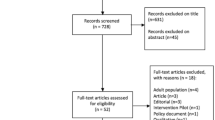
Abstract
The purpose of this study was to assess the combined effectiveness of a parenting intervention, Families Preparing the New Generation (FPNG), and a youth curriculum, keepin’ it REAL (kiR), on substance use prevention for middle school students in a large urban metro area of the southwest USA. The study aimed to generate usable knowledge on what works in adolescent substance use prevention and how it works best—a combined parent and youth programming or parent-only programming. A total of 532 adolescents in the 7th grade from 19 participating middle schools were randomly assigned into three intervention conditions: parent-youth (PY), parent-only (PO), and comparison (C). This article focuses on the comparison between PY and PO in order to determine which intervention strategy works best to reduce adolescent substance use including alcohol, inhalant, cigarette, and marijuana uses. A generalized estimating equation (GEE) model examined the longitudinal data. The results for alcohol use show that PO yielded better results than PY and that PY outperformed C after 20 months. Further, PO showed a decreasing trajectory in any substance use over time since the implementation of the intervention. The effect sizes based on Cohen’s h indicate small effects in any substance use and alcohol use for PO condition and smaller effects for the PY condition. These findings have implications for the design of future culturally specific parenting and youth prevention interventions with Latino families.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Austin, A. M., Macgowan, M. J., & Wagner, E. F. (2005). Effective family-based interventions for adolescents with substance use problems: A systematic review. Research on Social Work Practice, 15, 67–83.
Casey, B. J., & Jones, R. M. (2010). Neurobiology of the adolescent brain and behavior: Implications for substance use disorders. Journal of American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, 49, 1189–1201.
Center for Behavioral Health Statistics and Quality (2016). Key substance use and mental health indicators in the United States: Results from the 2015 National Survey on Drug Use and Health (HHS Publication No. SMA 16-4984, NSDUH Series H-51). Retrieved from https://www.samhsa.gov/data/report/key-substance-use-and-mental-health-indicators-united-states-results-2015-national-survey. Accessed 9 Nov 2018.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) (2018a). Fact sheets—Alcohol use and youth health. Retrieved from https://www.cdc.gov/alcohol/fact-sheets/alcohol-use.htm. Accessed 9 Nov 2018
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). (2018b). Fact sheets—Underage drinking. Washington, DC: Author Retrieved from https://www.cdc.gov/alcohol/fact-sheets/underage-drinking.htm. Accessed 9 Nov 2018.
Chen, P., & Jacobson, K. C. (2012). Developmental trajectories of substance use from early adolescence to young adulthood: Gender and racial/ethnic differences. Journal of Adolescent Health, 50, 154–163.
Cohen, J. (1988). Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences (2nd ed.). Hillsdale: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Inc..
Copello, A. G., Templeton, L., & Velleman, R. (2006). Family interventions for drug and alcohol misuse: Is there a best practice? Current Opinion in Psychiatry, 19, 271–276.
De Gaetano, Y. (2007). The role of culture in engaging Latino parents’ involvement in school. Urban Education, 42, 145–162.
Dishion, T. J., & Andrews, D. W. (1995). Preventing escalation in problem behaviors with high-risk young adolescents: immediate and 1-year outcomes. Journal of consulting and clinical psychology, 63(4), 538-548.
George, S. M. S., Parra-Cardona, J. R., Vidot, D. C., Molleda, L. M., Terán, A. Q., Onetto, D. C., Gibbons, J. B., & Prado, G. (2017). Cultural adaptation of preventive interventions in Hispanic youth. In S. J. Schwartz & J. Unger (Eds.), The Oxford handbook of acculturation and health (pp. 393–410). Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Germán, M., Gonzales, N. A., & Dumka, L. (2009). Familism values as a protective factor for Mexican-origin adolescents exposed to deviant peers. The Journal of Early Adolescence, 29, 16–42.
