Abstract
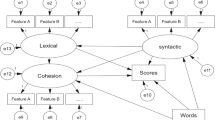
The study developed a model of linguistic constructs to predict writing quality for college basic writers and analyzed how those constructs changed following instruction. Analysis used a corpus of argumentative essays from a quasi-experimental, instructional study with 252 students (MacArthur, Philippakos, & Ianetta, 2015) that found large effects (ES = 1.22) on quality of argumentative writing. Coh-Metrix (McNamara, Graesser, McCarthy, & Cai, 2014) was used to analyze the essays for lexical and syntactic complexity and cohesion. Structural equation modeling found that referential cohesion (p < .001) and lexical complexity (p < .01) positively predicted quality on posttest essays while syntactic complexity (p < .001) was negatively related to quality. Length explained 30% of variance in quality; the full model explained 48.7%. Confirmatory factor analysis was used to impute factor scores for pretest and posttest essays. Analysis of covariance using these factors found that the treatment group wrote posttest essays with greater lexical complexity (p < .01) and referential cohesion (p < .01) and less use of connectives (p < .05) than a business-as-usual control group.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bailey, T., Jeong, D. W., & Cho, S.-W. (2010). Referral, enrollment, and completion in developmental education sequences in community colleges. Economics of Education Review, 29, 255–270. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.econedurev.2009.09.002.
Bremer, C. D., Center, B. A., Opsal, C. L., Medhanie, A., Jang, Y. J., & Geise, A. C. (2013). Outcome trajectories of developmental students in community colleges. Community College Review, 41, 154–175. https://doi.org/10.1177/0091552113484963.
Bulté, B., & Housen, A. (2014). Conceptualizing and measuring short-term changes in L2 writing complexity. Journal of Second Language Writing, 26, 42–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jslw.2014.09.005.
Chapelle, C. A., Cotos, E., & Lee, J. (2015). Validity arguments for diagnostic assessment using automated writing evaluation. Language Testing, 32, 385–405. https://doi.org/10.1177/0265532214565386.
Cohen, J. (1988). Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences (2nd ed.). New York: Academic Press.
Connor-Linton, J., & Polio, C. (2014). Comparing perspectives on L2 writing: Multiple analyses of a common corpus. Journal of Second Language Writing, 26, 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jslw.2014.09.002.
Crossley, S. A., Kyle, K., & McNamara, D. S. (2015). To aggregate or not? Linguistic features in automatic essay scoring and feedback systems. Journal of Writing Assessment, 8. http://journalofwritingassessment.org/article.php?article=80.
Crossley, S. A., & McNamara, D. S. (2014). Does writing development equal writing quality? A computational investigation of syntactic complexity in L2 learners. Journal of Second Language Writing, 26, 66–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jslw.2014.09.006.
Crossley, S. A., Weston, J. L., Sullivan, S. T. M., & McNamara, D. S. (2011). The development of writing proficiency as a function of grade level: A linguistic analysis. Written Communication, 28, 282–311. https://doi.org/10.1177/0741088311410188.
Dikli, S. (2006). An overview of automated scoring of essays. The Journal of Technology, Learning, and Assessment, 5(1), 1–36.
Dufty, D. F., Graesser, A. C., Louwerse, M. M., & Mcnamara, D. S. (2006). Assigning grade level to textbooks: Is it just readability? In R. Sun & N. Miyake (Eds.), Proceedings of the 28th annual conference of the cognitive science society (pp. 1251–1256). Austin: Cognitive Science Society.
Englert, C. S., Raphael, T. E., Anderson, L. M., Anthony, H. M., & Stevens, D. D. (1991). Making writing strategies and self-talk visible: Cognitive strategy instruction in writing in regular and special education classrooms. American Educational Research Journal, 28, 337–372. https://doi.org/10.3102/00028312028002337.
Field, A. (2013). Discovering statistics using SPSS Statistics (4th ed.). Los Angeles: Sage Publications Inc.
Graham, S. (2006). Strategy instruction and the teaching of writing: A meta-analysis. In C. A. MacArthur, S. Graham, & J. Fitzgerald (Eds.), Handbook of writing research (pp. 187–207). New York: Guilford.
Graham, S., Hebert, M., & Harris, K. R. (2015). Formative assessment and writing: A meta-analysis. The Elementary School Journal, 115, 523–547. https://doi.org/10.1086/681947.
Graham, S., McKeown, D., Kiuhara, S., & Harris, K. R. (2012). A meta-analysis of writing instruction for students in the elementary grades. Journal of Educational Psychology, 104, 879–896. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0029185.
Graham, S., & Perin, D. (2007). A meta-analysis of writing instruction for adolescent students. Journal of Educational Psychology, 99, 445–476. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-0663.99.3.445.
Halliday, M. A. K., & Hasan, R. (1976). Cohesion in English. London: Longman.
Harris, K. J., & Graham, S. (2009). Self-regulated strategy development in writing: Premises, evolution, and the future. In V. Connelly, A. L. Barnett, J. E. Dockrell, & A. Tolmie (Eds.), Teaching and learning writing (British journal of educational psychology monograph series II: Part 6 (pp. 113–135). Leicester: British Psychological Society.
Haswell, R. H. (2000). Documenting improvement in college writing: A longitudinal approach. Written Communication, 17, 307–352. https://doi.org/10.1177/0741088300017003001.
Hu, L., & Bentler, P. M. (1999). Cutoff criteria for fit indexes in covariance structure analysis: Conventional criteria versus new alternatives. Structural Equation Modeling, 6, 1–55. https://doi.org/10.1080/10705519909540118.
Hudson, R. (2009). Measuring maturity. In R. Beard, J. Riley, D. Myhill, & M. Nystrand (Eds.), The sage handbook of writing development (pp. 349–362). London: Sage Publishing. https://doi.org/10.4135/9780857021069.n24.
