Abstract
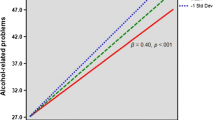
As little research has examined factors influencing increased and heavy drinking behavior among American sojourners abroad, this study was designed to examine how acculturation orientations (i.e., separation versus assimilation), host country per capita drinking rates, and perceptions about the drinking behavior among other sojourners and natives in the host country predicted alcohol risk abroad. A sample of 216 American college students completing study abroad programs completed a pre-abroad questionnaire to document their pre-abroad drinking levels, followed by a post-return questionnaire to assess drinking while abroad, acculturation orientations and perceived norms of drinking behavior within the foreign environment. A dichotomous variable was created to compare United States (U.S.) per capita drinking rates with those of the host country. Hierarchical repeated-measures ANOVAs examined the changes in drinking from pre-abroad to abroad levels. Participants studying in countries with higher drinking rates than the U.S. and those with higher perceptions about the drinking behavior in the country increased their drinking to a greater extent. Those with higher separation acculturation orientations and greater perceptions drank at heavier levels while abroad. Participants with a greater assimilation orientation and higher perceptions about native drinking, as well as those with a greater separation orientation and higher perceptions about other students’ alcohol use drank the heaviest while abroad. These findings have implications for future preventive work with American students and other sojourning groups to promote pre-abroad knowledge of more accurate drinking norms and greater engagement in the culture to potentially prevent increased and heavier drinking.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abraido-Lanza, A. F., Chao, M. T., & Florez, K. R. (2005). Do healthy behaviors decline with greater acculturation? Implications for the Latino mortality paradox. Social Science Medicine, 61, 1243–1255.
Amodeo, M., & Jones, L. K. (1997). Viewing alcohol and other drug use cross-culturally: A cultural framework for clinical practice. Families in Society: The Journal of Contemporary Human Services, 78, 240–254.
Association of Americans Resident Overseas. (2010). 5.25 million Americans (excluding military) live in 160-plus countries. Retrieved from http://aaro.org/.
Baer, J. S., Stacy, A., & Larimer, M. (1991). Biases in the perception of drinking norms among college students. Journal of Studies of Alcohol, 52, 580–586.
Berry, J. W. (1980). Social and cultural change. In H. C. Triandis & R. W. Brislin (Eds.), Handbook of cross-cultural psychology: Social psychology (pp. 211–279). Boston, MA: Allyn and Bacon.
Berry, J. W. (1997). Immigration, acculturation and adaptation. Applied Psychology: An International Review, 46, 1–30.
Berry, J. W. (1998). Acculturative stress. In P. B. Organista, K. M. Chun, & G. Marin (Eds.), Readings in ethnic psychology (pp. 113–117). New York: Routledge.
Berry, J. W. (2003). Conceptual approaches to acculturation. In K. M. Chun, P. B. Organista, & G. Marín (Eds.), Acculturation: Advances in theory, measurement and applied research (pp. 17–37). Washington, DC: American Psychological Association.
Borsari, B., & Carey, K. B. (2003). Descriptive and injunctive norms in college drinking: A meta-analytic integration. Journal of Studies on Alcohol, 64, 331–341.
Bray, R. M., & Hourani, L. L. (2007). Substance use trends among active duty military personnel: Findings from the United States Department of Defense Health Related Behavior Surveys, 1980–2005. Addiction, 102, 1092–1101.
Bremner, J. D., Southwick, S. M., Darnell, A., & Charney, D. S. (1996). Chronic PTSD in Vietnam combat veterans: Course of illness and substance abuse. American Journal of Psychiatry, 153, 369–375.
Brien, M., & David, K. (1971). Intercultural communication and the adjustment of the sojourner. Psychological Bulletin, 76, 215–230.
Buss, D. M. (1987). Selection, evocation, and manipulation. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 53, 1214–1221.
Caetano, R., & Medina Mora, M. E. (1988). Acculturation and drinking among people of Mexican descent in Mexico and the United States. Journal of Studies on Alcohol, 49, 462–471.
Caetano, R., & Medina Mora, M. E. (1990). Reasons and attitudes toward drinking and abstaining: A comparison of Mexicans and Mexican Americans. In: Epidemiologic Trends in Drug Abuse: Community Epidemiology Work Group, Proceedings June 1990 (pp. II–173–192). Division of Epidemiology and Prevention Research, National Institute on Drug Abuse, Rockville, Maryland.
Cardozo, B. L., & Salama, P. (2002). Mental health of humanitarian aid workers in complex emergencies. In Y. Danieli (Ed.), Sharing the front line and the back hills: Peacekeepers, humanitarian aid workers and the media in the midst of crisis (pp. 242–257). Amityville, NY: Baywood.
Chun, K. M., Balls Organista, P., & Marin, G. (2003). Acculturation: Advances in theory, measurement, and applied research. Washington, DC: American Psychological Association.
Church, A. (1982). Sojourner adjustment. Psychological Bulletin, 91, 540–572.
