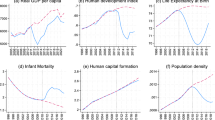
Abstract
This study’s multilevel statistical models quantify the effects of civilization zones and instrumental factors on the capacities for human agency that a country provides its citizens. These capacities are measured by the UN’s human development index, which synthesizes measures of literacy, longevity, and income. Indicators of political democracy, slavery, national debt, corruption, and internal conflict gauge the instrumental factors. Political freedom and emancipative employment coupled with civil order account for the regional differences in human development scores; civilization zones, heavily indebted poor countries, and corruption influence the variability among countries within the regions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adelman, I.: Fallacies in development theory and their implications for policy. In: Meier, G.M., Stiglitz, J.E.(eds) Frontiers of Development Economics, pp. 103–134. Oxford University Press, New York (2001)
Bales, K.: Disposable People. University of California Press, Berkeley, CA (1999)
Bales, K.: New Slavery. ABC-Clio, Santa Barbara, CA (2000)
Bales, K.: The Social Psychology of Modern Slavery. Scientific American 286(4), 82–88 (2002)
Bales, K.: International Labor Standards: Quality of Information and Measures of Progress in Combating Forced Labor. Free the Slaves, Washington DC (2004)
Barro, R.: Determinants of Democracy. J. Polit. Econ. 107, S158–S183 (1999)
Barro, R., McCleary, R.M.: Religion and economic growth across countries. Am. Sociol. Rev. 68(5), 760–781 (2003)
Basu, K.: On the Goals of Development. In: Meier, G.M., Stiglitz, J.E.(eds) Frontiers of Development Economics, pp. 61–86. Oxford University Press, New York (2001)
Beckfield, J.: Inequality in the world polity: the structure of international organization. Am. Sociol. Rev. 68, 401–424 (2003)
Bollen, K.A., Jackman, R.W.: Political democracy and the size distribution of income. Am. Sociol. Rev. 50, 438–457 (1985)
Bryk, A.S., Raudenbush, S.W.: Hierarchical Linear Models: Applications and Data Analysis Methods. Sage, Newbury Park, CA (1992)
Clark, M.A.: Trafficking in persons: an issue of human security. Journal of Human Development 4(2), 247–263 (2003)
Crafts, N..: Historical perspectives on development. In: Meier, G.M., Stiglitz, J.E.(eds) Frontiers of Development Economics, pp. 301–334. Oxford University Press, New York (2001)
Dahl, R.A.: Democracy and Its Critics. Yale University Press, New Haven (1989)
Dahl, R.A.: On counting democratic countries, Appendix C. In: On Democracy, Yale University Press, New Haven (1998)
Etzioni, A.: The Moral Dimension: Toward a New Economics. Free Press, New York (1988)
Firebaugh, G.: The new geography of global income inequality. Harvard University Press, Cambridge, MA (2003)
Freedom House: Freedom in the World 1999–2000. Freedom House, New York (2000)
Galtung, J.: The emerging conflict formations. In: Tehranian, K., Tehranian, M.(eds) Restructuring for World Peace, pp. 23–44. Hampton Press, Cresskill, NJ (1992)
George, A.L., Bennett, A.: Case Studies and Theory Development in the Social Sciences. MIT Press, Cambridge, Massachusetts (2005)
Haq, M.: Reflections on Human Development. Oxford University Press, New York (1995)
Heller, P.: The Labor of Development: Workers and the Transformation of Capitalism in Kerala, India. Cornell University Press, Ithaca (1999)
Hoff, K., Stiglitz, J.E.: Modern economic theory and development. In: Meier, G.M., Stiglitz, J.E.(eds) Frontiers of Development Economics, pp. 389–459. Oxford University Press, New York (2001)
Holland, P.: Statistics and causal inference (with comments). J. Am. Stat. Asso. 81, 945–970 (1986)
Huntington, S.P.: The clash of civilizations and the remaking of world order. Simon & Schuster, ([1996] 1997)
Inglehart, R.: Human Values and Social Change: Findings from the Values Surveys. Brill, Boston, MA (2003)
Kentor, J., Boswell, T.: Foreign capital dependence and development: a new direction. Am. Sociol. Rev. 68, 301–313 (2003)
King, G., Keohane, R.O., Verba, S.: Designing Social Inquiry: Scientific Inference in Qualitative Research. Princeton University Press, Princeton, NJ (1994)
Kreft, I., DeLeeuw, J.: Introducing multilevel modeling. Sage, Thousand Oaks, CA
Lazarsfeld, P.F.: Foreword to Survey Design and Analysis. In: Hyman H.H. (ed.) vol. xii Free Press, New York (1955)
Lazarsfeld, P.F., Menzel, H.: On the relation between individual and collective properties. In: Lazarsfeld, P.F., Pasanella, A.K., Rosenberg, M.(eds) Continuities in the Language of Social Research, pp. 219–237. The Free Press, New York ([1961] 1972)
