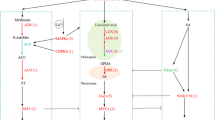
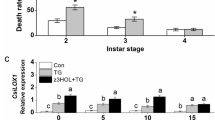
Abstract
Tea is the second most consumed beverage worldwide whose cultivation is greatly challenged by a large variety of biotic and abiotic stresses. Among the biotic factors, the hemipteran pest Helopeltis theivora Waterhouse is particularly devastating in Asia and Africa, rendering the crop unsuitable for any downstream processing. The present study, for the first time, endeavors to dissect the molecular events associated with such infestations and identify potential molecular protagonists influencing Helopeltis tolerance in Assam tea. We analyzed the transcriptome of infested tea plants having contrasting responses to pest feeding by suppression subtractive hybridization and quantified the relative abundances of defense-associated transcripts. We analyzed 445 unigenes derived from 1558 expressed sequence tags (ESTs) from three different infestation conditions. Our study indicate that defense responses to the pest greatly vary in temporal and cultivar-specific manner characterized by an exclusive upregulation of specific defense-associated genes in the tolerant cultivar. Moreover, it was observed that transcripts related to flavonoid biosynthesis, purine metabolism, formate metabolism, jasmonic acid biosynthesis and signaling, and cell wall metabolism are uniquely enriched in the same. Interestingly, those involved in caffeine biosynthesis remain comparatively low and unaltered. We report higher trichome densities on the abaxial surface of the leaf in tolerant cultivar while puncture causes their tender reorientation. SEM of the insect mouthparts reveal higher concentrations of sensilla-like structures near the distal end and tip of the proboscis which are known to act as chemoreceptors in other hemipterans. Our investigation provides the first ever glimpse of Helopeltis-induced defense gene network and provides the much needed platform for improvement of the crop for better Helopeltis tolerance through breeding and transgenic approaches. On a wider perspective, the study will augment our understanding of molecular responses to phloem herbivory in plants.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alonso C, Ossipova S, Ossipov V (2002) A high concentration of glucogallin, the common precursor of hydrolysable tannins, does not deter herbivores. J Insect Behav 15:649–657
Annual scientific report (TRA). 2008–09 p 6.
Arimura GI, Kost C, Boland W (2005) Herbivore-induced, indirect plant defences. Biochim Biophys Acta 1734:91–111
Ashburner M, Ball CA, Blake JA, Botstein D, Butler H, Cherry JM, Davis AP, Dolinski K, Dwight SS, Eppig JT, Harris MA, Hill DP, Issel-Tarver L, Kasarskis A, Lewis S, Matese JC, Richardson JE, Ringwald M, Rubin GM, Sherlock G (2000) Gene ontology: tool for the unification of biology. The gene ontology consortium. Nat Genet 25:25–29
Bandopadhyay L, Basu D, Sikdar SR (2013) Identification of genes involved in wild crucifer Rorippa indica resistance response on mustard aphid Lipaphis erysimi challenge. PLoS One 8(9):e73632
Bandyopadhyay T, Gohain B et al (2014) Identification, cloning and heterologous expression of a new lectin like protein in tea. J Appl Res Med Aromat Plants. doi:10.1016/j.jarmap.2014.03.003
Barbora BC, Singh K (1994) All about Helopeltis theivora: a serious pest of tea. Two Bud 41(2):19–21
Barua DN (1994) Science and practice in tea culture. Tea Res Assoc, Calcutta, 509 pp
Bora S, Sarmah M, Bahamans A, Gurusubramanian G (2007) Relative toxicity of pyrethroid and non-pyrethroid insecticides against male and female tea mosquito bug, Helopeltis theivora waterhouse (Darjeeling strain). J Dent Res 31(1):37–41
Bouché N, Yellin A, Snedden WA, Fromm H (2005) Plant-specific calmodulin-binding proteins. Annu Rev Plant Biol 56:435–466
Bu Q, Jiang H, Li CB, Zhai Q, Zhang J et al (2008) Role of the Arabidopsis thaliana NAC transcription factors ANAC019 and ANAC055 in regulating jasmonic acid-signaled defense responses. Cell Res 18:756–767
