Abstract
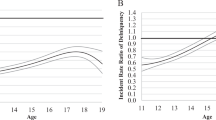
Preventive intervention effects on adolescent alcohol misuse may differ based on genotypes in gene-by-intervention (G x I) interactions, and these G x I interactions may vary as a function of age. The current study uses a novel statistical method, time-varying effect modeling (TVEM), to test an age-varying interaction between a single nucleotide polymorphism in the GABRA2 gene (rs279845) and a preventive intervention in predicting alcohol misuse in a longitudinal study of adolescents (ages 11–20). The preventive intervention was PROSPER, a community-based system for delivery of family and school programs selected from a menu of evidence-based interventions. TVEM results revealed a significant age-varying GABRA2 x intervention interaction from ages 12 to 18, with the peak effect size seen around age 13 (IRR = 0.50). The intervention significantly reduced alcohol misuse for adolescents with the GABRA2 TT genotype from ages 12.5 to 17 but did not reduce alcohol use for adolescents with the GABRA2 A allele at any age. Differences in intervention effects by GABRA2 genotype were most pronounced from ages 13 to 16—a period when drinking is associated with increased risk for alcohol use disorder. Our findings provide additional evidence that intervention effects on adolescent alcohol misuse may differ by genotype, and provide novel evidence that the interaction between GABRA2 and intervention effects on alcohol use may vary with age. Implications for interventions targeting adolescent alcohol misuse are discussed.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albert, D., Belsky, D. W., Crowley, D. M., Bates, J. E., Pettit, G. S., Lansford, J. E., . . . Dodge, K. A. (2015). Developmental mediation of genetic variation in response to the Fast Track prevention program. Development and Psychopathology, 27, 81–95.
Belsky, J., & Pluess, M. (2009). Beyond diathesis stress: Differential susceptibility to environmental influences. Psychological Bulletin, 135, 885–908.
Brody, G. H., Beach, S. R., Philibert, R. A., Chen, Y. f., & Murry, V. M. (2009). Prevention effects moderate the association of 5-HTTLPR and youth risk behavior initiation: Gene × environment hypotheses tested via a randomized prevention design. Child Development, 80, 645–661.
Brody, G. H., Chen, Y. f., & Beach, S. R. (2013). Differential susceptibility to prevention: GABAergic, dopaminergic, and multilocus effects. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 54, 863–871.
Brody, G. H., Chen, Y.-f., Beach, S. R., Kogan, S. M., Yu, T., DiClemente, R. J., . . . Philibert, R. A. (2014). Differential sensitivity to prevention programming: A dopaminergic polymorphism-enhanced prevention effect on protective parenting and adolescent substance use. Health Psychology, 33, 182–191.
Cardon, L. R., & Palmer, L. J. (2003). Population stratification and spurious allelic association. Lancet, 361, 598–604.
Chassin, L., Sher, K. J., Hussong, A., & Curran, P. (2013). The developmental psychopathology of alcohol use and alcohol disorders: Research achievements and future directions. Development and Psychopathology, 25, 1567–1584.
Cleveland, H. H., Schlomer, G. L., Vandenbergh, D. J., Feinberg, M., Greenberg, M., Spoth, R., . . . Hair, K. L. (2015). The conditioning of intervention effects on early adolescent alcohol use by maternal involvement and dopamine receptor D4 (DRD4) and serotonin transporter linked polymorphic region (5-HTTLPR) genetic variants. Development and Psychopathology, 27, 51–67.
Cleveland, H. H., Schlomer, G. L., Vandenbergh, D. J., & Wiebe, R. P. (2017). Gene × intervention designs: Promising step toward understanding etiology and building better preventive interventions. Criminology & Public Policy. doi:10.1111/1745-9133.12221
Cleveland, H. H., Griffin, A., Wolf, P. S. A., Weibe, R. P., Schlomer, G. L., Feinberg, M. E. Greenberg, M., Spoth, R. L., & Redmond, C., Vandenbergh, D. J. (2017). Transactions between substance use intervention, the oxytocin receptor (OXTR) gene, and peer substance use predicting youth alcohol use. Prevention Science. doi:10.1007/s11121-017-0749-5
Costello, E. J., Eaves, L., Sullivan, P., Kennedy, M., Conway, K., Adkins, D. E., . . . van den Oord, E. (2013). Genes, environments, and developmental research: Methods for a multi-site study of early substance abuse. Twin Research and Human Genetics, 16, 505–515.
