Abstract
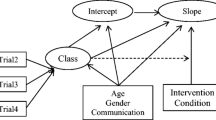
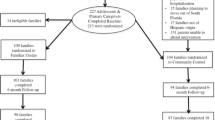
Hispanic adolescents are disproportionately affected by externalizing disorders, substance use and HIV infection. Despite these health inequities, few interventions have been found to be efficacious for this population, and even fewer studies have examined whether the effects of such interventions vary as a function of ecodevelopmental and intrapersonal risk subgroups. The aim of this study was to determine whether and to what extent the effects of Familias Unidas, an evidence-based preventive intervention, vary by ecodevelopmental and intrapersonal risk subgroups. Data from 213 Hispanic adolescents (mean age = 13.8, SD = 0.76) who were enrolled in a randomized clinical trial evaluating the relative efficacy of Familias Unidas on externalizing disorders, substance use, and unprotected sexual behavior were analyzed. The results showed that Familias Unidas was efficacious over time, in terms of both externalizing disorders and substance use, for Hispanic youth with high family ecodevelopmental risk (e.g., poor parent-adolescent communication), but not with youth with moderate ecodevelopmental or low ecodevelopmental risk. The results suggest that classifying adolescents based on their family ecodevelopmental risk may be an especially effective strategy for examining moderators of family-based preventive interventions such as Familias Unidas. Moreover, these results suggest that Familias Unidas should potentially be targeted toward youth with high family ecodevelopmental risk. The utility of the methods presented in this article to other prevention scientists, including genetic, neurobiological and environmental scientists, is discussed.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bandeen-Roche, K., Miglioretti, D. L., Zeger, S. L., & Rathouz, P. J. (1997). Latent variable regression for multiple discrete outcomes. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 92, 1375–1386.
Barnes, H. L., & Olson, D. H. (1985). Parent-adolescent communication and the circumplex model. Child Development, 56, 438–447. doi:10.2307/1129732.
Braveman, P., & Barclay, C. (2009). Health disparities beginning in childhood: A life-ourse perspective. Pediatrics, 124, S163–S175. doi:1O.1542/peds.2009-1100D.
Brody, G. H., Beach, S. R., Philibert, R. A., Chen, Y., Lei, M., Murry, V. M., & Brown, A. C. (2009). Parenting moderates a genetic vulnerability factor in longitudinal increases in youths' substance use. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 77, 1–11. doi:10.1037/a0012996.
Bronfenbrenner, U. (1979). The ecology of human development: Experiments by nature and design. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press.
Brown, E. C., Catalano, R. F., Fleming, C. B., Haggerty, K. P., & Abbott, R. D. (2005). Adolescent substance use outcomes in the Raising Healthy Children Project: A two-part latent growth curve analysis. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 73, 699–710. doi:10.1037/0022-006X.73.4.699.
Brown, C. H., Wang, W., Kellam, S. G., Muthén, B. O., Petras, H., Toyinbo, P., & Windham, A. (2008). Methods for testing theory and evaluating impact in randomized field trials: Intent-to-treat analyses for integrating the perspectives of person, place, and time [Supplement]. Drug and Alcohol Dependence, 95, S74–S104. doi:10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2007.11.013.
Centers for Disease Control & Prevention. (2010). Youth risk behavior surveillance -United States, 2009. MMWR Surveillance Summaries, 59(SS-05), 1–142. Retrieved from http://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/preview/mmwrhtml/ss5905a1.htm
Cicchetti, D., & Aber, J. L. (1998). Contextualism and developmental psychopathology. Development and Psychopathology, 10, 137–141.
Dubow, E. F., & Ullman, D. G. (1989). Assessing social support in elementary school children: The Survey of Children's Social Support. Journal of Clinical Child Psychology, 18, 52–64. doi:10.1207/s15374424jccp1801_7.
Gorman-Smith, D., Tolan, P. H., Zelli, A., & Huesmann, L. R. (1996). The relation of family functioning to violence among inner-city minority youths. Journal of Family Psychology, 10, 115–129. doi:10.1037/0893-3200.10.2.115.
Hawkins, J., Catalano, R., & Miller, J. (1992). Risk and protective factors for alcohol and other drug problems in adolescence and early adulthood: Implications for substance abuse prevention. Psychological Bulletin, 112, 64–105. doi:10.1037/0033-2909.112.1.64.
