Abstract
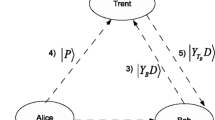
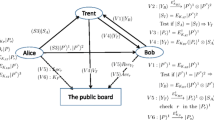
As a new model for signing both quantum and classical messages, the arbitrated quantum signature (AQS) protocols have recently attracted a lot of attentions. In this paper, we analyze their security from an important security aspect—the receiver’s forgery of the signature, and provide a detailed proof of the fact that the attempt to design an improved optimal encryption used in AQS cannot prevent the receiver’s forgery attack unless some assistant security strategies are introduced. In order to show that, we firstly summarize an explicit formalization of the general AQS model and propose the necessary and sufficient conditions against the receiver’s forgery attack. Then a contradiction of them has been pointed out. In order to complete our security analysis, we verify that the AQS protocols for signing classic messages are still susceptible to the receiver’s forgery. Finally, some assistant security strategies are provided to recover the security.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shor, P.: Polynomial-time algorithms for prime factorization and discrete logarithms on a quantum computer. SIAM J. Comput. 26(5), 1484–1509 (1997)
Grover, L.K.: A fast quantum mechanical algorithm for, database search, http://quant-ph/9605043v3 (1996)
Gisin, N., Ribordy, G., Tittel, W., et al.: Quantum cryptography. Rev. Mod. Phys. 74, 145–195 (2002)
Bennett, C.H., Brassard, G.: Quantum cryptography: public key distribution and coin tossing. In: Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Computers, Systems, and Signal Processing, pp. 175–179. IEEE Press, New York (1984)
Ekert, A.K.: Quantum cryptography based on bell theorem. Phys. Rev. Lett. 67, 661–663 (1991)
Bennett, C.H.: Quantum cryptography using any two nonorthogonal states. Phys. Rev. Lett. 68, 3121–3124 (1992)
Bennett, C.H., Brassard, G., et al.: Teleporting an unknown quantum state via dual classical and Einstein-Podolsky-Rosen channels. Phys. Rev. Lett. 70, 1895–1899 (1993)
Gao, F., Guo, F.Z., Wen, Q.Y., et al.: Quantum key distribution without alternative measurements and rotations. Phys. Lett. A 349, 53–58 (2006)
Cleve, R., Gottesman, D., Lo, H.K.: How to share a quantum secret. Phys. Rev. Lett. 83, 648–651 (1999)
Hillery, M., Buzĕk, V., Berthiaume, A.: Quantum secret sharing. Phys. Rev. A 59, 1829–1834 (1999)
Karlsson, A., Koashi, M., Imoto, N.: Quantum entanglement for secret sharing and secret splitting. Phys. Rev. A 59, 162–168 (1999)
Jiang, M., Huang, X., Zhou, L.L., Zhou, Y.M., Zeng, J.: An efficient scheme for multi-party quantum state sharing via non-maximally entangled states. Chin. Sci. Bull. 57(10), 1089–1094 (2012)
Long, G.L., Liu, X.S.: Theoretically efficient high-capacity quantum-key-distribution scheme. Phys. Rev. A 65, 032302 (2002)
Deng, F.G., Long, G.L., Liu, X.S.: Two-step quantum direct communication protocol using the Einstein-Podolsky-Rosen pair block. Phys. Rev. A 68, 042317 (2003)
Lin, S., Wen, Q.Y., Zhu, F.C.: Quantum secure direct communication with X-type entangled states. Phys. Rev. A 78, 064304 (2008)
Li, J., Jin, H.F., Jing, B.: Improved eavesdropping detection strategy based on four-particle cluster state in quantum direct communication protocol. Chin. Sci. Bull. 57(34), 4434–4441 (2012)
Song, S.Y., Wang, C.: Recent development in quantum communication. Chin. Sci. Bull. 57(36), 4694–4700 (2012)
Gottesman, D., Chuang, I.: Quantum Digital Signatures, http://quant-ph/0105032v2 (2001)
Buhrman, H., Cleve, R., Watrous, J., et al.: Quantum fingerprinting. Phys. Rev. Lett. 87, 167902 (2001)
Buhrman, H., Crepeau, C., Gottesman, D., et al.: Authentication of Quantum Messages, pp. 449–458. IEEE Computer Society Press, Washington DC (2002)
Zeng, G.H., Keitel, C.H.: Arbitrated quantum-signature scheme. Phys. Rev. A 65, 042312 (2002)
Boykin, P.O., Roychowdhury, V.: Optimal encryption of quantum bits. Phys. Rev. A 67, 042317 (2003)
Li, Q., Chan, W.H., Long, D.Y.: Arbitrated quantum signature scheme using Bell states. Phys. Rev. A 79, 054307 (2009)
Zou, X.F., Qiu, D.W.: Security analysis and improvements of arbitrated quantum signature schemes. Phys. Rev. A 82, 042325 (2010)
Yang, Y.G., Wen, Q.Y.: Threshold proxy quantum signature scheme with threshold shared verification. Sci. Chin. Ser. G Phys. Mech. Astron 51, 1079–1088 (2008)
Wang, T.Y., Wei, Z.L.: One-time proxy signature based on quantum cryptography. Quantum Inf. Proc. 11, 455–463 (2012)
Shi, J.H., Zhang, S.L., Chang, Z.G.: The security analysis of a threshold proxy quantum signature scheme. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 56(3), 519–523 (2013)
