Abstract
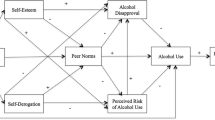
Mexican-heritage youth are members of the fastest growing minority group and are at particular risk for substance use including alcohol consumption. Youth face numerous risk factors including positive descriptions of substance use on media and peer offers that are potentially ameliorated by parental anti-substance use socialization efforts. Guided by primary socialization theory and the theory of planned behavior, the present study posited eight research questions to identify discrete subgroups/patterns of Mexican-heritage youth alcohol use behavior and parental influence on youth outcomes. Longitudinal survey data (n = 1147) from youth in 29 public schools located in Phoenix, Arizona, were collected over 3 years. Latent class and transition analyses identified four discrete subgroups characterized by response patterns of alcohol use behaviors and perceptions in Mexican-heritage youth: (1) non-drinker, (2) potential drinker, (3) experimenter, and (4) regular drinker. Targeted parent-child communication about alcohol and parental monitoring were found to be significant predictors for youth alcohol use. Research implications and future directions are suggested.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ackard, D. M., Neumark-Sztainer, D., Story, M., & Perry, C. (2006). Parent–child connectedness and behavioral and emotional health among adolescents. American Journal of Preventive Medicine, 30, 59–66. doi:10.1016/j.amepre.2005.09.013.
Ajzen, I. (1991). The theory of planned behavior. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes, 50, 179–211. doi:10.1016/0749-5978(91)90020-T.
Allen, M., Donohue, W. A., Griffin, A., Ryan, D., & Turner, M. M. M. (2003). Comparing the influence of parents and peers on the choice to use drugs: a meta-analytic summary of the literature. Criminal Justice and Behavior, 30, 163–186. doi:10.1177/0093854802251002.
Bean, R. A., Bush, K. R., McKenry, P. C., & Wilson, S. M. (2003). The impact of parental support, behavioral control, and psychological control on the academic achievement and self-esteem of African American and European American adolescents. Journal of Adolescent Research, 18, 523–541. doi:10.1177/0743558403255070.
Burrow-Sanchez, J. J. (2006). Understanding adolescent substance abuse prevalence, risk factors, and clinical implications. Journal of Counseling & Development, 84, 283–290. doi:10.1002/j.1556-6678.2006.tb00407.x.
Chen, C. Y., Storr, C. L., & Anthony, J. C. (2005). Influences of parenting practices on the risk of having a chance to try cannabis. Pediatrics, 115, 1631–1639. doi:10.1542/peds.2004-1926.
Chilcoat, H. D., & Anthony, J. C. (1996). Impact of parent monitoring on initiation of drug use through late childhood. Journal of the American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, 35, 91–100. doi:10.1097/00004583-199601000-00017.
Collins, L. M., & Lanza, S. T. (2010). Latent class and latent transition analysis: with applications in the social, behavioural, and health sciences. Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Davidson, T. M., & Cardemil, E. V. (2009). Parent-child communication and parental involvement in Latino adolescents. Journal of Early Adolescence, 29, 99–121. doi:10.1177/0272431608324480.
DiClemente, R. J., Wingood, G. M., Crosby, R., Sionean, C., Cobb, B. K., Harrington, K., et al. (2001). Parental monitoring: association with adolescents' risk behaviors. Pediatrics, 107, 1363–1368. doi:10.1542/peds.107.6.1363.
Dishion, T. J., & McMahon, R. J. (1998). Parental monitoring and the prevention of child and adolescent problem behavior: a conceptual and empirical formulation. Clinical Child and Family Psychology Review, 1, 61–75. doi:10.1023/A:1021800432380.
DiStefano, C., & Kamphaus, R. W. (2006). Investigating subtypes of child development: a comparison of cluster analysis and latent class cluster analysis in typology creation. Educational and Psychological Measurement, 66, 778–794. doi:10.1177/0013164405284033.
