Abstract
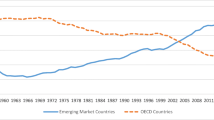
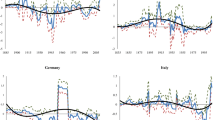
This paper samples the data of 138 countries during the 1971–2007 period, and performs an empirical test to validate the relationship between carbon dioxide emissions and economic growth. It first performs panel data analysis and quantile regression analysis to estimate the long-run elasticity relationships, and then analyzes the short-run error correction model to verify the causal relationship between the two. The empirical results indicate the following. (1) The long-run relationship between global carbon dioxide emissions and GDP is stable, with 32.6% of the sampled countries showing cross-coupling of the two (with an elasticity value of greater than 1), 47.1% reporting relative-decoupling (with an elasticity value between 0 and 1), and 20.3% seeing absolute-decoupling (with an elasticity value of smaller than 0). (2) The quantile regression shows that long-run elasticity declines along with the rise of carbon dioxide emission quantiles. In other words, cross-coupling turns into relative-decoupling. (3) The analysis of short-run panel data and quantile regressions mostly support the feedback relationship between carbon dioxide emissions growth and economic growth. This is consistent with the hypothesis developed by Kuznets. (4) According to the results of the quantile regression, the higher the quantiles, the faster and more stable of the short-run error-correction mechanism of the adjustments from short-run disequilibrium to long-run equilibrium. (5) Under the low-quantile carbon dioxide emissions growth and economic growth, the relationship between these two is not stable of the short-run disequilibrium adjustments in the error-correction adjustment process. However, the relationship between these two is steady and feedback in the case of high quantiles. Therefore, the first priority to combat global warming is to focus on the countries with high economic growth and high carbon dioxide emissions growth.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aldy J.E.: An environmental Kuznets curve analysis of U.S. state-level carbon dioxide emissions. Environ. Dev. Econ. 14, 48–72 (2005)
Ang J.B.: CO2 emissions, energy consumption, and output in France. Energy Policy 35(10), 4772–4778 (2007)
Auffhammer M., Carson R.T.: Forecasting the path of China’s CO2 emissions using province level information. J. Environ. Econ. Manage. 55, 229–247 (2008)
Azomahou T., Laisney F., Van Phu N.: Economic development and CO2 emissions: a nonparametric panel approach. J. Public Econ. 90, 1347–1363 (2006)
Azomahou, T., Van Phu, N.: Economic Growth and CO2 Emissions: a nonparametric approach, Working Papers of BETA 2001–01, Bureau d’Economie Théorique et Appliquée, UDS, Strasbourg (2001)
Breitung,J.: The local power of some unit root tests for panel data. In: Baltagi, B. (ed) Advances in Econometrics, vol. 15: Nonstationary Panels, Panel Cointegration, and Dynamic Panels, pp. 161–178. JAI Press, Amsterdam
Buchinsky M.: Recent advances in quantile regression models: a practical guidline for empirical research. J. Human Resources 33(1), 88–126 (1998)
Carson R.T.: The environmental Kuznets Curve: seeking empirical regularity and theoretical structure. Rev. Environ. Econ. Policy 4(1), 3–23 (2010)
Carson R.T., Jeon Y., McCubbin D.: The relationship between air pollution and emissions: U.S. data. Environ. Dev. Econ. 2, 433–450 (1997)
Choi I.: Unit root tests for panel data. J. Int. Money Finance 20, 249–272 (2001)
Culas R.J.: Deforestation and the environmental Kuznets curve: an institutional perspective. Ecol. Econ. 61, 429–437 (2007)
Dasgupta S., Laplante B., Wang H., Wheeler D.: Confronting the environmental Kuznet’s curve. J. Econ. Perspect. 16, 147–168 (2002)
Diao X.D., Zeng S.X., Tamb C.M., Tamc V.W.Y.: EKC analysis for studying economic growth and environmental quality: a case study in China. J. Clean. Prod. 17, 541–548 (2009)
Dijkgraaf E., Vollebergh H.R.J.: A Test for Parameter Heterogeneity in CO2 Panel EKC Estimations. Environ. Resource Econ. 32, 229–239 (2005)
Engle R.F., Granger C.W.J.: Co-integration and error correction: representation, estimation, and testing. Econometrica 55, 251–276 (1987)
Fodha M., Zaghdoud O.: Economic growth and pollutant emissions inTunisia: an empirical analysis of the environmental Kuznets curve. Energy Policy 38, 1150–1156 (2010)
Gallagher K.: Free Trade and the Environment: Mexico, NAFTA, and Beyond. Stanford University Press, Palo Alto (2004)
Grossman, G.M., Krueger, A.B.: Environmental Impacts of a North American Free Trade Agreement. Working paper No. 3914, National Bureau of Economic Research (1991)
Halicioglu F.: An econometric study of CO2 emissions, energy consumption, income and foreign trade in Turkey. Energy Policy 37(3), 1156–1164 (2009)
He H., Richard P.: Environmental Kuznets curve for CO2 in Canada. Ecol. Econ. 69(5), 1083–1093 (2010)