Wen, X.J., Tian, Y., Ji, L.P., Niu, X.M.: A group signature scheme based on quantum teleportation. Phys. Scr. 81, 055001 (2010)
Wen, X.J.: Quantum group blind signature scheme without entanglement. Phys. Scr. 82, 065403 (2010)
Xu, R., Huang, L.S., Yang, W., He, L.B.: Quantum group blind signature scheme without entanglement. Opt. Commun. 284, 3654–3658 (2011)
Wang, T.Y., Wen, Q.Y.: Fair quantum blind signatures. Chin. Phys. B 19, 060307 (2010)
Wen, X.J., Niu, X.M., Ji, L.P., Tian, Y.: A weak blind signature scheme based on quantum cryptography. Opt. Commun. 282, 666–669 (2009)
Yang, Y.G.: Multi-proxy quantum group signature scheme with threshold shared verification. Chin. Phys. B 17, 415 (2008)
Yang, Y.G., Wang, Y., Teng, Y.W., Chai, H.P., Wen, Q.Y.: Scalable arbitrated quantum signature of classical messages with multi-signers. Commun. Theor. Phys. 54, 84 (2010)
Gao, F., Qin, S.J., Guo, F.Z., Wen, Q.Y.: Cryptanalysis of the arbitrated quantum signature protocols. Phys. Rev. A 84, 022344 (2011)
Choi, J.W., Chang, K.Y., Hong, D.: Security problem on arbitrated quantum signature schemes. Phys. Rev. A 84, 062330 (2011)
Cai, Q.Y.: The “Ping-Pong” protocol can be attacked without eavesdropping. Phys. Rev. Lett. 91, 109801 (2003)
Gao, F., Guo, F.Z., Wen, Q.Y., Zhu, F.C.: Consistency of shared reference frames should be reexamined. Phys. Rev. A 77, 014302 (2008)
Gisin, N., Fasel, S., Kraus, B., Zbinden, H., Ribordy, G.: Trojan-horse attacks on quantum-key-distribution systems. Phys. Rev. A 73, 022320 (2006)
Deng, F.G., Li, X.H., Zhou, H.Y., Zhang, Z.J.: Improving the security of multiparty quantum secret sharing against Trojan horse attack. Phys. Rev. A 72, 044302 (2005)
Hwang, T., Luo, Y.P., Chong, S.K.: Comment on “security analysis and improvements of arbitrated quantum signature schemes”. Phys. Rev. A 85, 056301 (2012)
Zhang, K.J., Zhang, W.W., Li, D.: Improving the security of arbitrated quantum signature against the forgery attack. Quantum Inf. Proc. doi:10.1007/s11128-013-0554-4
Liang, M., Yang, L.: Public-key encryption and authentication of quantum information. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 55(9), 1618–1629 (2012)
Salemian, S., Mohammadnejad, S.: An error-free protocol for quantum entanglement distribution in long-distance quantum communication. Chin. Sci. Bull. 56(7), 618–625 (2011)
Gao, F., Guo, F.Z., Wen, Q.Y., Zhu, F.C.: Comment on “experimental demonstration of a quantum protocol for Byzantine agreement and Liar detection”. Phys. Rev. Lett. 101, 208901 (2008)
Zhang, Y.S., Li, C.F., Guo, G.C.: Comment on “quantum key distribution without alternative measurements”. Phys. Rev. A 63, 036301 (2001)
Gao, F., Qin, S.J., Wen, Q.Y., Zhu, F.C.: A simple participant attack on the bradler-dusek protocol. Quantum Inf. Comput. 7, 329 (2007)
Gao, F., Wen, Q.Y., Zhu, F.C.: Teleportation attack on the QSDC protocol with a random basis and order. Chin. Phys. B 17, 3189 (2008)
Gao, F., Qin, S.J., Guo, F.Z., Wen, Q.Y.: Dense-coding attack on three-party quantum key distribution protocols. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 47, 630 (2011)
Qin, S.J., Gao, F., Wen, Q.Y., Zhu, F.C.: Improving the security of multiparty quantum secret sharing against an attack with a fake signal. Phys. Lett. A 357, 101 (2006)
W’ojcik, A.: Eavesdropping on the ping-pong quantum communication protocol. Phys. Rev. Lett. 90, 157901 (2003)
W’ojcik, A.: Comment on “quantum dense key distribution”. Phys. Rev. A 71, 016301 (2005)
Gao, F., Wen, Q.Y., Zhu, F.C.: Comment on “quantum exam”. Phys. Lett. A 360, 748 (2007)
Gao, F., Lin, S., Wen, Q.Y., Zhu, F.C.: A special eavesdropping on one-sender versus N-receiver QSDC protocol. Chin. Phys. Lett. 25, 1561 (2008)
Gao, F., Lin, S., Wen, Q.Y., Zhu, F.C.: Cryptanalysis of multiparty controlled quantum secure direct communication using Greenberger-Horne-Zeilinger state. Opt. Commun. 283, 192 (2010)
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by NSFC (Grant Nos. 61103210, 61272057, 61202434, 61170270, 61100203, 61003286, 61121061), NCET (Grant No. NCET-10-0260), Beijing Natural Science Foundation (Grant Nos. 4112040, 4122054), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Grant Nos. 2011YB01, 2012RC0612).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, KJ., Qin, SJ., Sun, Y. et al. Reexamination of arbitrated quantum signature: the impossible and the possible. Quantum Inf Process 12, 3127–3141 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-013-0589-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-013-0589-6