Elek, E., Miller-Day, M., & Hecht, M. L. (2006). Influences of personal, injunctive, and descriptive norms on early adolescent substance use. Journal of Drug Issues, 36, 147–172. doi:10.1177/002204260603600107.
Fitzpatrick, M. A., & Ritchie, L. D. (1994). Communication schemata within the family: multiple perspectives on family interaction. Human Communication Research, 20, 275–301. doi:10.1111/j.1468-2958.1994.tb00324.x.
Graham, J. W., Flay, B. R., Johnson, C. A., Hansen, W. B., Grossman, L. M., & Sobel, J. L. (1984). Reliability of self-report measures of drug use in prevention research: evaluation of the Project SMART questionnaire via the test-retest reliability matrix. Journal of Drug Education, 14, 175–193.
Griffin, K. W., Botvin, G. J., Scheier, L. M., Diaz, T., & Miller, N. L. (2000). Parenting practices as predictors of substance use, delinquency, and aggression among urban minority youth: moderating effects of family structure and gender. Psychology of Addictive Behaviors, 14(2), 174–184. doi:10.1037/0893-164X.14.2.174.
Hansen, W. B., & Graham, J. W. (1991). Preventing alcohol, marijuana, and cigarette use among adolescents: peer pressure resistance training versus establishing conservativenorms. Preventive Medicine, 20, 414–430. doi:10.1016/0091-7435(91)90039-7.
Henry, K. L., & Muthén, B. (2010). Multilevel latent class analysis: an application of adolescent smoking typologies with individual and contextual predictors. Structural Equation Modeling, 17, 193–215. doi:10.1080/10705511003659342.
Jackson, N., Denny, S., Sheridan, J., Fleming, T., Clark, T., Teevale, T., & Ameratunga, S. (2014). Predictors of drinking patterns in adolescence: a latent class analysis. Drug and Alcohol Dependence, 135, 133–139. doi:10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2013.11.021.
Johnston, L. D., O'Malley, P. M., Bachman, J. G., & Schulenberg, J. E. (2006). Monitoring the future national results on adolescent drug use: Overview of key findings, 2005. (NIH Publication No. 06-5882). Bethesda, MD: National Institute on Drug Abuse. Retrieved from http://www.monitoringthefuture.org/pubs/monographs/overview2005.pdf
Johnston, L. D., O’Malley, P. M., Bachman, J. G., & Schulenberg, J. E. (2013). Demographic subgroup trends among adolescents for fifty-one classes of licit and illicit drugs, 1975–2012 (Monitoring the Future Occasional Paper No. 79). Ann Arbor, MI: Institute for Social Research. Retrieved from http://www.monitoringthefuture.org/
Kam, J. A., & Cleveland, M. J. (2011). Perceived discrimination as a risk factor for Latina/o youth’s substance use: do parent- and peer-based communication and relationshipresources act as protective factors? Health Communication, 26, 111–124. doi:10.1080/10410236.2010.539180.
Kam, J. A., Matsunaga, M., Hecht, M. L., & Ndiaye, N. (2009). Extending the theory of planned behavior to predict alcohol, tobacco, and marijuana use among youth of Mexican heritage. Prevention Science, 10, 41–53. doi:10.1007/s11121-008-0110-0.
Kam, J. A., Cleveland, M. J., & Hecht, M. L. (2010). Applying general strain theory to examine perceived discrimination's indirect relation to Mexican-heritage youth’s alcohol, cigarette, and marijuana use. Prevention Science, 11, 397–410. doi:10.1007/s11121-010-0180-7.
Kam, J. A., Potocki, B., & Hecht, M. L. (2012). Encouraging Mexican-heritage youth to intervene when friends drink: the role of targeted parent-child communication against alcohol. Communication Research, 41, 644–664. doi:10.1177/0093650212446621.
Kopak, A. M. (2013). The relative importance of immigrant generation for Mexican Americans’ alcohol and tobacco use from adolescence to early adulthood. Journal of Immigrant and Minority Health, 15, 569–576. doi:10.1007/s10903-012-9631-5.