Holtz-Eakin D., Selden T.: Stoking the fires? CO2 emissions and economic growth. J. Public Econ. 57, 85–101 (1995)
Im K.S., Pesaran M.H., Shin Y.: Testing for unit roots in heterogeneous panels. J. Economet. 115, 53–74 (2003)
Jalil A., Mahmud S.F.: Environment Kuznets curve for CO2 emissions: a cointegration analysis for China. Energy Policy 37, 5167–5172 (2009)
Jones, L.E., Manuelli, R.E.: Neoclassical models of endogenous growth: the effects of fiscal policy, innovation and fluctuations. In: Aghion, P., Durlauf, S.N. (eds.) Handbook of Economic Growth, 1A, pp. 13–65. Elsevier, Amsterdam (2005)
Jorgenson, D.W., Wilcoxen, P.J.: Energy, the environment and economic growth. In: Kneese, A.V., Sweeney, J.L. (eds.) Handbook of Natural Resource and Energy Economics, vol. 3, pp. 1267–1349. Elsevier, Amsterdam (1993)
Kao C.: Spurious regression and residual-based tests for cointegration in panel data. J. Economet. 90, 1–44 (1999)
Koenker R., Bassett G.: Quantile regression. Econometrica 46, 33–50 (1978)
Koenker R., d’Orey V.: Computing regression quantiles. Appl. Stat. 36, 383–393 (1987)
Koenker R., Hallock K.F.: Quantile regression. J. Econ. Perspect. 15, 143–156 (2001)
Kolstad C.D., Krautkraemer J.A.: Natural resource use and the environment. In: Kneese, A.V., Sweeney, J.L. (eds) Handbook of Natural Resource and Energy Economics, vol 3., pp. 1219–1265. Elsevier, Amsterdam (1993)
Levin A., Lin C.F., Chu C.: Unit root tests in panel data: asymptotic and finite-sample properties. J. Economet. 108, 1–24 (2002)
List J.A., Craig A.G.: The Environmental Kuznets curve: does one size fit all?. Ecol. Econ. 31, 409–423 (1999)
List J.A., Gallet C.A.: The environmental Kuznets curve: does one size fit all?. Ecol. Econ. 31, 409–424 (1999)
MacKinnon J.G., Haug A.A., Michelis L.: Numerical distribution functions of likelihood ratio tests for cointegration. J. Appl. Econom. 14(5), 563–577 (1999)
Maddala G.S., Wu S.: A comparative study of unit root tests with panel data and a new simple test. Oxford Bull Econ. Stat. 61, 631–652 (1999)
Menyah K., Wolde-Rufael Y.: CO2 emissions, nuclear energy, renewable energy and economic growth in the US. Energy Policy 38(6), 2911–2915 (2010)
Millimet D.L., List J.A., Stengos T.: The environmental Kuznets curve: real progress or misspecified models?. Rev. Econ. Stat. 85, 1038–1047 (2003)
Pedroni P.: Critical values for cointegration tests in heterogeneous panels with multiple regressors. Oxford Bull. Econ. Stat. 61, 653–670 (1999)
Pedroni P.: Fully modified OLS for heterogeneous cointegrated panels. Adv. Economet. 15, 93–130 (2000)
Pedroni P.: Panel cointegration: asymptotic and finite sample properties of pooled time series tests with an application to the PPP hypothesis. Economet. Theory 20, 597–625 (2004)
Perman R., Stern D.I.: Evidence from panel unit root and cointegration tests that the environmental Kuznets curve does not exist. Aust. J. Agricult. Resource Econ. 47, 325–347 (2003)
Romero-Ávila D.: Convergence in carbon dioxide emissions among 37 industrialised countries revisited. Energy Econ. 30, 2265–2282 (2008)
Sari R., Soytas U.: Are global warming and economic growth combatable? Evidence from five OPEC countries. Appl. Energy 86, 1887–1893 (2009)
Selden T., Song D.: Environmental quality and development: is there a kuznets curve for air pollution emissions?. J. Environ. Econ. Manage. 27, 147–162 (1994)
Shafik N.: Economic development and environmental quality: an econometric analysis. Oxford Econ. Papers 46, 757–773 (1994)
Shafik N., Bandyopadhyay S.: Economic growth and environmental quality: time series and cross section evidence. Working paper. World Development Report 1992. Oxford University Press, New York (1992)
Soytas U., Sari R.: Energy consumption, economic growth and carbon emissions: challenges faced by a EU candidate member. Ecol. Econ. 68, 1667–1675 (2009)
Stern N.H.: Stern Review: The Economics of Climate Change. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2007)
Taskin F., Zaim O.: Searching for a Kuznets curve in environmental efficiency using Kernel estimation. Econ. Lett. 68, 217–233 (2000)
Vincent J.R.: Testing for environmental Kuznets curves within a developing country. Environ. Dev. Econ. 2, 417–431 (1997)
Xepapadeas A.: Economic growth and the environment. In: Mäler, K.-G., Vincent, J.R. (eds) Handbook of Environmental Economics, vol. 3,, pp. 1219–1271. Elsevier, Amsterdam (2005)
Zhang X.P., Cheng X.M.: Energy consumption, carbon emissions, and economic growth in China. Ecol. Econ. 68, 2706–2712 (2009)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, KM. The relationship between carbon dioxide emissions and economic growth: quantile panel-type analysis. Qual Quant 47, 1337–1366 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11135-011-9594-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11135-011-9594-y