Abstract
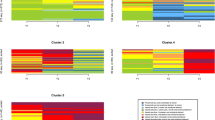
The purpose of this study was to examine the extent to which distinct patterns of fidelity of implementation emerged for 5331 schools over a 5-year course of implementing school-wide positive behavioral interventions and supports (SWPBIS). We used latent class analysis to classify schools based on their likelihood of implementing SWPBIS with fidelity each year, then assessed school and district predictors of classifications. A four-class solution fit the model well, with two patterns of sustained implementation (Sustainers and Slow Starters) and two patterns of practice abandonment (Late Abandoners and Rapid Abandoners). Significant predictors of group membership included grade levels served, enrollment, proportion of schools implementing SWPBIS in the district (“critical mass”), and size of the implementation cohort (“community of practice”). Elementary schools, larger schools, schools in districts with more schools already implementing SWPBIS, and those starting within a larger initial district cohort were more likely to be in the sustaining classes. Results are discussed in terms of understanding patterns of implementation in schools to enhance sustained implementation of school practices.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adelman, H. S., & Taylor, L. (1997). Toward a scale-up model for replicating new approaches to schooling. Journal of Educational and Psychological Consultation, 8, 197–230.
Adelman, H. S., & Taylor, L. (2003). On sustainability of project innovations as systemic change. Journal of Educational and Psychological Consultation, 14, 1–25.
Andreou, T. E., McIntosh, K., Ross, S. W., & Kahn, J. D. (2015). Critical incidents in the sustainability of school-wide positive behavioral interventions and supports. Journal of Special Education, 49, 157–167.
Asparouhov, T., & Muthén, B. (2014). Auxiliary variables in mixture modeling: Three-step approaches using Mplus. Structural Equation Modeling, 21, 329–341.
Baker, S., Gersten, R., Dimino, J. A., & Griffiths, R. (2004). The sustained use of research-based instructional practice: A case study of peer-assisted learning strategies in mathematics. Remedial and Special Education, 25, 5–24.
Becker, K. D., & Domitrovich, C. E. (2011). The conceptualization, integration, and support of evidence-based interventions in the schools. School Psychology Review, 40, 582–589.
Bertram, R. M., Blase, K. A., & Fixsen, D. L. (2015). Improving programs and outcomes: Implementation frameworks and organization change. Research on Social Work Practice, 25, 477–487.
Bohanon, H., Fenning, P., Carney, K. L., Minnis-Kim, M. J., Anderson-Harriss, S., Moroz, K. B., & Sailor, W. (2006). Schoolwide application of positive behavior support in an urban high school: A case study. Journal of Positive Behavior Interventions, 8, 131–145.
Bradshaw, C. P., & Pas, E. T. (2011). A state-wide scale-up of Positive Behavioral Interventions and Supports (PBIS): A description of the development of systems of support and analysis of adoption and implementation. School Psychology Review, 40, 530–548.
Bradshaw, C. P., Debnam, K., Koth, C. W., & Leaf, P. J. (2009a). Preliminary validation of the implementation phases inventory for assessing fidelity of schoolwide positive behavior supports. Journal of Positive Behavior Interventions, 11, 145–160.
Bradshaw, C. P., Koth, C. W., Thornton, L. A., & Leaf, P. J. (2009b). Altering school climate through school-wide positive behavioral interventions and supports: Findings from a group-randomized effectiveness trial. Prevention Science, 10, 100–115.
Bradshaw, C. P., Waasdorp, T. E., & Leaf, P. J. (2012). Effects of school-wide positive behavioral interventions and supports on child behavior problems and adjustment. Pediatrics, 130, e1136–e1145.
Buzhardt, J., Greenwood, C. R., Abbott, M., & Tapia, Y. (2006). Research on scaling up evidence-based instructional practice: Developing a sensitive measure of the rate of implementation. Educational Technology Research & Development, 54, 467–492.
Chiapa, A., Smith, J. D., Kim, H., Dishion, T. J., Shaw, D. S., & Wilson, M. N. (2015). The trajectory of fidelity in a multiyear trial of the family check-up predicts change in child problem behavior. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 83, 1006–1011.
Coburn, C. E. (2003). Rethinking scale: Moving beyond numbers to deep and lasting change. Educational Researcher, 32, 3–12.
Cohen, R., Kincaid, D., & Childs, K. E. (2007). Measuring school-wide positive behavior support implementation: Development and validation of the benchmarks of quality. Journal of Positive Behavior Interventions, 9, 203–213.
Cook, B. G., & Odom, S. L. (2013). Evidence-based practices and implementation science in special education. Exceptional Children, 79, 135–144.