Kopak, A. M., Chen, A. C. C., Haas, S. A., & Gillmore, M. R. (2012). The importance of family factors to protect against substance use related problems among Mexican heritage and White youth. Drug and Alcohol Dependence, 124, 34–41. doi:10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2011.12.004.
Kumpfer, K. L., Alvarado, R., & Whiteside, H. O. (2003). Family-based interventions for substance use and misuse prevention. Substance Use & Misuse, 38, 1759–1787. doi:10.1081/JA-120024240.
Lanza, S. T., & Collins, L. M. (2008). A new SAS procedure for latent transition analysis: transitions in dating and sexual behavior. Developmental Psychology, 44, 446–456. doi:10.1037/0012-1649.44.2.446.
Lanza, S. T., Collins, L. M., Lemmon, D. R., & Schafer, J. L. (2007). PROC LCA: a SAS procedure for latent class analysis. Structural Equation Modeling, 14, 671–694. doi:10.1080/10705510701575602.
Lanza, S. T., Dziak, J. J., Huang, L., Wagner, A., & Collins, L. M. (2013). PROC LCA & PROC LTA users' guide (Version 1.3.0). University Park: The Methodology Center, Penn State. Retrieved from http://methodology.psu.edu
Marsiglia, F. F., Nagoshi, J. L., Parsai, M., Booth, J. M., & Castro, F. G. (2014). The parent–child acculturation gap, parental monitoring, and substance use in Mexican heritage adolescents in Mexican neighborhoods of the Southwest US. Journal of Community Psychology, 42, 530–543. doi:10.1002/jcop.21635.
Martinez Jr, C. R., & Eddy, J. M. (2005). Effects of culturally adapted parent management training on Latino youth behavioral health outcomes. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 73(5), 841–851. doi:10.1037/0022-006X.73.5.841.
Martins, S. S., Storr, C. L., Alexandre, P. K., & Chilcoat, H. D. (2008). Adolescent ecstasy and other drug use in the National Survey of Parents and Youth: the role of sensation-seeking, parental monitoring and peer's drug use. Addictive Behaviors, 33, 919–933. doi:10.1016/j.addbeh.2008.02.010.
Martyn, K. K., Loveland-Cherry, C., Villarruel, A., Cabriales, E. G., Zhou, Y., Ronis, D., & Eakin, B. (2009). Mexican adolescents' alcohol use, family intimacy, and parent-adolescent communication. Journal of Family Nursing, 15, 152–170. doi:10.1177/1074840709332865.
Miller‐Day, M. (2008). Talking to youth about drugs: what do late adolescents say about parental strategies? Family Relations, 57, 1–12. doi:10.1111/j.1741-3729.2007.00478.x.
Miller-Day, M., & Kam, J. A. (2010). More than just openness: developing and validating a measure of targeted parent-child communication about alcohol. Health Communication, 25, 293–302. doi:10.1080/10410231003698952.
Mundt, M. P. (2011). The impact of peer social networks on adolescent alcohol use initiation. Academic Pediatrics, 11, 414–421. doi:10.1016/j.acap.2011.05.005.
Oetting, E. R., & Donnermeyer, J. F. (1998). Primary socialization theory: the etiology of drug use and deviance: I. Substance Use & Misuse, 33, 995–1026. doi:10.3109/10826089809056252.
Parker, J. S., & Benson, M. J. (2004). Parent-adolescent relations and adolescent functioning: self-esteem, substance abuse, and delinquency. Adolescence, 39, 519–530.
Parsai, M., Voisine, S., Marsiglia, F. F., Kulis, S., & Nieri, T. (2008). The protective and risk effects of parents and peers on substance use, attitudes, and behaviors of Mexican and Mexican American female and male adolescents. Youth & Society, 40, 353–376. doi:10.1177/0044118x08318117.
Parsai, M., Marsiglia, F. F., & Kulis, S. (2010). Parental monitoring, religious involvement and drug use among Latino and non-Latino youth in the Southwestern United States. British Journal of Social Work, 40, 100–114. doi:10.1093/bjsw/bcn100.