Hunt, K. W. (1964). Differences in grammatical structures written at three grade levels, the structures to be analyzed by transformational methods. ERIC Document Reproduction Service No. ED003322.
Loban, W. D. (1976). Language development: Kindergarten through grade twelve. Research report #18. Urbana, IL: National Council of Teachers of English.
MacArthur, C. A. (2016). Instruction in evaluation and revision. In C. A. MacArthur, S. Graham, & J. Fitzgerald (Eds.), Handbook of writing research (2nd ed., pp. 272–287). New York: Guilford.
MacArthur, C. A., & Philippakos, Z. A. (2013). Self-regulated strategy instruction in developmental writing: A design research project. Community College Review, 41, 176–195. https://doi.org/10.1177/0091552113484580.
MacArthur, C. A., Philippakos, Z. A., & Ianetta, M. (2015). Self-regulated strategy instruction in college developmental writing. Journal of Educational Psychology, 107, 855–867. https://doi.org/10.1037/edu0000011.
MacArthur, C. A., & Wilson, J. (2016). The reliability and validity of an automated essay scoring program for assessment of the outcomes of instruction. Paper presented at the annual conference of the Literacy Research Association, Nashville, TN.
McCarthy, P. M., & Jarvis, S. (2010). MTLD, vocd-D, and HD-D: A validation study of sophisticated approaches to lexical diversity assessment. Behavior Research Methods, 42, 381–392. https://doi.org/10.3758/BRM.42.2.381.
McNamara, D. S., Crossley, S. A., & McCarthy, P. M. (2010a). Linguistic features of writing quality. Written Communication, 27, 57–86. https://doi.org/10.1177/0741088309351547.
McNamara, D. S., Crossley, S. A., & Roscoe, R. (2013). Natural language processing in an intelligent writing strategy tutoring system. Behavior Research Methods, 45, 499–515. https://doi.org/10.3758/s13428-012-0258-1.
McNamara, D. S., Graesser, A. C., McCarthy, P., & Cai, Z. (2014). Automated evaluation of text and discourse with Coh-Metrix. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9780511894664.
McNamara, D. S., Kintsch, E., Songer, N. B., & Kintsch, W. (1996). Are good texts always better? Text coherence, background knowledge, and levels of understanding in learning from text. Cognition and Instruction, 14, 1–43. https://doi.org/10.1207/s1532690xci1401_1.
McNamara, D. S., Louwerse, M. M., McCarthy, P. M., & Graesser, A. C. (2010b). Coh-Metrix: Capturing linguistic features of cohesion. Discourse Processes, 42, 292–330. https://doi.org/10.1080/01638530902959943.
National Center for Education Statistics. (2012). The Nation’s Report Card: Writing 2011 (NCES 2012–470). Washington, DC: NCES, Institute of Education Sciences, U.S. Department of Education.
National Center for Education Statistics. (2013). 2011–2012 National Postsecondary Student Aid Study (NPSAS:12). Washington, DC: NCES, Institute for Education Sciences, U.S. Department of Education.
Perin, D. (2013). Literacy skills among academically underprepared students. Community College Review, 41, 118–136. https://doi.org/10.1177/0091552113484057.
Perin, D., & Lauterbach, M. (2016). Assessing text-based writing of low-skilled college students. International Journal of Artificial Intelligence in Education. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40593-016-0122-z.
Perin, D., Lauterbach, M., Raufman, J., & Kalamkarian, H. S. (2017). Text-based writing of low-skilled postsecondary students: Relation to comprehension, self-efficacy and teacher judgments. Reading and Writing: An Interdisciplinary Journal, 30, 887–915. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11145-016-9706-0.
Polio, C., & Shea, M. C. (2014). An investigation into current measures of linguistic accuracy in second language writing research. Journal of Second Language Writing, 26, 10–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jslw.2014.09.003.
Salahu-Din, D., Persky, H., & Miller, J. (2008). The Nation’s Report Card: Writing 2007 (No. (NCES 2008–468)). Washington, DC: National Center for Education Statistics, Institute of Education Sciences, U.S. Department of Education.
Shermis, M. D. (2014). State-of-the-art automated essay scoring: Competition, results, and future directions from a United States demonstration. Assessing Writing, 20, 53–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asw.2013.04.001.
Shermis, M. D., & Burstein, J. (Eds.). (2013). Handbook of automated essay evaluation: Current applications and new directions. New York: Routledge.
Widaman, K. F., Ferrer, E., & Conger, R. D. (2010). Factorial invariance within longitudinal structural equation models: Measuring the same construct across time. Child Development Perspectives, 4(1), 10–18. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1750-8606.2009.00110.x.
Wilson, J., Roscoe, R., & Yusra, A. (2017). Automated formative writing assessment using a levels of language framework. Assessing Writing. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asw.2017.08.002.
Witte, S. P., & Faigley, L. (1981). Coherence, cohesion, and writing quality. College Composition and Communication, 32, 189–204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asw.2017.08.002.
Wolfe, C. R. (2011). Argumentation across the curriculum. Written Communication, 28, 193–219. https://doi.org/10.1177/0741088311399236.
Acknowledgements
The research reported here was supported by the Institute of Education Sciences, U.S. Department of Education, through Grant R305A160242 to University of Delaware. The opinions expressed are those of the authors and do not represent views of the Institute or the U.S. Department of Education.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
MacArthur, C.A., Jennings, A. & Philippakos, Z.A. Which linguistic features predict quality of argumentative writing for college basic writers, and how do those features change with instruction?. Read Writ 32, 1553–1574 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11145-018-9853-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11145-018-9853-6