Abstract
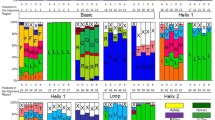
The AP2/ERF family transcription factors (TFs) act as the nodes of a regulatory network in a plant's response to abiotic and biotic stress. AP2-like genes from apple (Malus × domestica Borkh), one of the most widely cultivated fruit trees worldwide, were identified and analysed in order to understand the transcriptional regulation through the AP2/ERF family TFs. Starting from the M. domestica database, 58 AP2-like TFs were identified by in silico cloning using the AP2/ERF TFs amino acid sequence of Arabidopsis thaliana as a probe. The AP2/ERF TFs from apple were classified into four subfamilies, DREB, ERF, AP2 and RAV. To establish detailed expression data of this gene family in apple, six kinds of tissue (bud, flower, fruit, leaf, root and stem) and cell culture were examined for the presence of AP2-like genes. Most of the apple AP2-like genes indicate some degree of tissue specificity and were most abundant in root followed by stem, and expression levels were low in leaf and in bud.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agarwal PK, Agarwal P, Reddy MK, Sopory SK (2006) Role of DREB transcription factors in abiotic and biotic stress tolerance in plants. Plant Cell Rep 25:1263–1274
Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schäffer AA, Zhang J, Zhang Z (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res 25:3389–3402
Arabidopsis Genome Initiative (2000) Analysis of the genome sequence of the flowering plant Arabidopsis thaliana. Nature 408:796–815
Bhatnagar-Mathur P, Vadez V, Sharma KK (2008) Transgenic approaches for abiotic stress tolerance in plants: retrospect and prospects. Plant Cell Rep 27:411–424
Chen WJ, Zhu T (2004) Networks of transcription factors with roles in environmental stress response. Trends Plant Sci 9:591–596
Chen L, Zhang Z, Liang H, Liu H, Du L, Xu H, Xin Z (2008) Overexpression of TiERF1 enhances resistance to sharp eyespot in transgenic wheat. J Exp Bot 59:4195–4204
Chen M, Xu Z, Xia L, Li L, Cheng X, Dong J, Wang Q, Ma Y (2009) Cold-induced modulation and functional analyses of the DRE-binding transcription factor gene, GmDREB3, in soybean (Glycine max L). J Exp Bot 60:121–135
Chenna R, Sugawara H, Koike T, Lopez R, Gibson TJ (2003) Multiple sequence alignment with the Clustal series of programs. Nucleic Acids Res 31:3497–3500
Dubouzet JG, Sakuma Y, Ito Y, Kasuga M, Dubouzet EG (2003) OsDREB genes in rice, Oryza sativa L, encode transcription activators that function in drought-, high-salt- and cold-responsive gene expression. Plant J 33:751–763
Espley RV, Hellens RP, Putterill J, Stevenson DE, Kutty-Amma S, Allan AC (2007) Red colouration in apple fruit is due to the activity of the MYB transcription factor, MdMYB10. Plant J 49:414–427
Espley RV, Brendolise C, Chagné D, Kutty-Amma S, Green S, Volz R, Putterill J, Schouten HJ, Gardiner SE, Hellens RP, Allan AC (2009) Multiple repeats of a promoter segment causes transcription factor autoregulation in red apples. Plant Cell 21:168–183
Gasteiger E, Gattiker A, Hoogland C, Ivanyi I, Appel RD (2003) ExPASy: the proteomics server for in-depth protein knowledge and analysis. Nucleic Acids Res 31:3784–3788
Gil-Humanes J, Pistón F, Martín A, Barro F (2009) Comparative genomic analysis and expression of the APETALA2-like genes from barley, wheat, and barley–wheat amphiploids. BMC Plant Biol 29:66
Guo A, He K, Liu D, Bai S, Gu X (2005) DATF: a database of Arabidopsis transcription factors. Bioinformatics 21:2568–2569
Gutterson N, Reuber TL (2004) Regulation of disease resistance pathways by AP2/ERF transcription factors. Curr Opin Plant Biol 7:465–471