Covault, J., Gelernter, J., Hesselbrock, V., Nellissery, M., & Kranzler, H. R. (2004). Allelic and haplotypic association of GABRA2 with alcohol dependence. American Journal of Medical Genetics Part B: Neuropsychiatric Genetics, 129, 104–109.
Dawe, S., & Loxton, N. J. (2004). The role of impulsivity in the development of substance use and eating disorders. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 28, 343–351.
Dick, D. M., Bierut, L., Hinrichs, A., Fox, L., Bucholz, K. K., Kramer, J., . . . Almasy, L. (2006). The role of GABRA2 in risk for conduct disorder and alcohol and drug dependence across developmental stages. Behavior Genetics, 36, 577–590.
Dick, D. M., Latendresse, S. J., Lansford, J. E., Budde, J. P., Goate, A., Dodge, K. A., . . . Bates, J. E. (2009). Role of GABRA2 in trajectories of externalizing behavior across development and evidence of moderation by parental monitoring. Archives of General Psychiatry, 66, 649–657.
Dick, D. M., Latendresse, S. J., Lansford, J. E., Budde, J. P., Goate, A., Dodge, K. A., . . . Bates, J. E. (2011). Errors in table and results in: Role of GABRA2 in trajectories of externalizing behavior across development and evidence of moderation by parental monitoring. Archives of General Psychiatry, 68, 980–980.
Dick, D. M., Aliev, F., Latendresse, S., Porjesz, B., Schuckit, M., Rangaswamy, M., . . . Agrawal, A. (2013). How phenotype and developmental stage affect the genes we find: GABRA2 and impulsivity. Twin Research and Human Genetics, 16, 661–669.
Dick, D. M., Cho, S. B., Latendresse, S. J., Aliev, F., Nurnberger, J. I., Edenberg, H. J., . . . Bucholz, K. (2014). Genetic influences on alcohol use across stages of development: GABRA2 and longitudinal trajectories of drunkenness from adolescence to young adulthood. Addiction Biology, 19, 1055–1064.
Edenberg, H. J., Dick, D. M., Xuei, X., Tian, H., Almasy, L., Bauer, L. O., . . . Jones, K. (2004). Variations in GABRA2, encoding the α2 subunit of the GABA-A receptor, are associated with alcohol dependence and with brain oscillations. The American Journal of Human Genetics, 74, 705–714.
Ellis, B. J., Boyce, W. T., Belsky, J., Bakermans-Kranenburg, M. J., & van Ijzendoorn, M. H. (2011). Differential susceptibility to the environment: An evolutionary-neurodevelopmental theory. Development and Psychopathology, 23, 7–28.
Enoch, M.-A. (2008). The role of GABA A receptors in the development of alcoholism. Pharmacology Biochemistry and Behavior, 90, 95–104.
Fehr, C., Sander, T., Tadic, A., Lenzen, K. P., Anghelescu, I., Klawe, C., . . . Szegedi, A. (2006). Confirmation of association of the GABRA2 gene with alcohol dependence by subtype-specific analysis. Psychiatric Genetics, 16, 9–17.
Fillman, S. G., Duncan, C. E., Webster, M. J., Elashoff, M., & Weickert, C. S. (2010). Developmental co-regulation of the β and γ GABA A receptor subunits with distinct α subunits in the human dorsolateral prefrontal cortex. International Journal of Developmental Neuroscience, 28, 513–519.
Grant, B. F., & Dawson, D. A. (1997). Age at onset of alcohol use and its association with DSM-IV alcohol abuse and dependence: Results from the National Longitudinal Alcohol Epidemiologic Survey. Journal of Substance Abuse, 9, 103–110.
Johnston, L. D., O’Malley, P. M., Miech, R. A., Bachman, J. G., & Schulenberg, J. E. (2014). Monitoring the Future national results on drug use: 1975–2013: Overview, key findings on adolescent drug use. Ann Arbor: Institute for Social Research, The University of Michigan.
