Abstract
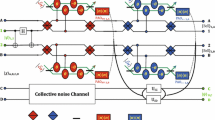
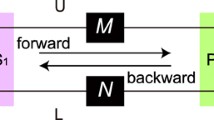
We present two error-tolerance transmission protocols of a single-photon polarization state when bit-flip error is taken into account. For achieving the transmission target of the single-photon state, the first protocol needs to encode it to a nonmaximally entangled Bell state. Exploiting the interaction of the polarization entanglement with spatial entanglement between two photons, its success probability is 100 %. Different from the first protocol, the second one utilizes the idea of teleportation with an auxiliary Bell state. By performing quantum nondemolition measurement to analyze the parity, conventional measurement, and unitary transformation operations, the success probability of the second protocol is approximately unity. Furthermore, the second protocol can be generalized to the error-tolerance transmission of an arbitrary mixed state or the distribution of an arbitrary multi-photon entangled state.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shor, P.W.: Scheme for reducing decoherence in quantum computer memory. Phys. Rev. A 52(4), R2493–R2496 (1995)
Steane, A.M.: Error correcting codes in quantum theory. Phys. Rev. Lett. 77(5), 793–797 (1996)
Bennett, C.H., DiVincenzo, D.P., Smolin, J.A., Wootters, W.K.: Mixed-state entanglement and quantum error correction. Phys. Rev. A 54(5), 3824–3851 (1996)
Laflamme, R., Miquel, C., Paz, J.P., Zurek, W.H.: Perfect quantum error correcting code. Phys. Rev. Lett. 77(1), 198–201 (1996)
Bouwmeester, D.: Bit-flip-error rejection in optical quantum communication. Phys. Rev. A 63(3), 040301 (2001)
Kalamidas, D.: Feasible quantum error detection with linear optics. Phys. Lett. A 321(2), 87–93 (2004)
Wang, X.-B.: Quantum error-rejection code with spontaneous parametric down-conversion. Phys. Rev. A 69(2), 022320 (2004)
Yamamoto, T., Shimamura, J., Özdemir, S.K., Koashi, M., Imoto, N.: Faithful qubit distribution assisted by one additional qubit against collective noise. Phys. Rev. Lett. 95(4), 040503 (2005)
Kalamidas, D.: Single-photon quantum error rejection and correction with linear optics. Phys. Lett. A 343(5), 331–335 (2005)
Li, X.-H., Deng, F.-G., Zhou, H.-Y.: Faithful qubit transmission against collective noise without ancillary qubits. Appl. Phys. Lett. 91(14), 144101 (2007)
Li, X.-H., Zhao, B.-K., Sheng, Y.-B., Deng, F.-G., Zhou, H.-Y.: Efficient faithful qubit transmission with frequency degree of freedom. Opt. Commun. 282(19), 4025–4027 (2009)
Deng, F.-G., Li, X.-H., Zhou, H.-Y.: Passively self-error-rejecting qubit transmission over a collective-noise channel. Quantum Inf. Comput. 11, 0913–0924 (2011)
Salemian, S., Mohammadnejad, S.: An error-free protocol for quantum entanglement distribution in long-distance quantum communication. Chin. Sci. Bull. 56(7), 618–625 (2011)
Pan, J.-W., Chen, Z.-B., Lu, C.-Y., Weinfurter, H., Zeilinger, A., Zukowski, M.: Multiphoton entanglement and interferometry. Rev. Mod. Phys. 84(2), 777–838 (2012)
Zanardi, P., Rasetti, M.: Noiseless quantum codes. Phys. Rev. Lett. 79(17), 3306–3309 (1997)
Boileau, J.-C., Gottesman, D., Laflamme, R., Poulin, D., Spekkens, R.: Robust polarization-based quantum key distribution over a collective-noise channel. Phys. Rev. Lett. 92(1), 017901 (2004)
Wang, X.-B.: Fault tolerant quantum key distribution protocol with collective random unitary noise. Phys. Rev. A 72(5), 050304(R) (2005)
