Abstract
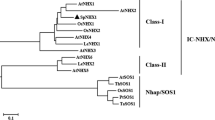
The vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporter NHX gene is a salt tolerance determinant in higher plants. Pyrus betulaefolia, a popular rootstock in Asia, can improve pear salt tolerance through grafting. In this study, two novel NHX genes were isolated from P. betulaefolia using its NaCl-treated transcriptome information. Both PbNHX2.1 and PbNHX2.2 have typical DNA structures and conservative protein motifs often found in vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporters. They are classified as the same NHXs in the phylogenetic tree. Furthermore, both PbNHX2s localized to the plant cell tonoplast. The NaCl treatment strongly induced the expression of PbNHX2.1 in shoots and PbNHX2.2 in the whole plant, but the transcript levels of PbNHX2.2 were much higher. This result meant that they have diverse functions during sodium ion transport in P. betulaefolia. The PbNHX2.2 transcription was influenced by polyethylene glycol and abscisic acid (ABA). An ABA cis-acting element was found in its promoter region, which indicated that PbNHX2.2 transcriptional regulation under salt and osmotic stresses may be ABA-dependent. Yeast recombined experiments revealed that PbNHX2.1 and PbNHX2.2 restored, with different efficacies, the Na+-sensitive phenotype of a endosomal/vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporter mutant, AXT3. These PbNHX2s proteins, especially PbNHX2.2, facilitated Na+ ion transport and maintained intracellular K+ status. The results suggest that PbNHX2.2 was a salt tolerance determinant and had a major function in the vacuolar compartmentalization of Na+. The information on gene features, transcriptional pattern, and the basic function of the NHX family members in P. betulaefolia will help reveal the molecular mechanism underlying salt tolerance in this species.






Similar content being viewed by others

Abbreviations
- ABA:
-
Abscisic acid
- GFP:
-
Green fluorescent protein
- Hyg:
-
Hygromycin
- MEGA:
-
Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis
- NHX:
-
Na+/H+ antiporter
- OD600 :
-
Absorbance value at 600 nm
- ORF:
-
Open reading frame
- PEG:
-
Polyethylene glycol
- qPCR:
-
Quantitative PCR
References
Andres Z, Perez-Hormaeche J, Leidi EO, Schlucking K, Steinhorst L, McLachlan DH, Schumacher K, Hetherington AM, Kudla J, Cubero B, Pardo JM (2014) Control of vacuolar dynamics and regulation of stomatal aperture by tonoplast potassium uptake. Proc Natl Acad Sci 111(17):E1806–E1814
Bailey TL, Elkan C (1994) Fitting a mixture model by expectation maximization to discover motifs in biopolymers. Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Intelligent Systems for Molecular Biology. AAAI Press, Menlo Park, pp. 28–36
Bañuelos MA, Sychrová H, Bleykasten-Grosshans C, Souciet JL, Potier S (1998) The Nha1 antiporter of Saccharomyces cerevisiae mediates sodium and potassium efflux. Microbiology 144:2749–2758
Barragan V, Leidi EO, Andres Z, Rubio L, Luca AD, Fernandez JA, Cubero B, Pardoa JM (2012) Ion exchangers NHX1 and NHX2 mediate active potassium uptake into vacuoles to regulate cell turgor and stomatal function in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 24:1127–1142
Bassil E, Blumwald E (2014) The ins and outs of intracellular ion homeostasis: NHX-type cation/H+ transporters. Curr Opin Plant Biol 22:1–6
Bassil E, Tajima H, Liang YC, Ohto M, Ushijima K, Nakano R, Esumi T, Coku A, Belmonte M, Blumwald E (2011) The Arabidopsis Na+/H+ antiporters NHX1 and NHX2 control vacuolar pH and K+ homeostasis to regulate growth, flower development, and reproduction. Plant Cell 23:3482–3497
Bassil E, Coku A, Blumwald E (2012) Cellular ion homeostasis: emerging roles of intracellular NHX Na+/H+ antiporters in plant growth and development. J Exp Bot 63:5727–5740
Cao B, Long D, Zhang M, Liu C, Xiang Z, Zhao A (2016) Molecular characterization and expression analysis of the mulberry Na+ /H+ exchanger gene family. Plant Physiol Biochem 99:49–58
Chanroj S, Wang GY, Venema K, Zhang MW, Delwiche CF, Sze H (2012) Conserved and diversified gene families of monovalent cation/H+ antiporters from algae to flowering plants. Front Plant Sci 3(25):25
Fukuda A, Nakamura A, Hara N, Toki S, Tanaka Y (2011) Molecular and functional analyses of rice NHX-type Na+/H+ antiporter genes. Planta 233:175–188
Gietz D, St. Jean A, Woods RA, Schiestl RH (1992) Improved method for high efficiency transformation of intact yeast cells. Nucleic Acids Res 20:1425
Lescot M, Déhais P, Thijs G, Marchal K, Moreau Y, Van de Peer Y, Rouze P, Rombauts S (2002) PlantCARE, a database of plant cis-acting regulatory elements and a portal to tools for in silico analysis of promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res 30:325–327