Hallfors, D. D., Waller, M. W., Ford, C. A., Halpern, C. T., Brodish, P. H., & Iritani, B. (2004). Adolescent depression and suicide risk: Association with sex and drug behavior. American Journal of Preventive Medicine, 27, 224–231.
Handwerk, M. L., Field, C. E., & Friman, P. C. (2000). The iatrogenic effects of group intervention for antisocial youth: Premature extrapolations? Journal of Behavioral Education, 10, 223–238.
Hecht, M. L., Marsiglia, F. F., Elek, E., Wagstaff, D. A., Kulis, S., & Dustman, P. A. (2003). Culturally-grounded substance use prevention: An evaluation of the keepin’ it REAL curriculum. Prevention Science, 4(4) 233–248.
Hernandez Robles, E., Maynard, B. R., Salas-Wright, C. P., & Todic, J. (2016). Culturally adapted substance use interventions for Latino adolescents: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Research on Social Work Practice, 1–13.
Johnston, L. D., O'Malley, P. M., Miech, R. A., Bachman, J. G., & Schulenberg, J. E. (2017). Demographic subgroup trends among adolescents in the use of various licit and illicit drugs, 1975–2016. Ann Arbor: Institute for Social Research, The University of Michigan.
Johnston, L. D., Miech, R. A., O'Malley, P. M., Bachman, J. G., Schulenberg, J. E., & Patrick, M. E. (2018). Monitoring the future, National Survey Results on drug use, 1975–2017: Overview, key findings on adolescent drug use. Ann Arbor: Institute for Social Research, The University of Michigan.
Kann, L., McManus, T., Harris, W. A., Shanklin, S. L., Flint, K. H., Queen, B., Lowry, R., Chyen, D., Whittle, L., Thornton, J., Lim, C., Bradford, D., Yamakawa, Y., Leon, M., Brener, N., & Ethier, K. A. (2018). Youth risk behavior surveillance—United States, 2017. MMWR Surveillance Summaries, 67, 1–114.
Kulis, S., Marsiglia, F. F., Elek, E., Dustman, P., Wagstaff, D. A., & Hecht, M. L. (2005). Mexican/Mexican American adolescents and keepin'it REAL: An evidence-based substance use prevention program. Children & Schools, 27(3), 133-145.
Kuperminc, G., Darnell, A., & Alvarez-Jimenez, A. (2008). Parent involvement in the academic adjustment of Latino middle and high school youth: Teacher expectations and school belonging as mediators. Journal of Adolescence, 31, 469–483.
Marshall, E. J. (2015). Adolescent alcohol use: Risks and consequences. Alcohol and Alcoholism, 49, 160–164.
Marsiglia, F. F., & Hecht, M. L. (2005). Keepin’it REAL: An evidence-based program. Santa Cruz: ETR Associates.
Marsiglia, F. F., Williams, L. R., Ayers, S. L., & Booth, J. M. (2014). Familias: Preparando la Nueva Generación: A randomized control trial testing the effects on positive parenting practices. Research on Social Work Practice, 24, 310–320.
Marsiglia, F. F., Ayers, S. L., Baldwin-White, A., & Booth, J. (2016). Changing Latino adolescents’ substance use norms and behaviors: The effects of synchronized youth and parent drug use prevention interventions. Prevention Science, 17, 1–12.
Marsiglia, F. F., Ayers, S. L., & Kiehne, E. (in press). Reducing inhalant use in Latino adolescents through synchronized parent-adolescent interventions. Journal of Prevention and Intervention in the Community.
Martinez, M. J., Huang, S., Estrada, Y., Sutton, M. Y., & Prado, G. (2017). The relationship between acculturation, ecodevelopment, and substance use among Hispanic adolescents. The Journal of Early Adolescence, 37, 948–974.
Odgers, C. L., Caspi, A., Nagin, D. S., Piquero, A. R., Slutske, W. S., Milne, B. J., Dickson, N., Poulton, R., & Moffitt, T. E. (2008). Is it important to prevent early exposure to drugs and alcohol among adolescents? Psychological Science, 19, 1037–1044.