Aolita, L., Walborn, S.: Quantum communication without alignment using multiple-qubit single-photon states. Phys. Rev. Lett. 98(10), 100501 (2007)
Li, X.-H., Deng, F.-G., Zhou, H.-Y.: Efficient quantum key distribution over a collective noise channel. Phys. Rev. A 78(2), 022321 (2008)
Sheng, Y.-B., Deng, F.-G.: Efficient quantum entanglement distribution over an arbitrary collective-noise channel. Phys. Rev. A 81(4), 042332 (2010)
Li, X.-H.: Deterministic polarization-entanglement purification using spatial entanglement. Phys. Rev. A 82(4), 044304 (2010)
Deng, F.-G.: One-step error correction for multipartite polarization entanglement. Phys. Rev. A 83(6), 062316 (2011)
Dong, L., Xiu, X.-M., Gao, Y.-J., Yi, X.X.: Controlled quantum key distribution with three-photon polarization-entangled states via the collective noise channel. J. Exp. Theor. Phys. 113(4), 583–591 (2011)
Yang, Y.-G., Teng, Y.-W., Chai, H.-P., Wen, Q.-Y.: Fault-tolerant quantum secret sharing against collective noise. Phys. Scr. 83(2), 25003 (2011)
Andersson, E., Curty, M., Jex, I.: Experimentally realizable quantum comparison of coherent states and its applications. Phys. Rev. A 74(2), 022304 (2006)
He, B., Ren, Y., Bergou, J.: Creation of high-quality long-distance entanglement with flexible resources. Phys. Rev. A 79(5), 052323 (2009)
Turchette, Q.A., Hood, C.J., Lange, W., Mabuchi, H., Kimble, H.J.: Measurement of conditional phase shifts for quantum logic. Phys. Rev. Lett. 75(25), 4710–4713 (1995)
Rauschenbeutel, A., Nogues, G., Osnaghi, S., Bertet, P., Brune, M., Raimond, J., Haroche, S.: Coherent operation of a tunable quantum phase gate in cavity QED. Phys. Rev. Lett. 83(24), 5166–5169 (1999)
Koashi, M., Yamamoto, T., Imoto, N.: Probabilistic manipulation of entangled photons. Phys. Rev. A 63(1), 030301(R) (2001)
Knill, E., Laflamme, R., Milburn, G.J.: A scheme for efficient quantum computation with linear optics. Nature 409(6816), 46–52 (2001)
Yi, X.X., Su, X.H., You, L.: Conditional quantum phase gate between two 3-state atoms. Phys. Rev. Lett. 90(9), 097902 (2003)
Knill, E.: Bounds on the probability of success of postselected nonlinear sign shifts implemented with linear optics. Phys. Rev. A 68(6), 064303 (2003)
Xiu, X.-M., Dong, L., Shen, H.-Z., Gao, Y.-J., Yi, X.X.: Construction scheme of a two-photon polarization controlled arbitrary phase gate mediated by weak cross-phase modulation. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 30(3), 589–597 (2013)
Pittman, T., Jacobs, B., Franson, J.: Probabilistic quantum logic operations using polarizing beam splitters. Phys. Rev. A 64(6), 062311 (2001)
Pittman, T., Fitch, M., Jacobs, B., Franson, J.: Experimental controlled-NOT logic gate for single photons in the coincidence basis. Phys. Rev. A 68(3), 032316 (2003)
Scheel, S., Munro, W., Eisert, J., Nemoto, K., Kok, P.: Feed-forward and its role in conditional linear optical quantum dynamics. Phys. Rev. A 73(3), 034301 (2006)
Kok, P., Nemoto, K., Ralph, T.C., Dowling, J.P., Milburn, G.J.: Linear optical quantum computing with photonic qubits. Rev. Mod. Phys. 79(1), 135–174 (2007)
Nemoto, K., Munro, W.J.: Nearly deterministic linear optical controlled-NOT gate. Phys. Rev. Lett. 93(25), 250502 (2004)
Lin, Q., Li, J.: Quantum control gates with weak cross-Kerr nonlinearity. Phys. Rev. A 79(2), 022301 (2009)
Wang, M.-F., Jiang, N.-Q., Jin, Q.-L., Zheng, Y.-Z.: Continuous-variable controlled-Z gate using an atomic ensemble. Phys. Rev. A 83(6), 062339 (2011)
