Abstract
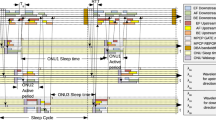
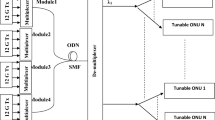
We propose an energy-aware mechanism (EAM) applicable to the multichannel Ethernet Passive Optical Network that can minimize the number of wavelength channels used and save energy. Wavelength channel minimization is processed by collecting the information such as request message, allocated grant, and start time of each optical network unit (ONU) transmission in the previously elapsed scheduling cycles and comparing it with the buffer occupancy and packet delay conditions of the ONUs required by the user’s quality-of-service requirement. They are exchanged between the optical line terminal (OLT) and the ONUs via the multipoint control protocol. In this way, at the beginning of each scheduling cycle, the ONU’s buffer occupancy and packet delay conditions can be evaluated, and then, the OLT decides the smallest number of wavelength channels to be used in the current scheduling cycle. By turning off the OLT receivers corresponding to the unused wavelength channels, the OLT can save energy. The performance of the proposed EAM was evaluated through simulations using nonjoint off-line dynamic bandwidth allocation and dynamic wavelength assignment algorithms. The results showed that the OLT receivers’ power consumption could be reduced by 48 % on average.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yan, Y., Wong, S.-W., Valcarenghi, L., Yen, S.-H., Campelo, D.R., Yamashita, S., Kazovsky, L., Dittmann, L.: Energy management mechanism for Ethernet Passive Optical Networks (EPONs). In: Proc. 2010 IEEE Int. Conf. Commun, Cape Town, South Africa, (May. 2010), pp 1-5
Kubo, R., Kani, J., Ujikawa, H., Sakamoto, T., Fujimoto, Y., Yoshimoto, N., Hadama, H.: Study and demonstration of sleep and adaptive link rate control mechanism for energy efficient 10G-EPON. J. Opt. Commun. Netw. 2(9), 716–729 (2010)
Shi, L., Mukherjee, B., Lee, S.-S.: Energy-efficient PON with sleep-mode ONU: progress, challenges, and solutions. IEEE Netw. Mag. 26(2), 36–41 (2012)
Garfias, P., Sallent, S., Gutierrez, L., Andrade, M.D., Tornatore, M., Buttaboni, A.: A novel traffic-aware mechanism for energy-saving at the OLT in WDM/TDM PON. 18th European Conference on NOC/OC&I (2013)
IEEE Standard for Ethernet 802.3-2012, Section Five
Zhang, J., Ansari, N.: Scheduling hybrid WDM/TDM Passive Optical Networks with nonzero laser tuning time, IEEE/ACM Trans. Netw. (2010)
Dhaini, A.R., Assi, C.M., Maier, M., Shami, A.: Dynamic wavelength and bandwidth allocation in hybrid TDM/WDM EPON networks. J. Lightwave Technol. 25(1), 277–286 (2007)
McGarry, M.P., Reisslein, M., Maier, M.: WDM ethernet passive optical networks. IEEE Opt. Commun. 44(2), 15–22 (2006)
Kramer, G., Mukherjee, B., Pesavento, G.: Interleaved polling with adaptive cycle time (IPACT): a dynamic bandwidth distribution scheme in an optical access network. photonic Netw. Commu. 4(1), 89–107 (2002)
Kani, J.: Enabling technologies for future scalable and flexible WDM-PON and WDM/TDM-PON systems. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 16(5), 1290–1297 (2010)
Zhou, Z., Xiao, S., Bi, M., Zhu, M., Li, P., Qi, T., Hu, W.: Tolerant-scheduling with channel switch latency consideration for hybrid WDM/TDM PON, ONDM, Brest, (France, 2013)
Yoshida, T., Kaneko, S., Kimura, S., Yoshimoto, N.: An automatic load-balancing DWBA algorithm considering long-time tuning devices for \(\lambda \)-tunable WDM/TDM-PON (2013)
Rafig, A., Zaidi, S.M.H., Ramzan, M.: Comparative analyses of scheduling frameworks for efficient wavelength utilization in WDM EPONs, IEEE
Kiaei, Mohammad S., Meng, L., Assi, C., Maier, M.: Efficient scheduling and Grant sizing method for WDM PONs. IEEE, J. Lightwave Technol., 28(13), 1922–1931 (2010)
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the MSIP (Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning), Korea, under the C-ITRC (Convergence Information Technology Research Center) (IITP-2015-H8601-15-1006) supervised by the IITP (Institute for Information & communications Technology Promotion).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shagdar, G., Kim, J. & Park, CS. Wavelength channel minimization-based energy-aware mechanism in a multichannel EPON. Photon Netw Commun 32, 61–72 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11107-015-0576-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11107-015-0576-1