Conesa A, Gotz S, Garcia-Gomez JM, Terol J, Talon M, Robles M (2005) Blast2GO: a universal tool for annotation, visualization and analysis in functional genomics research. Bioinformatics 21:3674–3676
Das A, Das S, Mondal TK (2012) Identification of differentially expressed gene profiles in young roots of tea [Camellia sinensis (L.) O. Kuntze] subjected to drought stress using suppression subtractive hybridization. Plant Mol Biol Rep 30:1088–1101
Davies KM, Schwinn KE, Deroles SC, Manson DG, Lewis DH, Bloor SJ, Bradley JM (2003) Enhancing anthocyanin production by altering competition for substrate between flavonol synthase and dihydroflavonol 4-reductase. Euphytica 131(3):259–268
Deka A, Deka PC, Mondal TK (2006) Tea. In: Parthasarathy VA, Chattopadhyay PK, Bose TK (eds) Plantation crops, vol 1. Naya Udyog, Kolkata, pp 1–147, xi, 519 p
Dey S, Baul TSB, Roy B, Dey D (1989) A new rapid method of air-drying for scanning electron microscopy using tetramethylsilane. J Microsc 156:259–261
Ebbole DJ, Jin Y, Thon M, Pan H, Bhattarai E, Thomas T, Dean R (2004) Gene discovery and gene expression in the rice blast fungus, Magnaporthe grisea: analysis of expressed sequence tags. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 17(12):1337–1347
Gao LL, Klingler JP, Anderson JP, Edwards OR, Singh KB (2008) Characterization of pea aphid resistance in Medicago truncatula. Plant Physiol 146:996–1009
Gohain B, Borchetia S, Bhorali P, Agarwal N, Bhuyan LP, Rahman A, Sakata K, Mizutani M, Shimizu B, Gurusubramaniam G, Ravindranath R, Kalita MC, Hazarika M, Das S (2012) Understanding Darjeeling tea flavour on a molecular basis. Plant Mol Biol 78(6):577–597
Goławska S, Sprawka I, Łukasik I, Goławski A (2014) Are naringenin and quercetin useful chemicals in pest-management strategies? J Pest Sci 87(1):173–180
Gu SH, Wang WX, Wang GR, Zhang XY, Guo YY et al (2011) Functional characterization and immunolocalization of odorant binding protein 1 in the lucerne plant bug, Adelphocoris lineolatus (GOEZE). Arch Insect Biochem Physiol 77(2):81–99. doi:10.1002/arch.20427
Gupta S, Bharalee R, Bhorali P, Das SK, Bhagawati P, Bandyopadhyay T, Gohain B, Agarwal N, Ahmed P, Borchetia S, Kalita MC, Handique AK, Das S (2013) Molecular analysis of drought tolerance in tea by cDNA-AFLP based transcript profiling. Mol Biotechnol 53(3):237–248. doi:10.1007/s12033-012-9517-8
Hare JD (2002) Seasonal variation in the leaf resin components of Mimulus aurantiacus. Biochem Syst Ecol 30:709–720
Hazarika LK, Bhuyan M, Hazarika BN (2009) Insect pests of tea and their management. Ann Rev Entomol 54:267–284
Jain NK (1999) (ed) Global Advances in Tea Science. Aravali Books, New Delhi, 882 pp
Jang CS, Kim JY, Haam JW, Lee MS, Kim DS, Li YW, Seo YW (2003) Expressed sequence tags from a wheat–rye translocation line (2BS/2RL) infested by larvae of Hessian fly [Mayetiola destructor (Say)]. Plant Cell Rep 22:150–158
Kang JH, Liu G, Shi F, Jones AD, Beaudry RM, Howe GA (2010a) The tomato odorless-2 mutant is defective in trichome-based production of diverse specialized metabolites and broad-spectrum resistance to insect herbivores. Plant Physiol 154:262–272
Kang JH, Shi F, Jones AD, Marks MD, Howe GA (2010b) Distortion of trichome morphology by the hairless mutation of tomato affects leaf surface chemistry. J Exp Bot 61:1053–1064
Kempema LA, Cui XP, Holzer FM, Walling LL (2007) Arabidopsis transcriptome changes in response to phloem-feeding silverleaf whitefly nymphs. Similarities and distinctions in responses to aphids. Plant Physiol 143:849–865
Keon J, Antoniw J, Rudd J, Skinner W, Hargreaves J, Hammond-Kosack K (2005) Analysis of expressed sequence tags from the wheat leaf blotch pathogen Mycosphaerella graminicola (anamorph Septoria tritici). Fungal Genet Biol 42:376–389