Xiu, X.-M., Dong, L., Gao, Y.-J., Yi, X.X.: Nearly deterministic controlled-not gate with weak cross-kerr nonlinearities. Quantum Info. Comput. 12(1–2), 0159–0170 (2012)
Barrett, S.D., Kok, P., Nemoto, K., Beausoleil, R.G., Munro, W.J., Spiller, T.P.: Symmetry analyzer for nondestructive Bell-state detection using weak nonlinearities. Phys. Rev. A 71(6), 060302 (2005)
Munro, W.J., Nemoto, K., Spiller, T.P.: Weak nonlinearities: a new route to optical quantum computation. N. J. Phys. 7(1), 137 (2005)
Guo, Q., Bai, J., Cheng, L.-Y., Shao, X.-Q., Wang, H.-F., Zhang, S.: Simplified optical quantum-information processing via weak cross-Kerr nonlinearities. Phys. Rev. A 83(5), 054303 (2011)
Wang, X.-W., Zhang, D.-Y., Tang, S.-Q., Xie, L.-J., Wang, Z.-Y., Kuang, L.-M.: Photonic two-qubit parity gate with tiny cross-Kerr nonlinearity. Phys. Rev. A 85(5), 052326 (2012)
Xiu, X.-M., Dong, L., Gao, Y.-J., Yi, X.X.: Quantum key distribution with Einstein–Podolsky–Rosen pairs associated with weak cross-Kerr nonlinearities. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 29(10), 2869–2874 (2012)
Wang, X.-W., Tang, S.-Q., Xie, L.-J., Zhang, D.-Y.: Nondestructive two-photon parity detector with near unity efficiency. Opt. Commun. 296, 153–157 (2013)
Munro, W.J., Nemoto, K., Beausoleil, R.G., Spiller, T.P.: High-efficiency quantum-nondemolition single-photon-number-resolving detector. Phys. Rev. A 71(3), 033819 (2005)
Fleischhauer, M., Imamoglu, A., Marangos, J.P.: Electromagnetically induced transparency: optics in coherent media. Rev. Mod. Phys. 77(2), 633–673 (2005)
Chen, Y.-F., Wang, C.-Y., Wang, S.-H., Yu, I.: Low-light-level cross-phase-modulation based on stored light pulses. Phys. Rev. Lett. 96(4), 043603 (2006)
Wang, Z.-B., Marzlin, K.-P., Sanders, B.C.: Large cross-phase modulation between slow copropagating weak pulses in \(^{87}\)Rb. Phys. Rev. Lett. 97(6), 063901 (2006)
Sheng, Y.-B., Deng, F.-G., Zhou, H.-Y.: Efficient polarization-entanglement purification based on parametric down-conversion sources with cross-Kerr nonlinearity. Phys. Rev. A 77(4), 042308 (2008)
Sheng, Y.-B., Deng, F.-G., Zhou, H.-Y.: Nonlocal entanglement concentration scheme for partially entangled multipartite systems with nonlinear optics. Phys. Rev. A 77(6), 062325 (2008)
Lin, Q., He, B.: Single-photon logic gates using minimal resources. Phys. Rev. A 80(10), 042310 (2009)
Sheng, Y.-B., Deng, F.-G.: Deterministic entanglement purification and complete nonlocal Bell-state analysis with hyperentanglement. Phys. Rev. A 81(3), 032307 (2010)
Lin, Q., He, B.: Efficient generation of universal two-dimensional cluster states with hybrid systems. Phys. Rev. A 82(8), 022331 (2010)
Bing, H., Ren, Y.-H., Bergou, J.: Universal entangler with photon pairs in arbitrary states. J. Phys. B At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 43(2), 025502 (2010)
He, B., MacRae, A., Han, Y., Lvovsky, A., Simon, C.: Transverse multimode effects on the performance of photon-photon gates. Phys. Rev. 83(2), 022312 (2011)
Lo, H.-Y., Chen, Y.-C., Chen, H.-C., Chen, J.-X., Chen, Y.-C., Yu, I.A., Chen, Y.-F.: Electromagnetically-induced-transparency-based cross-phase-modulation at attojoule levels. Phys. Rev. A 83(4), 041804(R) (2011)
He, B., Scherer, A.: Continuous-mode effects and photon-photon phase gate performance. Phys. Rev. A 85(3), 033814 (2012)
Siomau, M., Kamli, A.A., Moiseev, S.A., Sanders, B.C.: Entanglement creation with negative index metamaterials. Phys. Rev. A 85(5), 050303(R) (2012)