Pasch, L. A., Deardorff, J., Tschann, J. M., Flores, E., Penilla, C., & Pantoja, P. (2006). Acculturation, parent-adolescent conflict, and adolescent adjustment in Mexican American families. Family Process, 45, 75–86. doi:10.1111/j.15455300.2006.00081.x.
Reimuller, A., Hussong, A., & Ennett, S. T. (2011). The influence of alcohol-specific communication on adolescent alcohol use and alcohol-related consequences. Prevention Science, 12, 389–400. doi:10.1007/s11121-011-0227-4.
Sargent, J. D., Wills, T. A., Stoolmiller, M., Gibson, J., & Gibbons, F. X. (2006). Alcohol use in motion pictures and its relation with early-onset teen drinking. Journal of Studieson Alcohol, 67, 54–65. doi:10.15288/jsa.2006.67.54.
Shin, Y., & Hecht, M. L. (2013). Does parentification place Mexican-heritage youth at risk for substance use? Identifying the intervening nature of parent-child communication about alcohol. Journal of Adolescence, 36, 149–159. doi:10.1016/j.adolescence.2012.10.010.
Shin, Y., Lee, J. K., & Miller-Day, M. (2013). The effects of maternal emotional wellbeing on mother-child communication and youth emotional wellbeing in low-income families. Communication Research Reports, 30, 137–147. doi:10.1080/08824096.2012.763025.
Strunin, L., Díaz-Martínez, A., Díaz-Martínez, L. R., Heeren, T., Kuranz, S., Winter, M., … Solís-Torres, C. (2013). Parental monitoring and alcohol use among Mexican students. Addictive Behaviors, 38, 2601-2606. doi: 10.1016/j.addbeh.2013.06.011.
Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration, National Survey of Substance Abuse Treatment Services (N-SSATS): 2012. Data on Substance Abuse Treatment Facilities. BHSIS Series S-66, HHS Publication No. (SMA) 14-4809. Rockville, MD. Retrieved from http://www.samhsa.gov/data/DASIS/NSSATS2012_Web.pdf
U.S. Census Bureau (2006). Ethnicity and Ancestry Statistics Branch Population Division U.S. Census Bureau. Retrieved from https://www.census.gov/population/hispanic/files/2006/CPS_Powerpoint_2006.pdf
Warner, T. D., Fishbein, D. H., & Krebs, C. P. (2010). The risk of assimilating alcohol use among immigrant and US-born Mexican youth. Social Science Research, 39, 176–186. doi:10.1016/j.ssresearch.2009.07.001.
Warren, J. R., Wagstaff, D. A., Hecht, M. L., & Elek, E. (2008). The effects of Mexican origin family structure on parental monitoring and preadolescent substance use expectancies and substance use. Journal of Substance Use, 13, 283–292. doi:10.1080/14659890802170745.
Webb, J. A., Bray, J. H., Getz, J. G., & Adams, G. (2002). Gender, perceived parental monitoring, and behavioral adjustment: influences on adolescent alcohol use. American Journal of Orthopsychiatry, 72, 392–400. doi:10.1037/0002-9432.72.3.392.
Wills, T., Sargent, J., Gibbons, F., Gerrard, M., & Stoolmiller, M. (2009). Movie exposure to alcohol cues and adolescent alcohol problems: a longitudinal analysis in a national sample. Psychology of Addictive Behaviors, 23, 23–35. doi:10.1037/a0014137.
Acknowledgments
This manuscript was supported by Grant Numbers R01DA005629 from the National Institute on Drug Abuse to The Pennsylvania State University (Grant Recipient), Michael Hecht, Principal Investigator. Its contents are solely the responsibility of the authors and do not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shin, Y., Lee, JK., Lu, Y. et al. Exploring Parental Influence on the Progression of Alcohol Use in Mexican-Heritage Youth: a Latent Transition Analysis. Prev Sci 17, 188–198 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11121-015-0596-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11121-015-0596-1