Kendler, K. S. (2011). A conceptual overview of gene-environment interaction and correlation in a developmental context. In K. S. Kendler, S. R. Jaffee, & D. Romer (Eds.), The dynamic genome and mental health: The role of genes and environments in youth development (pp. 5–28). New York: Oxford University Press.
Kilb, W. (2012). Development of the GABAergic system from birth to adolescence. The Neuroscientist, 18, 613–630.
Kumar, S., Porcu, P., Werner, D. F., Matthews, D. B., Diaz-Granados, J. L., Helfand, R. S., & Morrow, A. L. (2009). The role of GABA-A receptors in the acute and chronic effects of ethanol: A decade of progress. Psychopharmacology, 205, 529–564.
Lenroot, R. K., & Giedd, J. N. (2011). Annual research review: Developmental considerations of gene by environment interactions. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 52, 429–441.
Li, Y. I., van de Geijn, B., Raj, A., Knowles, D. A., Petti, A. A., Golan, D., . . . Pritchard, J. K. (2016). RNA splicing is a primary link between genetic variation and disease. Science, 352, 600–604.
Lind, P. A., Macgregor, S., Agrawal, A., Montgomery, G. W., Heath, A. C., Martin, N. G., & Whitfield, J. B. (2008). The role of GABRA2 in alcohol dependence, smoking, and illicit drug use in an Australian population sample. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research, 32, 1721–1731.
McLean, P. J., Farb, D. H., & Russek, S. J. (1995). Mapping of the α 4 subunit gene (GABRA4) to human chromosome 4 defines an α 2—α 4—β 1—γ 1 gene cluster: Further evidence that modern GABA-A receptor gene clusters are derived from an ancestral cluster. Genomics, 26, 580–586.
Moffitt, T. E., Caspi, A., & Rutter, M. (2006). Measured gene-environment interactions in psychopathology: Concepts, research strategies, and implications for research, intervention, and public understanding of genetics. Perspectives on Psychological Science, 1, 5–27.
NIAAA. (2003). Underage drinking: A major public health challenge. Retrieved from http://pubs.niaaa.nih.gov/publications/aa59.htm.
Onori, N., Turchi, C., Solito, G., Gesuita, R., Buscemi, L., & Tagliabracci, A. (2010). GABRA2 and alcohol use disorders: No evidence of an association in an Italian case–control study. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research, 34, 659–668.
Sakai, J. T., Stallings, M. C., Crowley, T. J., Gelhorn, H. L., McQueen, M. B., & Ehringer, M. A. (2010). Test of association between GABRA2 (SNP rs279871) and adolescent conduct/alcohol use disorders utilizing a sample of clinic referred youth with serious substance and conduct problems, controls and available first degree relatives. Drug and Alcohol Dependence, 106, 199–203.
Schulenberg, J.E., & Maggs, J.L. (2002). A developmental perspective on alcohol use and heavy drinking during adolescence and the transition to young adulthood. Journal of Studies on Alcohol, Supplement, 54–70.
Schwarzer, C., Berresheim, U., Pirker, S., Wieselthaler, A., Fuchs, K., Sieghart, W., & Sperk, G. (2001). Distribution of the major γ‐aminobutyric acid A receptor subunits in the basal ganglia and associated limbic brain areas of the adult rat. Journal of Comparative Neurology, 433, 526–549.
Smith, G. T., McCarthy, D. M., & Goldman, M. S. (1995). Self-reported drinking and alcohol-related problems among early adolescents: Dimensionality and validity over 24 months. Journal of Studies on Alcohol, 56, 383–394.
Soyka, M., Preuss, U., Hesselbrock, V., Zill, P., Koller, G., & Bondy, B. (2008). GABA-a2 receptor subunit gene (GABRA2) polymorphisms and risk for alcohol dependence. Journal of Psychiatric Research, 42, 184–191.
Spoth, R. (2007). Opportunities to meet challenges in rural prevention research: Findings from an evolving community‐university partnership model. The Journal of Rural Health, 23, 42–54.
Spoth, R., Greenberg, M., Bierman, K., & Redmond, C. (2004a). PROSPER community–university partnership model for public education systems: Capacity-building for evidence-based, competence-building prevention. Prevention Science, 5, 31–39.