Sheng, Y.-B., Zhou, L., Zhao, S.-M., Zheng, B.-Y.: Efficient single-photon-assisted entanglement concentration for partially entangled photon pairs. Phys. Rev. A 85(1), 012307 (2012)
Sheng, Y.-B., Zhou, L., Zhao, S.-M.: Efficient two-step entanglement concentration for arbitrary W states. Phys. Rev. A 85(4), 042302 (2012)
Zhou, L., Sheng, Y.-B., Cheng, W.-W., Gong, L.-Y., Zhao, S.-M.: Efficient entanglement concentration for arbitrary less-entangled NOON states. Quantum Info. Process. 12(2), 1307–1320 (2013)
Sheng, Y.-B., Zhou, L., Long, G.-L.: Hybrid entanglement purification for quantum repeaters. Phys. Rev. A 88(2), 022302 (2013)
Sheng, Y.-B., Zhou, L.: Quantum entanglement concentration based on nonlinear optics for quantum communications. Entropy 15(5), 1776–1820 (2013)
Zhou, L., Sheng, Y.-B., Cheng, W.-W., Gong, L.-Y., Zhao, S.-M.: Efficient entanglement concentration for arbitrary single-photon multimode W state. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 30(1), 71 (2013)
Xia, Y., Lu, M., Song, J., Lu, P-m, Song, H-s: Effective protocol for preparation of four-photon polarization-entangled decoherence-free states with cross-Kerr nonlinearity. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 30(2), 421–428 (2013)
Xiu, X.-M., Dong, L., Shen, H.-Z., Gao, Y.-J., Yi., X.X.: Preparing, linking, and unlinking cluster-type polarization-entangled states by integrating modules. Prog. Theor. Exp. Phys. 2013(9), 093A01 (2013)
Wang, X.-W., Zhang, D.-Y., Tang, S.-Q., Xie, L.-J.: Nondestructive Greenberger–Horne–Zeilinger–state analyzer. Quantum Inf. Process. 12(2), 1065–1075 (2013)
Dong, L., Xiu, X.-M., Gao, Y.-J., Yi, X.X.: A nearly deterministic scheme for generating \(\chi \)-type entangled states with weak cross-Kerr nonlinearities. Quantum Inf. Process. 12(4), 1787–1795 (2013)
Xiu, X.-M., Dong, L., Shen, H.-Z., Gao, Y.-J., Yi, X.X.: Two-party quantum privacy comparison with polarization-entangled Bell states and the Coherent states. Quantum Inf. Comput. 14(3–4), 0236–0254 (2014)
Shapiro, J.: Single-photon Kerr nonlinearities do not help quantum computation. Phys. Rev. A 73(6), 062305 (2006)
Shapiro, J.H., Razavi, M.: Continuous-time cross-phase modulation and quantum computation. N. J. Phys. 9(1), 16 (2007)
Gea-Banacloche, J.: Impossibility of large phase shifts via the giant Kerr effect with single-photon wave packets. Phys. Rev. A 81(4), 043823 (2010)
He, B., Lin, Q., Simon, C.: Cross-Kerr nonlinearity between continuous-mode coherent states and single photons. Phys. Rev. A 83(5), 053826 (2011)
Feizpour, A., Xing, X., Steinberg, A.M.: Amplifying single photon nonlinearly using weak measurement. Phys. Rev. Lett. 107(13), 133603 (2011)
Hoi, I.-C., Kockum, A.F., Palomaki, T., Stace, T.M., Fan, B., Tornberg, L., Sathyamoorthy, S.R., Johansson, G., Delsing, P., Wilson, C.M.: Giant cross-Kerr effect for propagating microwaves induced by an artificial atom. Phys. Rev. Lett. 111(5), 053601 (2013)
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 11305016, 61301133, 11271055) and the Research Programs of the Educational Office of Liaoning Province of China (Grant No. L2013425). We acknowledge anonymous reviewers for enlightening instructions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dong, L., Wang, JX., Shen, HZ. et al. Deterministic transmission of an arbitrary single-photon polarization state through bit-flip error channel. Quantum Inf Process 13, 1413–1424 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-014-0736-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-014-0736-8