Abstract
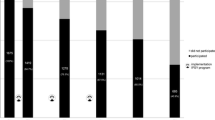
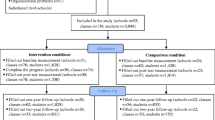
The objective of the present research was to examine the contribution of two intervention components, social skills training and problem solving training, to alcohol- and drug-related outcomes in a school-based substance use prevention program. Participants included 341 Spanish students from age 12 to 15 who received the prevention program Saluda in one of four experimental conditions: full program, social skills condition, problem solving condition, and a wait-list control group. Students completed self-report surveys at the pretest, posttest and 12-month follow-up assessments. Compared to the wait-list control group, the three intervention conditions produced reductions in alcohol use and intentions to use other substances. The intervention effect size for alcohol use was greatest in magnitude for the full program with all components. Problem-solving skills measured at the follow-up were strongest in the condition that received the full program with all components. We discuss the implications of these findings, including the advantages and disadvantages of implementing tailored interventions to students by selecting intervention components after a skills-based needs assessment.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ajzen, I. (1985). From intentions to action: A theory of planned behavior. In J. Kull & J. Beckmann (Eds.), Action control from cognition to behaviour (pp. 11–39). Heidelberg, Germany: Springer.
Anderson, P. (2006). Global use of alcohol, drugs and tobacco. Drug and Alcohol Review, 25, 489–502.
Arco, J. L., & Fernández, A. (2002). Porque los programas de prevención no previenen [why preventive programs don’t prevent]. Revista Internacional de Psicología Clínica y de la Salud/International Journal of Clinical and Health Psychology, 2, 209–226.
Ashby, T., Baker, E., & Botvin, G. J. (1989). Dimensions of assertiveness: Differential relationships to substance use in early adolescence. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 57, 473–478.
Bangert-Drowns, R. L. (1986). Review of developments in meta-analytic method. Psychological Bulletin, 99, 388–399.
Barkin, S. L., Smith, K. S., & DuRant, R. H. (2002). Social skills and attitudes associated with substance use behaviors among young adolescents. Journal of Adolescent Health, 3, 448–454.
Belcher, H. M., & Shinitzky, H. E. (1998). Substance abuse in children: Prediction, protection and prevention. Archives of Pediatric Medicine, 152, 952–960.
Botvin, G. J., Baker, E., Dusenbury, L., Botvin, E. M., & Diaz, T. (1995). Long-term follow-up results of a randomized drug abuse prevention trial in a white middle-class population. Journal of the American Medical Association, 273, 1106–1112.
Caplan, M., Weissberg, R., Grober, J., Sivo, P., Grady, K., & Jacoby, C. (1992). Social competence promotion with inner city and suburban young adolescents: Effects on social adjustment and alcohol use. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 60, 56–63.
Cohen, J. (1988). Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences (2nd ed.). Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Earlbaum Associates.
Cuijpers, P. (2002). Effective ingredients of school-based drug prevention programs: A systematic review. Addictive Behaviors, 27, 1009–1023.
D’Zurilla, T. J., & Goldfried, M. R. (1971). Problem solving and behaviour modification. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 78, 107–126.
Ellickson, P., & Bell, R. (1990). Drug prevention in junior high: A multiside longitudinal test. Science, 247, 1299–1305.
Espada, J. P., & Méndez, F. X. (2003). Programa Saluda: Prevención del abuso de alcohol y drogas de síntesis [Program Saluda: Alcohol and synthetic substances abuse prevention] (pp. 167–168). Madrid, Spain: Piramide.
Espada, J. P., Méndez, F. X., & Hidalgo, M. D. (2003). Cuestionario de consumo. In J. P. Espada & F. X. Méndez (Eds.), Programa Saluda: Prevención del abuso de alcohol y del consumo de drogas de síntesis [Program Saluda: Prevention of Alcohol Abuse and Synthetic Drugs Use] (pp. 167–168). Madrid, Spain: Pirámide.
Espada, J. P., Méndez, F. X., Botvin, G. J., Griffin, K. W., Orgilés, M., & Rosa, A. I. (2002). ¿Éxito o fracaso de la prevención del abuso de drogas en el contexto escolar? un meta-análisis de los programas en España [Success or failure of school-based drug prevention? a meta-analysis of the programs in Spain]. Psicología Conductual, 10, 581–602.
Espada, J. P., Méndez, F. X., Orgilés, M., García-Fernández, J. M., & Inglés, C. J. (2008). Efectos del programa de prevención Saluda sobre factores cognitivos relacionados con el consumo de drogas [Effects of the prevention program Saluda on cognitive factors associated with substance use]. Salud y Drogas/Health and Addictions, 8, 23–31.
Espada, J. P., Méndez, X., Griffin, K. W., & Botvin, G. J. (2003). Adolescencia: Consumo de alcohol y otras drogas [Adolescence: Alcohol and other substances use]. Papeles del Psicólogo, 23, 9–17.
Espada, J. P., Pereira, J. R., & García-Fernández, J. M. (2008). Influencia de los modelos sociales en el consumo de alcohol de los adolescents [Influence of social models in alcohol use among adolescents]. Psicothema, 20, 531–537.
Eysenck, H. J. (1981). El modelo de condicionamiento del proceso de socialización [The conditioning model of the socialization process]. Análisis y Modificación de Conducta, 7, 5–29.
Faggiano, F., Vigna-Taglianti, F. D., Versino, E., et al. (2008). School-based prevention for illicit drugs use: A systematic review. Preventive Medicine, 46, 385–396.