Kumar D, Klessig DF (2003) High-affinity salicylic acid-binding protein 2 is required for plant innate immunity and has salicylic acid-stimulated lipase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100:16101–16106
Laudert D, Weiler EW (1998) Allene oxide synthase: a major control point in Arabidopsis thaliana octadecanoid signaling. Plant J 15:675–684
Leon J, Rojo E, Sanchez-Serrano JJ (2001) Wound signalling in plants. J Exp Bot 52:1–9
Li C et al (2005) Role of beta-oxidation in jasmonate biosynthesis and systemic wound signaling in tomato. Plant Cell 17:971–986
Liu S, Han B (2010) Differential expression pattern of an acidic 9/13-lipoxygenase in flower opening and senescence and in leaf response to phloem feeders in the tea plant. BMC Plant Biol 10:228
Liu X, Meng J, Starkey S, Smith CM (2011) Wheat gene expression is differentially affected by a virulent Russian wheat aphid biotype. J Chem Ecol 37:472–482
Logemann J, Schell J, Willmitzer L (1987) Improved method for the isolation of RNA from plant tissues. Anal Biochem 163:16–20
Mohase L, Van Der Westhuizen AJ (2002) Salicylic acid is involved in resistance responses in the Russian wheat aphid-wheat interaction. J Plant Physiol 159:585–590
Moran PJ, Thompson GA (2001) Molecular responses to aphid feeding in Arabidopsis in relation to plant defense pathways. Plant Physiol 125:1074–1085
Mukhopadhyay A, Roy S (2013) Development of tolerant traits in tea mosquito bug (Helopeltis Theivora Waterhouse) (Hemiptera: Miridae) under insecticide stress. Int J Bioresour Stress Manag 4(3):418
Muraleedharan N (1992) Pest control in Asia. In: Wilson KC, Clifford MN (eds) Tea: cultivation to consumption. Chapman & Hall Inc., London, pp 375–412
Neubert C, Graham LA, Black-Maier EW, Coonrod EM, Liu T-Y, Stierhof Y-D, Seidel T, Stevens TH, Schumacher K (2008) Arabidopsis has two functional orthologs of the yeast V-ATPase assembly factor Vma21p. Traffic 9:1618–1628
O’Donnell PJ, Calvert C, Atzorn R, Wasternack C, Leyser HMO, Bowles DJ (1996) Ethylene as a signal mediating the wound response of tomato plants. Science 274:1914–1917
Peiffer M, Tooker JF, Luthe DS, Felton GW (2009) Plants on early alert: glandular trichomes as sensors for insect herbivores. New Phytol 184:644–656
Reich M, Liefeld T, Gould J, Lerner J, Tamayo P, Mesirov JP (2006) GenePattern 2.0. Nat Genet 38:500–501
Reinbothe S, Reinbothe C, Lehmann J, Becker W, Apel K, Parthier B (1994) JIP60, a methyl jasmonate-induced ribosome-inactivating protein involved in plant stress reactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 91:7012–7016
Roy S, Mukhopadhyay A, Gurusubramanian G (2009) The synergists action of piperonyl butoxide on toxicity of certain insecticides applied against Helopeltis theivora Waterhouse (Heteroptera: Miridae) in the Dooars tea plantations of North Bengal India. J Plant Prot Res 49(2):226–229
Rozen S, Skaletsky H (2000) Primer3 on the WWW for general users and for biologist programmers. Methods Mol Biol 132:365–386
Ruuhola T, Tikkanen O, Tahvanainen J (2001) Differences in host use efficiency of larvae of a generalist moth, Operophtera brumata on three chemically divergent Salix species. J Chem Ecol 27:1595–1615
Sabhapondit S, Bhattacharyya P, Bhuyan LP, Hazarika M, Goswami BC (2014) Optimisation of withered leaf moisture during the manufacture of black tea based upon theaflavins fractions. Int J Food Sci Technol 49:205–209
Sadeghi A, Van Damme EJM, Peumans WJ, Smagghe G (2006) Deterrent activity of plant lectins on cowpea weevil Callosobruchus maculatus (F.) oviposition. Phytochemistry 67:2078–2084
Sarker M, Mukhopadhyay A (2006) Studies on some enzymes related to insecticide esistance in Helopeltis theivora Waterhouse (Insecta: Heteroptera: Miridae) from Darjeeling foothills and plains. J Plant Crops 34:423–428
Schmelz EA, Alborn HT, Banchio E, Tumlinson JH (2003) Quantitative relationships between induced jasmonic acid levels and volatile emission in Zea mays during Spodoptera exigua herbivory. Planta 216:665–673