Lieberson, S.: The big broad issues in society and social history: Application of a probabilistic perspective. In: McKim, V.R., Turner, S.P.(eds) Causality in crisis: Statistical Methods and the Search for Causal Knowledge in the Social Sciences, pp. 359–385. University of Notre Dame Press, South Bend (1997)
Linz, J.J.: Totalitarian and Authoritarian Regimes. Lynne Rienner Publishers, Boulder, CO (2000)
Lipset, S.M.: Economic development and democracy. In: Political Man: the Social Bases of Politics. Johns Hopkins University Press, Baltimore, MD ([1959] 1981)
Lipset, S.M., Lenz, G.S.: Corruption, culture, and markets. In: Harrison, L.E., Huntington, S.P.(eds) Culture Matters: How Values Shape Human Progress, Basic Books, New York (2000)
Littell, R.C., Milliken, G.A., Stroup, W.W., Wolfinger, R.D.: SAS® System for Mixed Models. SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC (1996)
Mehrotra, S.: Social development in high-achieving countries: Common elements and diversities. In: Mehrotra, S., Jolly, R.(eds) Development with a Human Face: Experiences in Social Achievement and Economic Growth, pp. 359–385. Oxford University Press, New York (1997a)
Mehrotra, S.: Health and education policies in high-achieving countries: Some Lessons. In: Mehrotra, S., Jolly, R.(eds) Development with a Human Face: Experiences in Social Achievement and Economic Growth, pp. 63–110. Oxford University Press, New York (1997b)
Moore, D.S., McCabe, G.P.: Introduction to the Practice of Statistics. W. H. Freeman and Company, New York (1989)
Myrdal, G.: Asian Drama: An Inquiry into the Poverty of Nations, Abridged Edition. Pantheon, New York (1971)
Patterson, O.: Slavery and Social Death: A Comparative Study. Harvard University Press, Cambridge, MA (1982)
Paxton, P.: Social Capital and Democracy: An Interdependent Relationship. Am. Socio. Rev. 67, 254–277 (2002)
Pearl, J.: Causality: Models, Reasoning, and Inference. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK (2000)
Prezeworski, A., Alvarez, M.E., Cheibub, J.A., Limongi, F.: Democracy and Development: Political Institutions and Well-Being in the World, 1950–1990. Cambridge University Press, New York (2000)
SAS Institute Inc.: Chapter 18, the MIXED procedure. In: SAS/STAT® Software: Changes and Enhancements Through Release 6.12, pp. 571–702. SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC (1997)
Schwarz, G.: Estimating the Dimension of a Model. Ann. Stat. 6, 461–464 (1978)
Sen, A.: Development as Freedom. Alfred A. Knopf, New York (1999)
Sen, A.: What is development about?. In: Meier, G.M., Stiglitz, J.E. (eds.) Frontiers of Development Economics, pp. 506–513. Oxford University Press, New York (2001)
Sen, A.: Cultural imprisonment. The New Republic 10(6), 28–33 (2002)
Shastri, L.B.: Incidence of Bonded Labour in India: Area, Nature and Extent. National Academy of Administration, (1990)
Thomas, V.: Revisiting the challenge of development. In: Meier, G.M., Stiglitz, J.E.(eds) Frontiers of Development Economics, pp. 149–182. oxford University Press, New York (2001)
Tilly, C.: Democracy is a lake. In: Tilly, C. (ed.) Roads from Past to Future, pp. 193–215. Rowman & Littlefield, Lanham, MD ([1995] 1997)
Tilly, C.: Processes and mechanisms of democratization. Sociol. Theory 18, 1–16 (2000)
Tilly, C.: Contention and Democracy in Europe. Cambridge University Press, New York (2004)
Tilly, C.: Democracy. Cambridge University Press, New York (2007)
Tukey, J.W.: Exploratory Data Analysis. Addison-Wesley, Reading, MA (1977)
United Nations, Department of Public Information: Yearbook of the United Nations 2000. New York (2002)
United Nations Development Program: Human Development Report 1990. Oxford University Press, New York (1990)
United Nations Development Program: Human Development Report 1999. Oxford University Press, New York (1999)
United Nations Development Program: Human Development Report 2002: Deepening Democracy in a Fragmented World. Oxford University Press, New York (2002)
United Nations Statistics Division, Department of Economic Social Affairs: Statistical Yearbook. United Nations Publications, New York (2001)
Welzel, C., Inglehart, R., Klingemann, H.: The theory of human development: a cross-cultural analysis. European Journal of Political Research 42, 341–379 (2003)
York, R., Rosa, E.A., Dietz, T.: Footprints of the earth: the environmental consequences of modernity. Am. Sociol. Rev. 68, 279–300 (2003)
Zweifel, T.D., Navia, P.: Democracy, dictatorship, and infant mortality. J. Democracy 11, 98–114 (2000)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Smith, R.B. Global human development: accounting for its regional disparities. Qual Quant 43, 1–34 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11135-007-9155-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11135-007-9155-6