Gomez-Fraguela, J. A., Luengo, M. A., Romero, E., & Villar, P. (2003). Drug-abuse prevention in the school: Four-year follow-up of a programme. Psychology in Spain, 7, 29–38.
Griffin, K. W. (2010). The epidemiology of substance use among adolescents and young adults: A developmental perspective. In L. M. Scheier (Ed.), Handbook of drug use etiology: Theory, methods, and empirical findings (pp. 73–92). Washington, DC: American Psychological Association.
Hawkins, J., Catalano, R., & Arthur, M. (2002). Promoting science based prevention in communities. Addictive Behaviors, 27, 951–976.
Hibell, B., Guttormsson, U., Ahlström, S., Balakireva, O., Bjarnason, T., Kokkevi, A., et al. (2009). The 2007 European School Survey Project on Alcohol and other Drugs (ESPAD) report: Substance use among students in 35 European countries. Stockholm: Swedish Council for Information on Alcohol and Other Drugs.
Ibrahim, J. K., & Glantz, S. (2007). The rise and fall of tobacco control media campaigns, 1967–2006. American Journal of Public Health, 87, 1383–1396.
Inglés, C. J., Méndez, F. X., & Hidalgo, M. D. (2000). Cuestionario de evaluación de las dificultades interpersonales para adolescentes [Interpersonal difficulties questionnaire for adolescents]. Psicothema, 12, 390–398.
Lee, C., & Kahende, J. (2007). Factors associated with successful smoking cessation in the United States. American Journal of Public Health, 97, 1503–1509.
Leukefeld, C. G., & Bukoski, W. J. (1995). Estudio sobre intervenciones en prevención del abuso de drogas: Aspectos metodológicos [Study on interventions in drug abuse prevention: Methodological aspects]. Madrid, Spain: Centro de Estudios sobre Promoción de la Salud.
Luengo, A., Romero, E., Gómez-Fragüela, J. A., Guerra, A., & Lence, M. (1999). La prevención del consumo de drogas y la conducta antisocial en la escuela: Análisis y evaluación de un programa [The prevention of drug use and antisocial behavior in schools: Analysis and evaluation of a program]. Madrid, Spain: Delegación del Gobierno para el Plan Nacional sobre Drogas.
Maydeu-Olivares, A., & D’Zurilla, T. J. (1996). A factor-analytic study of the social problem-solving inventory: An integration of theory and data. Cognitive Therapy and Research, 20, 115–133.
Newcomb, M. D., & Locke, T. (2005). Health, social, and psychological consequences of drug use and abuse. In Z. Sloboda (Ed.), Epidemiology of drug abuse (pp. 45–59). New York: Springer.
Pentz, M. A. (1994). Estrategias innovadoras para la prevención del consumo de drogas en el ámbito escolar y en la comunidad [Innovative strategies for the prevention of drug use in schools and community]. In J. A. García & J. Ruiz (Eds.), Tratado sobre prevención de las drogodependencias [Handbook on drug prevention]. (pp. 121–147). Bilbao, Spain: Edex.
Rundall, T. G., & Bruvold, W. H. (1988). A meta-analysis of school-based smoking and alcohol use prevention programs. Health Education Quarterly, 15, 317–334.
Salvador, T., & Martinez, I. (1997). La evaluación de programas de prevención de las drogodependencias [The evaluation of drug prevention programs]. Revista de Estudios de Juventud, 40, 95–108.
Skara, S., & Sussman, S. (2003). A review of 25 long-term adolescent tobacco and other drug use prevention programme evaluations. Preventive Medicine 37, 451–74
Skara, S., Rohrbach, L. A., Sun, P., & Sussman, S. (2005). An evaluation of the fidelity of implementation of a school-based drug abuse prevention program: Project Toward No Drug Abuse (TND). Journal of Drug Education, 35, 305–329.
Snow, D. L., Tebes, J. K., Arthur, M. W., & Tapasak, R. C. (1992). Two-year follow-up of a social-cognitive intervention to prevent substance use. Journal of Drug Education, 22, 101–114.
Spanish Drugs Observatory. (2006). Encuesta sobre drogas a población escolar [Scholar national survey on substance use]. Madrid, Spain: Spanish Department of Internal Affairs.
Tobler, N. (1986). Meta-analysis of 143 adolescent drug prevention programs: Quantitative outcomes results of program participants compared to a control or comparison group. Journal of Drug Issues, 16, 537–567.
Tobler, N. (1992). Drug prevention programs can work: Research findings. Journal of Addictive Diseases, 11, 1–28.
Tobler, N. S., Roona, M., Ochshorn, P., et al. (2000). School-based adolescent drug prevention programs: 1998 meta-analysis. Journal of Primary Prevention, 20, 275–336.
Walters, S., Vader, A., & Harris, T. (2008). A dismantling trial of motivational interviewing and feedback among heavy drinking college students. Alcoholism, Clinical and Experimental Research, 32, 368A.
West, S. G., Aiken, L. S., & Todd, M. (1993). Probing the effects of individual components in multiple component prevention programs. American Journal of Community Psychology, 21, 571–605.
World Health Organization. (2007). Annual report on health and disease. Retrieved April 24, 2007 from http://www.who.int/whr/2007/es/index.html
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Espada, J.P., Griffin, K.W., Pereira, J.R. et al. Component Analysis of a School-Based Substance Use Prevention Program in Spain: Contributions of Problem Solving and Social Skills Training Content. Prev Sci 13, 86–95 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11121-011-0249-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11121-011-0249-y