Pantin, H., Schwartz, S. J., Sullivan, S., Coatsworth, J. D., & Szapocznik, J. (2003). Preventing substance abuse in Hispanic immigrant adolescents: An ecodevelopmental, parent-centered approach. Hispanic Journal of Behavioral Sciences, 25, 469–500.
Parsai, M. B., Castro, F. G., Marsiglia, F. F., Harthun, M. L., & Valdez, H. (2011). Using community based participatory research to create a culturally grounded intervention for parents and youth to prevent risky behaviors. Prevention Science, 12, 34–47.
Pena, D. C. (2000). Parent involvement: Influencing factors and implications. Journal of Educational Research, 94, 42–54.
Roosa, M. W., Morgan-Lopez, A. A., Cree, W. K., & Specter, M. M. (2002). Ethnic culture, poverty, and context: Sources of influence on Latino families and children. In Latino children and families in the United States: Current research and future directions, pp 27–44.
Schinke, S., Brounstein, P., & Gardner, S. (2002). Science-based prevention programs and principles, 2002, DHHS Pub No. (SMA) 03–3764. Rockville: Center for Substance Abuse Prevention, Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration.
Slesnick, N., & Prestopnik, J. L. (2005). Ecologically based family therapy outcome with substance abusing runaway adolescents. Journal of Adolescence, 28, 277–298.
Smit, E., Verdurmen, J., Monshouwer, K., & Smit, F. (2008). Family interventions and their effect on adolescent alcohol use in general populations; a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Drug and Alcohol Dependence, 97, 195–206.
Tinkler, B. (2002). A review of literature on Hispanic/Latino parent involvement in K-12 Education. Retrieved from https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/ED469134.pdf. ED469134. Accessed 9 Nov 2018.
Van Ryzin, M. J., Roseth, C. J., Fosco, G. M., Lee, Y. K., & Chen, I. C. (2016). A component-centered meta-analysis of family-based prevention programs for adolescent substance use. Clinical Psychology Review, 45, 72–80.
Williams, L. R., Ayers, S. L., Garvey, M. M., Marsiglia, F. F., & González Castro, F. (2012). Efficacy of a culturally based parenting intervention: Strengthening open communication between Mexican-heritage parents and adolescent children. Journal of the society for Social Work and Research, 3(4), 296-307.
Williams, L. R., Marsiglia, F. F., Baldwin, A., & Ayers, S. (2015). Unintended effects of an intervention supporting Mexican-heritage youth: Decreased parent heavy drinking. Research on Social Work Practice, 25, 181–189.
Williams, L. R., Ayers, S., Baldwin, A., & Marsiglia, F. F. (2016). Delaying youth substance-use initiation: A cluster randomized controlled trial of complementary youth and parenting interventions. Journal of the Society for Social Work and Research, 7, 177–200.
Zarate, M. E. (2007). Understanding Latino parental involvement in education: Perceptions, expectations, and recommendations. Tomas Rivera policy institute. Retrieved from https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/ED502065.pdf. Accessed 9 Nov 2018.
Funding
This research was supported by funding from the National Institutes of Health/National Institute on Minority Health and Health Disparities (NIMHD/NIH), award P20 MD002316 (F. Marsiglia, P.I.). The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the NIMHD or the NIH.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
All study procedures involving human participants were approved by the Arizona State University’s Institutional Review Board and in accordance with standards for ethical research practice, including the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments.
Informed Consent
Participants were informed of their rights and parental informed consent coupled with youth assent was obtained prior to any data collection.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marsiglia, F.F., Ayers, S.L., Han, S. et al. The Role of Culture of Origin on the Effectiveness of a Parents-Involved Intervention to Prevent Substance Use Among Latino Middle School Youth: Results of a Cluster Randomized Controlled Trial. Prev Sci 20, 643–654 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11121-018-0968-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11121-018-0968-4