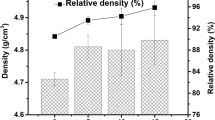
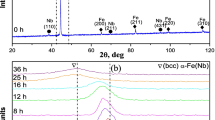
Starting mixtures of BaCO3, ZnO, and TiO2 powders are mechanically activated in a planetary ball mill for various periods of time. The powders obtained are sintered isothermally at 1100°C for 120 min. Non-isothermal sintering process is followed by measurements with a sensitive dilatometer, as well. Results of microstructure characterization using SEM analyses along with DTA analyses are provided. These results are correlated with the values of electric resistivity, capacitance, and loss tangent of the samples, and it is found that with increasing milling time, the increase in values of electrical properties is noticed.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
W. Guoquing, W. Shunhua, and S. Hao, “Microwave dielectric ceramics in the BaO–TiO2–ZnO system doped with MnCO3 and SnO2,” Mat. Lett., 59, 2229 (2005).
J.-H. Choy, Y.-S. Han, and S.-H. Hwang, “Citrate route to Sn-doped BaTi4O9 with microwave dielectric properties,” J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 81, 3197 (1998).
K. H. Yoon, J. B. Kim, W. S. Kim, and E. S. Kim, “Effect of BaSnO3 on the microwave dielectric properties of BaTi9O20,” J. Mater. Res., 11, 1996 (1996).
T. Negas, G. Yeager, S. Bell, and N. Coats, “BaTi4O9/Ba2Ti9O20–based ceramics resurrected for modern microwave applications,” Am. Ceram. Soc. Bull., 72, 80 (1993).
W.-Y. Lin, R. F. Speyer, W. S. Hackenberger, and T. R. Shrout, “Microwave properties of Ba2Ti9O20 doper with zirconium and tin oxides,” J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 82, 1207 (1999).
X. Wang, M. Gu, B. Yang, S. Zhu, and W. CaO, “Hall effect and dielectric properties of Mn-doped barium titanate,” Microelectron. Eng., 66, 855 (2003).
B. D. Stojanovic, A. Z. Simoes, C. O. Paiva-Santos, C. Jovalekic, V. V. Mitic, and J. A. Varela, “Mechanochemical synthesis of barium titanate,” J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 25, 1985 (2005).
A. Balous, O. Ovchar, M. Macek-Krzmanc, and M. Valant, “The homogeneity range and microwave dielectric properties of the BaZn2Ti4O11 ceramics,” J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 26, 3733 (2006).
O. Yamaguchi, M. Morimi, H. Kawabata, and K. Shimizu, “Formation and transformation of ZnTiO3,” J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 70, 97 (1987).
K. T. Paul, S. K. Satpathy, I. Manna, K. K. Chakraborty, and G. B. Nando, “Preparation and characterization of nanostructured materials from fly ash: a waste from thermal power stations, by high energy ball milling,” Nanoscale Res. Lett., 2, 397-404 (2007).
Acknowledgement
This study is a part of Project 142011 G financed by the Ministry of Science of Republic of Serbia and F7 Project financed by the Serbian Academy of Sciences and Arts.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Published in Poroshkovaya Metallurgiya, Vol. 50, No. 11–12 (482), pp. 48–53, 2011.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Obradovic, N., Filipovic, S., Mitric, M. et al. Influence of mechanical activation on electrical properties of barium–zinc–titanate ceramics sintered at 1100°C. Powder Metall Met Ceram 50, 714–718 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11106-012-9380-y
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11106-012-9380-y