Huang X, Madan A (1999) CAP3: a DNA sequence assembly program. Genome Res 9:868–877
Ito Y, Katsura K, Maruyama K, Taji T, Kobayashi M, Seki M, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2006) Functional analysis of rice DREB1/CBF-type transcription factors involved in cold-responsive gene expression in transgenic rice. Plant Cell Physiol 47:141–153
Jaillon O, Aury JM, Noel B, Policriti A, Clepet C, Casagrande A, Choisne N, Aubourg S, Vitulo N, Jubin C (2007) The grapevine genome sequence suggests ancestral hexaploidization in major angiosperm phyla. Nature 449:463–467
James DJ, Passey AJ, Barbara DJ, Bevan M (1989) Genetic transformation of apple (Malus pumila Mill) using a disarmed Ti-binary vector. Plant Cell Rep 7:658–661
Kazuko YS, Kazuo S (2006) Transcriptional regulatory networks in cellular responses and tolerance to dehydration and cold stresses. Annu Rev Plant Biol 57:781–803
Kizis D, Lumbreras V, Pagès M (2001) Role of AP2/EREBP transcription factors in gene regulation during abiotic stress. FEBS Lett 498:187–189
Li Y, Su X, Zhang B, Huang Q, Zhang X, Huang R (2009) Expression of jasmonic ethylene responsive factor gene in transgenic poplar tree leads to increased salt tolerance. Tree Physiol 29:273–279
Mitsuda N, Ohme-Takagi M (2009) Functional analysis of transcription factors in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Physiol 50:1232–1248
Nakano T, Suzuki K, Fujimura T, Shinshi H (2006) Genome-wide analysis of the ERF gene family in Arabidopsis and rice. Plant Physiol 140:411–432
Navarro M, Marque G, Ayax C, Keller G, Borges JP, Marque C, Teulières C (2009) Complementary regulation of four eucalyptus CBF genes under various cold conditions. J Exp Bot 60:2713–2724
Nakashima K, Ito Y, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2009) Transcriptional regulatory networks in response to abiotic stresses in Arabidopsis and grasses. Plant Physiol 149:88–95
Potter D, Eriksson T, Evans RC, Oh SH, Smedmark JEE, Morgan DR, Kerr M, Robertson KR, Arsenault MP, Dickinson TA, Campbell CS (2007) Phylogeny and classification of Rosaceae. Plant Syst Evol 266:5–43
Qin QL, Liu JG, Zhang Z, Peng RH, Xiong AS (2007) Isolation, optimization, and functional analysis of the cDNA encoding transcription factor RdreB1 in Oryza sativa L. Mol Breed 19:329–340
Riano PDM, Ruzicic S, Dreyer I, Mueller RB (2007) PlnTFDB: an integrative plant transcription factor database. BMC Bioinform 8:42
Riechmann JL, Meyerowitz EM (1998) The AP2/EREBP family of plant transcription factors. Biol Chem 379:633–646
Sakuma Y, Liu Q, Dubouzet JG, Abe H, Shinozaki K (2002) DNA-binding specificity of the ERF/AP2 domain of Arabidopsis DREBs, transcription factors involved in dehydration- and cold-inducible gene expression. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 290:998–1009
Singh K, Foley RC, Oñate-Sánchez L (2002) Transcription factors in plant defense and stress responses. Curr Opin Plant Biol 5:430–436
Takos AM, Jaffé FW, Jacob SR, Bogs J, Robinson SP, Walker AR (2006) Light-induced expression of a MYB gene regulates anthocyanin biosynthesis in red apples. Plant Physiol 142:1216–1232
Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S (2007) MEGA4: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis MEGA software version 4.0. Mol Biol Evol 24:1596–1599
Tuskan GA, Difazio S, Jansson S, Bohlmann J, Grigoriev I, Hellsten U (2006) The genome of black cottonwood, Populus trichocarpa (Torr & Gray). Science 313:1596–1604
Yamaguchi SK, Shinozaki K (2006) Transcriptional regulatory networks in cellular responses and tolerance to dehydration and cold stresses. Annu Rev Plant Biol 57:781–803
Yang TW, Zhang LJ, Zhang TG, Zhang H, Xu SJ (2005) Transcriptional regulation network of cold-responsive genes in higher plants. Plant Sci 169:987–995