Shahidi-Noghabi S, Van Damme EJM, Smagghe G (2008) Carbohydrate-binding activity of the type-2 ribosome-inactivating protein SNA-I from elderberry (Sambucus nigra) is a determining factor for its insecticidal activity. Phytochemistry 69:2972–2978
Shahidi-Noghabi S, Van Damme EJM, Smagghe G (2009) Expression of Sambucus nigra agglutinin (SNA-I’) from elderberry bark in transgenic tobacco plants results in enhanced resistance to different insect species. Transgenic Res 18:249–259
Shoji T, Nakajima K, Hashimoto T (2000) Ethylene suppresses jasmonate-induced gene expression in nicotine biosynthesis. Plant Cell Physiol 41:1072–1076
Simmonds MSJ, Stevenson PC (2001) Effects of isoflavonoids from Cicer on larvae of Helicoverpa armigera. J Chem Ecol 27:965–977
Sundararaju D, Sundarababu PC (1999) Helopeltis spp. (Heteroptera: Miridae) and their management in plantation and horticultural crops of India. J Plant Crops 27:155–174
Tian D, Tooker J, Peiffer M, Chung SH, Felton GW (2012) Role of trichomes in defense against herbivores: comparison of herbivore response to woolly and hairless trichome mutants in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum). Planta 236:1053–1066
Treutter D (2006) Significance of flavonoids in plant resistance: a review. Environ Chem Lett 4:147–157
Van Damme EJM (2008) Plant lectins as part of the plant defense system against insects. In : Schaller A (ed) Induced plant resistance to herbivory, Springer, Netherlands, pp 285-307
Vandesompele J, De Preter K, Pattyn F, Poppe B, Van Roy N et al (2002) Accurate normalization of real-time quantitative RT-PCR data by geometric averaging of multiple internal control genes. Genome Biol 3:RESEARCH0034
Wagner GJ (1991) Secreting glandular trichomes—more than just hairs. Plant Physiol 96:675–679
Wei GQ, Liu RS, Wang Q, Liu WQ (2004) Toxicity of two type II ribosome-inactivating proteins (cinnamomin and ricin) to domestic silkworm larvae. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol 57:160–165
Wilson KC, Clifford MN (eds) (1992a) Tea: Cultivation to Consumption. Chapman & Hall, London, 769 pp.
Wilson KC, Clifford MN (eds) (1992b) Tea: cultivation to consumption. Chapman & Hall, London, pp 331–352
Xu J, Wang H, Fan J (2007) Expression of a ribosome-inactivating protein gene in bitter melon is induced by Sphaerotheca fuliginea and abiotic stimuli. Biotechnol Lett 29:1605–1610
Yazaki K (2006) ABC transporters involved in the transport of plant secondary metabolites. FEBS Lett 580:1183–1191
Yu O, Shi J, Hession AO, Maxwell CA, McGonigle B, Odell JT (2003) Metabolic engineering to increase isoflavone biosynthesis in soybean seed. Phytochemistry 63:753–763
Zhou JM, Trifa Y, Silva H, Pontier D, Lam E, Shah J, Klessig DF (2000) NPR1differentially interacts with members of the TGA/OBF family of transcription factors that bind an element of the PR-1 gene required for induction by salicylic acid. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 13:191–202
Acknowledgments
The authors thank A. Rahman for helping with the infestation experiment and R. Bordoloi for help with the cultivars. We are grateful to Department of Biotechnology, Govt. of India for their generous funding for the research.
Accession Numbers
EST data was deposited to NCBI database having accession number HS398504- HS399976.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary File 1
(XLSX 20 kb)
Supplementary File 2
(XLSX 58 kb)
Supplementary File 3
(XLSX 16 kb)
Supplementary File 4
(XLSX 92 kb)
Supplementary File 5
(XLSX 16 kb)
Supplementary File 6
(XLSX 18 kb)
Supplementary File 7
(XLSX 18 kb)
Supplementary File 8
(XLSX 137 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bandyopadhyay, T., Gohain, B., Bharalee, R. et al. Molecular Landscape of Helopeltis theivora Induced Transcriptome and Defense Gene Expression in Tea. Plant Mol Biol Rep 33, 1042–1057 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11105-014-0811-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11105-014-0811-4