Li H, Lin J, Yang QS, Li XG, Chang YH (2017) Comprehensive analysis of differentially expressed genes under salt stress in pear (Pyrus betulaefolia) using RNA-Seq. Plant Growth Regul 82:409–420. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-017-0266-3
Liu L, Zeng YL, Pan XY, Zhang FC (2012) Isolation, molecular characterization, and functional analysis of the vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporter genes from the halophyte Karelinia caspica. Mol Biol Rep 39:7193–7202
Maathuis FJM (2009) Physiological functions of mineral macronutrients. Curr Opin Plant Biol 12:250–258
Matsumoto K, Chun JP, Tamura F, Kamamoto Y, Tanabe K (2006) Salt tolerance in Pyrus species is linked to levels of Na and cl translocation from roots to leaves. J Jpn Soc Hortic Sci 75:385–391
Matsumoto K, Tamura F, Chun JP, Ikeda T, Imanishi K, Tanabe K (2007) Enhancement in salt tolerance of Japanese pear by using Pyrus betulaefolia rootstock. Hortic Res-Japan 6:47–52
Montiel V, Ramos J (2007) Intracellular Na+ and K+ distribution in Debaryomyces hansenii. Cloning and expression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae of DhNHX1. FEMS Yeast Res 7:102–109
Nass R, Rao R (1998) Novel localization of a Na+/H+ exchanger in a late endosomal compartment of yeast: implications for vacuole biogenesis. J Biol Chem 273:21054–21060
Ohnishi M, Fukada-Tanaka S, Hoshino A, Takada J, Inagaki Y, Iida S (2005) Characterization of a novel Na+/H+ antiporter gene InNHX2 and comparison of InNHX2 with InNHX1, which is responsible for blue flower coloration by increasing the vacuolar pH in Japanese morning glory. Plant Cell Physiol 46:259–267
Okubo M, Sakuratani T (2000) Effects of sodium chloride on survival and stem elongation of two Asian pear rootstock seedlings. Sci Hortic 85:85–90
Okubo M, Furukawa Y, Sakuratani T (2000) Growth, flowering and leaf properties of pear cultivars grafted on two Asian pear rootstock seedlings under NaCl irrigation. Sci Hortic 85:91–101
Rodríguez-Rosales MP, Jiang X, Gálvez FJ, Aranda MN, Cubero B, Venema K (2008) Overexpression of the tomato K+/H+ antiporter LeNHX2 confers salt tolerance by improving potassium compartmentalization. New Phytol 179:366–377
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28:2731–2739
Tuteja N (2007) Chapter twenty-four—mechanisms of high salinity tolerance in plants. Methods Enzymol 428:419–438
Wang B, Zhai H, He SZ, Zhang H, Ren ZT, Zhang DD, Liu QC (2016) A vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporter gene, IbNHX2, enhances salt and drought tolerance in transgenic sweetpotato. Sci Hortic 201:153–166
Wei Q, Guo YJ, Cao HM, Kuai BK (2011) Cloning and characterization of an AtNHX2-like Na+/H+ antiporter gene from Ammopiptanthus mongolicus (Leguminosae) and its ectopic expression enhanced drought and salt tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 105:309–316
Wu GX, Wang G, Ji J, Li Y, Gao HL, Wu J, Guan WZ (2015) A chimeric vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporter gene evolved by DNA family shuffling confers increased salt tolerance in yeast. J Biotechnol 203:1–8
Xu Y, Zhou Y, Hong S, Xia Z, Cui D, Guo J, Xu H, Jiang X (2013) Functional characterization of a wheat NHX antiporter gene TaNHX2 that encodes a K+/H+ exchanger. PLoS One 8(11):e78098
Yokoi S, Quintero FJ, Cubero B, Ruiz MT, Bressan RA, Hasegawa PM, Pardo JM (2002) Differential expression and function of Arabidopsis thaliana NHX Na+/H+ antiporters in the salt stress response. Plant J 30:529–539
Yu JN, Huang J, Wang ZN, Zhang JS, Chen SY (2007) An Na+/H+ antiporter gene from wheat plays an important role in stress tolerance. J Biosci 32:1153–1161
Zhu JK (2003) Regulation of ion homeostasis under salt stress. Curr Opin Plant Biol 6:441–445
Acknowledgments
We thank International Science Editing (http://www.internationalscienceediting.com) for editing this manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Jiangsu Agriculture Science and Technology Innovation Fund of China [Grant No. CX (14) 5018], the Jiangsu Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. BK20151361), and the National Natural Sciences Foundation of China (Grant No. 1372051).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic Supplementary Material
ESM 1
(DOCX 19 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, H., Liu, W., Yang, QS. et al. Isolation and Comparative Analysis of Two Na+/H+ Antiporter NHX2 Genes from Pyrus betulaefolia. Plant Mol Biol Rep 36, 439–450 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11105-018-1089-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11105-018-1089-8