure in the course of roasting of acid-resistant materials, Izv. Vuzov. Stroitel’stvo, No. 9, 38 – 41 (2000).
V. Z. Abdrakhimov, M. P. Zeling, E. S. Abdrakhimova, et al., Interaction of porous-capillary structure and frost resistance of ceramic materials, Materialovedenie, No. 6, 19 – 24 (2005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Translated from Novye Ogneupory, No. 9, pp. 45 – 48, September, 2010.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abdrakhimov, V.Z., Semenychev, V.K. Influence of high-alumina petrochemical waste products on the porosity structure of acid-resistant materials. Refract Ind Ceram 51, 382–385 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11148-011-9330-0
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11148-011-9330-0