Citron, J. (1996). Short-term study abroad: Integration, third culture formation, and re-entry. Paper presented at the NAFSA Annual Conference, Phoenix, AZ. Retrieved from http://www.nafsa.org.
Cohen, J., Cohen, P., West, S. G., & Aiken, L. S. (2003). Applied multiple regression/correlation analysis for the behavioral sciences (3rd ed.). Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
Collins, R. L., Parks, G. A., & Marlatt, G. A. (1985). Social determinants of alcohol consumption: The effects of social interaction and model status on the self-administration of alcohol. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 53, 189–200.
Department of Defense. (2010). DoD Personnel and Procurement Statistics: U.S. military personnel on selected active duty in foreign countries. Retrieved from http://siadapp.dmdc.osd.mil/.
Gong, F., Takeuchi, D. T., Agbayani-Siewert, P., & Tacata, L. (2003). Acculturation, psychological distress, and alcohol use: Investigating the effects of ethnic identity and religiosity. In K. M. Chun, P. Balls Organista, & G. Marin (Eds.), Acculturation: Advances in theory, measurement, and applied research (pp. 189–206). Washington, D.C.: American Psychological Association.
Hahm, H. C., Lahiff, M., & Guterman, N. B. (2003). Acculturation and parental attachment in Asian American adolescents’ alcohol use. Journal of Adolescent Health, 33, 119–129.
Hahm, H. C., Lahiff, M., & Guterman, N. B. (2004). Asian American adolescents’ acculturation, binge drinking, and alcohol- and tobacco-using peers. Journal of Community Psychology, 32, 295–308.
Harley, B. (2001). Education abroad—going native or standing firm. Transitions Abroad Magazine, Jan/Feb. Retrieved from http://www.transitionsabroad.com.
Hendershot, C. S., Dillworth, T. M., Neighbors, C., & George, W. H. (2008). Differential effects of acculturation on drinking behavior in Chinese- and Korean-American college students. Journal of Studies on Alcohol and Drugs, 69, 121–128.
Hendershot, C. S., MacPherson, L., Myers, M. G., Carr, L. G., & Wall, T. L. (2005). Psychosocial, cultural and genetic influences on alcohol use in Asian American youth. Journal of Studies on Alcohol, 66, 185–195.
Hummer, J. F., Pedersen, E. R., Mirza, T., & LaBrie, J. W. (2010). Factors associated with general and sexual alcohol-related consequences: An examination of college students while studying abroad. Journal of Student Affairs Research and Practice, 47, 427–444.
Hunt, L. M., Schneider, S., & Comer, B. (2004). Should “acculturation” be a variable in health research? A critical review of research on U. S. Hispanics. Social Science and Medicine, 59, 973–986.
Institute of International Education (IIE). (2009). Open Doors 2009 Report of International Education Exchange. Retrieved from http://www.iie.org.
Jacobson, I. G., Ryan, M. A. K., Hooper, T. I., Smith, T. C., Amoroso, P. J., et al. (2008). Alcohol use and alcohol-related problems before and after military combat deployment. JAMA, 300, 663–675.
Kahler, C. W., Read, J. P., Wood, M. D., & Palfai, T. P. (2003). Social environmental selection as a mediator of gender, ethnic, and personality effects on college student drinking. Psychology of Addictive Behaviors, 17, 226–234.
Kitsantas, A. (2004). Studying abroad: The role of college students’ goals on the development of cross-cultural skills and global understanding. College Student Journal, 38, 441–453.
Kohls, R. (1979). Survival kit for overseas living. Chicago, IL: Intercultural Press.
Kyrpi, K., Saunders, J. B., Williams, S. M., McGee, R. O., Langley, J. D., et al. (2004). Web-based screening and brief intervention for hazardous drinking: A double-blind randomized controlled trial. Addiction, 99, 1410–1417.
Larimer, M. E., & Cronce, J. M. (2007). Identification, prevention, and treatment revisited: Individual-focused college drinking prevention strategies: 1999–2006. Addictive Behaviors, 32, 2439–2468.
Latane, B. (1981). The psychology of social impact. American Psychologist, 36, 343–356.
Lewis, M. A., Neighbors, C., Oster-Aaland, L., Kirkeby, B., & Larimer, M. E. (2007). Indicated prevention for incoming college freshmen: Personalized feedback and high risk drinking. Addictive Behaviors, 32, 2495–2508.
Makimoto, K. (1998). Drinking patterns and drinking problems among Asian-Americans and Pacific Islanders. Alcohol Health and Research World, 22, 270–275.
Mori, S. (2000). Addressing the mental health concerns of international students. Journal of Counseling & Development, 78, 137–144.
Mumford, D. B. (1998). The measurement of culture shock. Social Psychiatry and Psychiatric Epidemiology, 33, 149–158.
Neff, R. K., Prihoda, T. J., & Hoppe, S. K. (1991). “Machismo,” self-esteem, education and high maximum drinking among Anglo, Black, and Mexican-American male drinkers. Journal of Studies on Alcohol, 52, 458–463.