Jemmott, J. B., Jemmott, L. S., & Fong, G. T. (1998). Abstinence and safer sex HIV risk-reduction interventions for African American adolescents. Journal of the American Medical Association, 279, 1529–1536. doi:10.1001/jama.281.16.1485.
Johnston, L.D., O'Malley, P.M., Bachman, J.G., & Schulenberg, J.E. (2009). Monitoring the future: National survey results on drug use, 1975–2008: Volume I, secondary school students (NIH publication no. 09–7402). Bethesda, MD: National Institute on Drug Abuse.
Kraemer, H. C., Kazdin, A. E., Offord, D. R., Kessler, R. C., Jensen, P. S., & Kupfer, D. J. (1997). Coming to terms with the terms of risk. Archives of General Psychiatry, 54(4), 337–343. doi:10.1001/archpsyc.1997.01830160065009.
Lopez, B., Schwartz, S. J., Prado, G., Campo, A. E., & Pantin, H. (2008). Adolescent Neurological development and its implicataions for adolescent substance use prevention. The Journal of Primary Prevention, 29, 5–35. doi:10.1007/s10935-007-0119-3.
Lucas, C. P., Zhang, H., Fisher, P. W., Shaffer, D., Regier, D. A., Narrow, W. E., & Friman, P. (2001). The DISC Predictive Scales (DPS): Efficiently screening for diagnoses. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 40, 443–449. doi:10.1097/00004583-200104000-00013.
Luna, B., & Sweeney, J. A. (2004). The emergence of collaborative brain function: fMRI studies of the development of response inhibition. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1021, 296–309. doi:10.1196/annals.1308.035.
O’Connell, M. E., Boat, T., & Warner, K. E. (2009). Preventing mental, emotional, and behavioral disorders among young people: Progress and possibilities. Washington D.C.: The National Academies Press.
Pantin, H., Prado, G., Schwartz, S., & Sullivan, S. (2005). Methodological challenges in designing efficacious drug abuse and HIV preventive interventions for Hispanic adolescent subgroups. Journal of Urban Health, 82, iii92-iii102. doi:10.1093/jurban/jti067
Pantin, H., Prado, G., Lopez, B., Huang, S., Tapia, M. I., Schwartz, S. J., & Branchini, J. (2009). A randomized controlled trial of Familias Unidas for Hispanic adolescents with behavior problems. Psychosomatic Medicine, 71(9), 987–995. doi:10.1097/PSY.0b013e3181bb2913.
Pentz, M. A., Dwyer, J. H., MacKinnon, D. P., Flay, B. R., Hansen, W. B., Wang, E. Y., & Johnson, C. A. (1989). A multicommunity trial for primary prevention of adolescent drug abuse. Journal of the American Medical Association, 261, 3259–3266. doi:10.1001/jama.1989.03420220073030.
Prado, G., & Pantin, H. (2011). Reducing substance use and HIV health disparities among Hispanic youth in the U.S.A.: The Familias Unidas program of research. Psychosocial Intervention, 20(1), 63–73.
Prado, G. J., Pantin, H., Briones, E., Schwartz, S. J., Feaster, D., Huang, S., & Szapocznik, J. (2007). A randomized controlled trial of a parent-centered intervention in preventing substance use and HIV risk behaviors in Hispanic adolescents. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 75, 914–926. doi:10.1037/0022-006X.75.6.914.
Prado, G. J., Schwartz, S. J., Maldonado-Molina, M., Huang, S., Pantin, H. M., Lopez, B., & Szapocznik, J. (2009). Ecodevelopmental x intrapersonal risk: Substance use and sexual behavior in Hispanic adolescents. Health Education & Behavior, 36, 45–61. doi:10.1177/1090198107311278.
Prado, G., Shi, H., Maldonado-Molina, M., Bandiera, F., Schwartz, S. J., de la Vega, P., & Pantin, H. (2010). An empirical test of ecodevelopmental theory in predicting HIV risk behaviors among Hispanic youth. Health Education & Behavior, 37, 97–114. doi:10.1177/1090198109349218.
Quay, H. C., & Peterson, D. R. (1993). The revised behavior problem checklist: Manual. Odessa, FL: Psychological Assessment Resources.