Spoth, R., Redmond, C., Shin, C., & Azevedo, K. (2004b). Brief family intervention effects on adolescent substance initiation: School-level growth curve analyses 6 years following baseline. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 72, 535–542.
Spoth, R., Redmond, C., Shin, C., Greenberg, M., Clair, S., & Feinberg, M. (2007). Substance-use outcomes at 18 months past baseline: The PROSPER community–university partnership trial. American Journal of Preventive Medicine, 32, 395–402.
Spoth, R., Greenberg, M., & Turrisi, R. (2008). Preventive interventions addressing underage drinking: State of the evidence and steps toward public health impact. Pediatrics, 121, S311–S336.
Spoth, R., Redmond, C., Clair, S., Shin, C., Greenberg, M., & Feinberg, M. (2011). Preventing substance misuse through community–university partnerships: Randomized controlled trial outcomes 4½ years past baseline. American Journal of Preventive Medicine, 40, 440–447.
Spoth, R., Redmond, C., Shin, C., Greenberg, M., Feinberg, M., & Schainker, L. (2013). PROSPER community–university partnership delivery system effects on substance misuse through 6 1/2 years past baseline from a cluster randomized controlled intervention trial. Preventive Medicine, 56, 190–196.
Tan, X., Shiyko, M. P., Li, R., Li, Y., & Dierker, L. (2012). A time-varying effect model for intensive longitudinal data. Psychological Methods, 17, 61–77.
Trucco, E. M., Villafuerte, S., Heitzeg, M. M., Burmeister, M., & Zucker, R. A. (2014). Rule breaking mediates the developmental association between GABRA2 and adolescent substance abuse. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 55, 1372–1379.
Trucco, E. M., Villafuerte, S., Heitzeg, M. M., Burmeister, M., & Zucker, R. A. (2016). Susceptibility effects of GABA receptor subunit alpha-2 (GABRA2) variants and parental monitoring on externalizing behavior trajectories: Risk and protection conveyed by the minor allele. Development and Psychopathology, 28, 15–26.
Uhart, M., Weerts, E. M., McCaul, M. E., Guo, X., Yan, X., Kranzler, H. R., . . . Wand, G. S. (2013). GABRA2 markers moderate the subjective effects of alcohol. Addiction Biology, 18, 357–369.
van Ijzendoorn, M. H., & Bakermans-Kranenburg, M. J. (2015). Genetic differential susceptibility on trial: Meta-analytic support from randomized controlled experiments. Development and Psychopathology, 27, 151–162.
Williams, R. L. (2000). A note on robust variance estimation for cluster-correlated data. Biometrics, 56, 645–646.
Windle, M., Spear, L. P., Fuligni, A. J., Angold, A., Brown, J. D., Pine, D., . . . Dahl, R. E. (2008). Transitions into underage and problem drinking: Developmental processes and mechanisms between 10 and 15 years of age. Pediatrics, 121, S273–S289.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Kerry Hair, Dr. Deborah Grove, and Ashley Price of the Penn State Genomics Core Facility; Amanda Griffin of Penn State; Shirley Huck, Cathy Owen, Debra Bahr, and Anthony Connor of the Behavioral Research Services at Iowa State University Survey; and Rob Schofield and Dean Stankowski of the Penn State University Survey Research. PROSPER and gPROSPER projects were supported by grant numbers DA013709 and DA030389 from the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA), respectively. The preparation of this article was supported by NIDA awards P50 DA010075 and P50 DA039838. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institute on Drug Abuse or the National Institutes of Health.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Funding
Michael A. Russell is supported by grant numbers P50-DA010075 and P50-DA039838 from the National Institute on Drug Abuse.
This PROSPER and gPROSPER projects were supported by National Institute on Drug Abuse Grants DA013709 and DA030389, respectively.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Russell, M.A., Schlomer, G.L., Cleveland, H.H. et al. PROSPER Intervention Effects on Adolescents’ Alcohol Misuse Vary by GABRA2 Genotype and Age. Prev Sci 19, 27–37 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11121-017-0751-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11121-017-0751-y