Domitrovich, C. E., Bradshaw, C. P., Poduska, J. M., Hoagwood, K., Buckley, J. A., Olin, S., & Ialongo, N. S. (2008). Maximizing the implementation quality of evidence-based preventive interventions in schools: A conceptual framework. Advances in School Mental Health Promotion, 1, 6–28.
Elliott, D. S., & Mihalic, S. F. (2004). Issues in disseminating and replicating effective prevention programs. Prevention Science, 5, 47–53.
Fixsen, D. L., Naoom, S. F., Blase, K. A., Friedman, R. M., & Wallace, F. (2005). Implementation research: Synthesis of the literature. Tampa: University of South Florida, Louis de la Parte Florida Mental Health Institute, The National Implementation Research Network (FMHI Publication #231).
Flannery, K. B., Fenning, P., Kato, M. M., & McIntosh, K. (2014). Effects of school-wide positive behavioral interventions and supports and fidelity of implementation on problem behavior in high schools. School Psychology Quarterly, 29, 111–124.
Gottfredson, G. D., Jones, E. M., & Gore, T. W. (2002). Implementation and evaluation of a cognitive–behavioral intervention to prevent problem behavior in a disorganized school. Prevention Science, 3, 43–56.
Greenberg, M. T., Feinberg, M. E., Johnson, L. E., Perkins, D. F., Welsh, J. A., & Spoth, R. L. (2015). Factors that predict financial sustainability of community coalitions: Five years of findings from the PROSPER partnership project. Prevention Science, 16, 158–167.
Hagan-Burke, S., Burke, M. D., Martin, E., Boon, R. T., Fore, C., III, & Kirkendoll, D. (2005). The internal consistency of the school-wide subscales of the effective behavioral support survey. Education and Treatment of Children, 28, 400–413.
Hall, L. J. (2015). Sustaining evidence-based practices by graduated special educators of students with ASD creating a community of practice. Teacher Education and Special Education, 38, 28–43.
Han, S. S., & Weiss, B. (2005). Sustainability of teacher implementation of school-based mental health programs. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 33, 665–679.
Horner, R. H. (2016). Schools implementing PBIS. Technical working paper, OSEP Center on PBIS.
Horner, R. H., & Sugai, G. (2015). School-wide PBIS: An example of applied behavior analysis implemented at a scale of social importance. Behavior Analysis in Practice, 8, 80–85.
Horner, R. H., Todd, A. W., Lewis-Palmer, T., Irvin, L. K., Sugai, G., & Boland, J. B. (2004). The School-Wide Evaluation Tool (SET): A research instrument for assessing school-wide positive behavior support. Journal of Positive Behavior Interventions, 6, 3–12.
Horner, R. H., Sugai, G., Smolkowski, K., Eber, L., Nakasato, J., Todd, A. W., & Esparanza, J. (2009). A randomized, wait-list controlled effectiveness trial assessing school-wide positive behavior support in elementary schools. Journal of Positive Behavior Interventions, 11, 133–144.
Hunter, S. B., Han, B., Slaughter, M. E., Godley, S. H., & Garner, B. R. (2015). Associations between implementation characteristics and evidence-based practice sustainment: A study of the adolescent community reinforcement approach. Implementation Science, 10, 173. doi:10.1186/s13012-015-0364-4.
Kincaid, D., Childs, K. E., & George, H. (2005). School-wide benchmarks of quality. Unpublished instrument. University of South Florida.
Lanza, S. T., Tan, X., & Bray, B. C. (2013). Latent class analysis with distal outcomes: A flexible model-based approach. Structural Equation Modeling, 20, 1–26.
Latham, G. (1988). The birth and death cycles of educational innovations. Principal, 68, 41–43.
McIntosh, K., & Goodman, S. (2016). Integrated multi-tiered systems of support: Blending RTI and PBIS. New York: Guilford.
McIntosh, K., Mercer, S. H., Hume, A. E., Frank, J. L., Turri, M. G., & Mathews, S. (2013). Factors related to sustained implementation of schoolwide positive behavior support. Exceptional Children, 79, 293–311.
McIntosh, K., Predy, L. K., Upreti, G., Hume, A. E., Turri, M. G., & Mathews, S. (2014). Perceptions of contextual features related to implementation and sustainability of school-wide positive behavior support. Journal of Positive Behavior Interventions, 16, 29–41.
McIntosh, K., Kim, J., Mercer, S. H., Strickland-Cohen, M. K., & Horner, R. H. (2015). Variables associated with enhanced sustainability of school-wide positive behavioral interventions and supports. Assessment for Effective Intervention, 40, 184–191.