Soper, A. C., Wolchik, S. A., Tein, J.-Y., & Sandler, I. N. (2010). Mediation of a preventive intervention's 6-year effects on health risk behaviors. Psychology of Addictive Behaviors, 24, 300–310. doi:10.1037/a0019014.
Spoth, R., Randall, G. K., Shin, C., & Redmond, C. (2005). Randomized study of combined universal family and school preventive interventions: Patterns of long-term effects on initiation, regular use, and weekly drunkenness. Psychology of Addictive Behaviors, 19, 372–381. doi:10.1037/0893-164X.19.4.372.
Szapocznik, J., & Coatsworth, J.D. (1999). An ecodevelopmental framework for organizing the influences on drug abuse: A developmental model of risk and protection. In M. D. Glantz & C. R. Hartel (Eds.), Drug abuse: Origins & interventions (pp. 331–366). Washington, DC: American Psychological Association. doi: 10.1037/10341-014
Szapocznik, J., Prado, G., Burlew, A. K., Williams, R. A., & Santisteban, D. A. (2007). Drug abuse in African American and Hispanic adolescents: Culture, development, and behavior. Annual Review of Clinical Psychology, 3, 77–105. doi:10.1146/annurev.clinpsy.3.022806.091408.
Tein, J.-Y., Sandler, I. N., MacKinnon, D. P., & Wolchik, S. A. (2004). How did it work? Who did it work for? Mediation in the context of a moderated prevention effect for children of divorce. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 72, 617–624. doi:10.1037/0022-006X.72.4.617.
Tein, J.-Y., Sandler, I., Ayers, T., & Wolchik, S. (2006). Mediation of the effects of the Family Bereavement Program on mental health problems of bereaved children and adolescents. Prevention Science, 7, 179–195. doi:10.1007/s11121-006-0037-2.
Tolan, P. H., Gorman-Smith, D., Huesmann, L. R., & Zelli, A. (1997). Assessment of family relationship characteristics: A measure to explain risk for antisocial behavior and depression among urban youth. Psychological Assessment, 9, 212–223. doi:10.1037/1040-3590.9.3.212.
Turner, C. F., Ku, L., Rogers, S. M., Lindberg, L. D., Pleck, J. H., & Sonenstein, F. L. (1998). Adolescent sexual behavior, drug use, and violence: Increased reporting with computer survey technology. Science, 280, 867–873. doi:10.1126/science.280.5365.867.
Villarruel, A. M., Jemmott, L. S., & Jemmott, J. B. (2005). Designing a culturally based intervention to reduce HIV sexual risk for Latino adolescents. Journal of the Association of Nurses in AIDS Care, 16, 23–31. doi:10.1016/j.jana.2005.01.001.
Wang, C.-P., Brown, C. H., Bandeen-Roche, K., & Jaccard, J. (2005). Residual diagnostics for growth mixture models: Examining the impact of a preventive intervention on multiple trajectories of aggressive behavior. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 100, 1054–1076. doi:10.1198/016214505000000501.
Webb, P. M., Zimet, G. D., Fortenberry, J. D., & Blythe, M. J. (1999). Comparability of a computer-assisted versus written method for collecting health behavior information from adolescent patients. Journal of Adolescent Health, 24, 383–388. doi:10.1016/S1054-139X(99)00005-1.
Wolchik, S.A., Sandler, I.N., Millsap, R.E., Plummer, B.A., Greene, S.M., Anderson, E.R.,… Haine, R.A. (2002). Six-year follow-up of preventive interventions for children of divorce. The Journal of the American Medical Association, 288, 1874–1881. doi:10.1001/jama.288.15.1874
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article was supported by NIH grant # R01 DA017462 to Hilda Pantin as well as NIH grants # 1R01DA025192, 1R01DA025894, R01DA025192, R01DA025192-01A1S1, and CDC grant # U01PS0000671 awarded to Guillermo Prado. We would like to thank our research team (including our facilitators, assessors, and data analyst), Miami-Dade County Public Schools, and the families that have contributed to this program of research over the years.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Prado, G., Huang, S., Cordova, D. et al. Ecodevelopmental and Intrapersonal Moderators of a Family Based Preventive Intervention for Hispanic Youth: A Latent Profile Analysis. Prev Sci 14, 290–299 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11121-012-0326-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11121-012-0326-x