Neighbors, C., Lee, C. M., Lewis, M. A., Fossos, N., & Larimer, M. E. (2007). Are social norms the best predictor of outcomes among heavy drinking college students? Journal of Studies on Alcohol and Drugs, 68, 556–565.
Oetting, E. R., Donnermeyer, J. F., Trimble, J. E., & Beauvais, F. (1998). Primary socialization theory: Culture, ethnicity, and cultural identification. The links between culture and substance use. IV. Substance Use & Misuse, 33, 2075–2107.
Office of Applied Studies. (2008). Results from the 2007 National Survey on Drug Use and Health: National findings (DHHS Publication No. SMA 08-4343, NSDUH Series H-34). Rockville, MD: Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration.
Pedersen, E. R., LaBrie, J. W., & Hummer, J. F. (2009). Perceived behavioral alcohol norms predict drinking for college students while studying abroad. Journal of Studies on Alcohol and Drugs, 70, 924–928.
Pedersen, E. R., LaBrie, J. W., Hummer, J. F., Larimer, M. E., & Lee, C. M. (2010a). Heavier drinking American college students may self-select into study abroad programs: An examination of sex and ethnic differences within a high-risk group. Addictive Behaviors, 35, 844–847.
Pedersen, E. R., Larimer, M. E., & Lee, C. M. (2010b). When in Rome: Factors associated with changes in drinking behavior among American college students studying abroad. Psychology of Addictive Behaviors, 24, 535–540.
Perkins, H. W. (2002). Social norms and the prevention of alcohol misuse in collegiate contexts. Journal of Studies on Alcohol, 14, 164–172.
Perkins, H. W., & Berkowitz, A. D. (1986). Perceiving the community norms of alcohol use among students: Some research implications for campus alcohol education programming. International Journal of the Addictions, 21, 961–976.
Poyrazli, S., Arbona, C., Nora, A., McPherson, R., & Pisecco, S. (2002). Relation between assertiveness, academic self-efficacy, and psychosocial adjustment among international graduate students. Journal of College Student Development, 43, 632–642.
Robins, G., Elliott, P., & Pattison, P. (2001). Network models for social selection processes. Social Networks, 23, 1–30.
Ryder, A. G., Alden, L. E., & Paulhus, D. L. (2000). Is acculturation unidimensional or bidimensional? A head-to-head comparison in the prediction of personality, self-identity, and adjustment. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 79, 49–65.
Salant, T., & Lauderdale, D. S. (2003). Measuring culture: A critical review of acculturation and health in Asian immigrant populations. Social Science & Medicine, 57, 71–90.
Sue, S., Zane, N., & Ito, J. (1979). Alcohol drinking patterns among Asian and Caucasian Americans. Journal of Cross-Cultural Psychology, 10, 41–56.
Taft, R. (1977). Coping with unfamiliar cultures. In N. Warren (Ed.), Studies in cross-cultural psychology, vol. 1 (pp. 121–153). London: Academic.
Thombs, D. L., Beck, K. H., & Pleace, D. J. (1993). The relationship of social context and expectancy factors to alcohol use intensity among 18–22 year olds. Addiction Research, 1, 59–68.
Unger, J. B., Gallaher, P., Shakib, S., Ritt-Olson, A., Palmer, P. H., & Johnson, C. A. (2002). The AHIMSA Acculturation Scale: A new measure of acculturation for adolescents in a multicultural society. Journal of Early Adolescence, 22, 225–251.
Walters, S. T., & Neighbors, C. (2005). Feedback interventions for college alcohol misuse: What, why, and for whom? Addictive Behaviors, 30, 1168–1182.
White, H. R. (2006). Reduction of alcohol-related harm on United States college campuses: The use of personal normative feedback interventions. International Journal of Drug Policy, 17, 310–319.
Wilkinson, S. (1998). On the nature of immersion during study abroad: Some participant perspectives. Frontiers: The Interdisciplinary Journal of Study Abroad, 4, 121–138.
Wood, M. D., Read, J. P., Palfai, T. P., & Stevenson, J. F. (2001). Social influence processes and college student drinking: The mediational role of alcohol outcome expectancies. Journal of Studies on Alcohol, 62, 32–43.
World Health Organization (WHO). (2004). Global status report: Alcohol policy. Geneva: World Health Organization (WHO).
Zenmore, S. E. (2007). Acculturation and alcohol among Latino adults in the United States: A comprehensive review. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research, 31, 1968–1990.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This research was supported by a National Research Service Award (1F31AA018591) awarded to Eric Pedersen from the National Institute of Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (NIAAA).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pedersen, E.R., Cruz, R.A., LaBrie, J.W. et al. Examining the Relationships Between Acculturation Orientations, Perceived and Actual Norms, and Drinking Behaviors of Short-Term American Sojourners in Foreign Environments. Prev Sci 12, 401–410 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11121-011-0232-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11121-011-0232-7