McIntosh, K., Kelm, J. L., & Canizal Delabra, A. (2016a). In search of how principals change: A qualitative study of events that help and hinder administrator support for school-wide PBIS. Journal of Positive Behavior Interventions, 18, 100–110.
McIntosh, K., Mercer, S. H., Nese, R. N. T., Strickland-Cohen, M. K., & Hoselton, R. (2016b). Predictors of sustained implementation of school-wide positive behavioral interventions and supports. Journal of Positive Behavior Interventions (in press).
McLaughlin, M. W., & Mitra, D. (2001). Theory-based change and change-based theory: Going deeper, going broader. Journal of Educational Change, 2, 301–323.
Mercer, S. H., McIntosh, K., & Hoselton, R. (2016). Comparability of fidelity measures for assessing tier 1 school-wide positive behavioral interventions and supports. Submitted for publication.
Molloy, L. E., Moore, J. E., Trail, J., Van Epps, J. J., & Hopfer, S. (2013). Understanding real-world implementation quality and “active ingredients” of PBIS. Prevention Science, 14, 593–605.
Nese, R. N. T., McIntosh, K., Nese, J. F. T., Bloom, J., Johnson, N. W., Phillips, D., Hoselton, R. (2016). Predicting abandonment of school-wide behavior interventions. Behavioral Disorders (in press).
Payne, A. A., & Eckert, R. (2010). The relative importance of provider, program, school, and community predictors of the implementation quality of school-based prevention programs. Prevention Science, 11, 126–141.
Rimm-Kaufman, S. E., Fan, X., Chiu, Y.-J., & You, W. (2007). The contribution of the responsive classroom approach on children’s academic achievement: Results from a three year longitudinal study. Journal of School Psychology, 45, 401–421.
Rogers, E. (2003). Diffusion of innovations (5th ed.). New York: The Free Press.
Safran, S. P. (2006). Using the effective behavior supports survey to guide development of schoolwide positive behavior support. Journal of Positive Behavior Interventions, 8, 3–9.
Saldana, L., Chamberlain, P., Wang, W., & Brown, C. H. (2012). Predicting program start-up using the stages of implementation measure. Administration and Policy in Mental Health and Mental Health Services Research, 39, 419–425.
Samuelsen, K. M., & Dayton, C. M. (2010). Latent class analysis. In G. R. Hancock & R. O. Mueller (Eds.), The reviewer’s guide to quantitative methods in the social sciences (pp. 173–184). New York: Routledge.
Sanford DeRousie, R. M., & Bierman, K. L. (2012). Examining the sustainability of an evidence-based preschool curriculum: The REDI program. Early Childhood Research Quarterly, 27, 55–65.
Schaper, A., McIntosh, K., & Hoselton, R. (2016). Within-year fidelity growth of SWPBIS during installation and initial implementation. School Psychology Quarterly (in press).
Schwartzbeck, T. D. (2002). Patterns in implementing comprehensive school reform: What the researchers say. Washington, DC: National Clearinghouse for Comprehensive School Reform (ERIC Document Reproduction Service no. ED470023).
Slavin, R. E. (2004). Built to last: Long-term maintenance of success for all. Remedial and Special Education, 25, 61–66.
Sugai, G., & Horner, R. H. (2009). Defining and describing schoolwide positive behavior support. In W. Sailor, G. Dunlap, G. Sugai, & R. H. Horner (Eds.), Handbook of positive behavior support (pp. 307–326). New York: Springer.
Sugai, G., Horner, R. H., & Todd, A. W. (2000). PBIS self-assessment survey. Eugene: Educational and Community Supports. http://www.pbis.org.
Sugai, G., Horner, R. H., & Lewis-Palmer, T. L. (2001). Team implementation checklist (TIC). Eugene: Educational and Community Supports. http://www.pbis.org.
Vernez, G., Karam, R., Mariano, L. T., & DeMartini, C. (2006). Evaluating comprehensive school reform models at scale: Focus on implementation. Santa Monica: RAND Corporation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
The research reported here was supported by the Institute of Education Sciences, U.S. Department of Education, through grant R324A120278 to the University of Oregon. The opinions expressed are those of the authors and do not represent views of the Institute or the U.S. Department of Education.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Research Involving Human Participants
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. For this type of study, formal consent is not required.
Additional information
The research reported here was supported by the Institute of Education Sciences, U.S. Department of Education, through grant R324A120278 to the University of Oregon. The opinions expressed are those of the authors and do not represent views of the Institute or the U.S. Department of Education.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McIntosh, K., Mercer, S.H., Nese, R.N.T. et al. Identifying and Predicting Distinct Patterns of Implementation in a School-Wide Behavior Support Framework. Prev Sci 17, 992–1001 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11121-016-0700-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11121-016-0700-1