Yu J, Hu S, Wang J, Wong GK, Li S, Liu B (2002) A draft sequence of the rice genome (Oryza sativa L ssp indica). Science 296:79–92
Zhang G, Chen M, Chen X, Xu Z, Guan S, Li LC, Li A, Guo J, Mao L, Ma Y (2008) Phylogeny, gene structures, and expression patterns of the ERF gene family in soybean (Glycine max L). J Exp Bot 59:4095–4107
Zhang G, Chen M, Li L, Xu Z, Chen X, Guo J, Ma Y (2009) Overexpression of the soybean GmERF3 gene, an AP2/ERF type transcription factor for increased tolerances to salt, drought, and diseases in transgenic tobacco. J Exp Bot 60:3781–3796
Zhuang J, Cai B, Peng RH, Zhu B, Jin XF, Xue Y, Gao F, Fu XY, Tian YS, Zhao W, Qiao YS, Zhang Z, Xiong AS, Yao QH (2008) Genome-wide analysis of the AP2/ERF gene family in Populus trichocarpa. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 371:468–474
Zhuang J, Peng RH, Cheng ZM, Zhang J, Cai B, Zhang Z, Gao F, Zhu B, Fu XY, Jin XF, Chen JM, Qiao YS, Xiong AS, Yao QH (2009) Genome-wide analysis of the putative AP2/ERF family genes in Vitis vinifera. Sci Hortic 123:73–81
Acknowledgements
The research was supported by the International Scientific and Technological Cooperation of Canada–China (Shanghai–Alberta); Hi-tech Research and Development Program of China (2006AA10Z117); National key Project of Transgenic Crops of China (2009ZX08002-011B); Shanghai Rising-Star Program and Natural Science Foundation (08QH14021, 08ZR1417200).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Table S1
The apple AP2/ERF family member expression profiles suggested by analysis of EST counts based UniGene (Transcripts per millon (TPM). (/: means the cDNA Sources from mixed whole plant) (DOC 97 kb)
Supplementary Figure S1
Comparison of deduced amino acid sequences of the AP2 DNA-binding domains of the AP2 subfamily proteins from A. thaliana and M. domestica. The black background represents conserved amino acid residues in each group. (DOC 134 kb)
Supplementary Figure S2
Comparison of deduced amino acid sequences of the AP2 and B3 DNA-binding domains of the RAV subfamily proteins from A. thaliana and M. domestica. The black background represents conserved amino acid residues in each group. (DOC 104 kb)
Supplementary Figure S3
The classification of AP2/ERF family factors among A. thaliana, O. sativa, V. vinifera and M. domestica. The size of each piece is proportional to the relative abundance to the AP2/ERF genes assigned to this group. (DOC 371 kb)
Supplementary Figure S4
The deduced amino acid sequence alignment of the AP2/ERF DNA-binding domain of ERF subfamily proteins from apple in this study and Arabidopsis. The black background represents conserved amino acid residues in each group. (DOC 348 kb)
Supplementary Figure S5
The deduced amino acid sequences alignment of the AP2/ERF DNA-binding domain of DREB subfamily proteins from apple in this study and Arabidopsis. The black background represents conserved amino acid residues in each group. (DOC 309 kb)
Supplementary Figure S6
Comparison of full length of deduced amino acid sequences of the ERF-B1 group proteins from apple and Arabidopsis. The black background represents conserved amino acid residues in each group. (DOC 106 kb)
Supplementary Figure S7
Comparison of full length of deduced amino acid sequences of the ERF-B2 group proteins from apple and Arabidopsis. The black background represents conserved amino acid residues in each group. (DOC 62 kb)
Supplementary Figure S8
Comparison of full length of deduced amino acid sequences of the ERF-B3 group proteins from apple and Arabidopsis. The black background represents conserved amino acid residues in each group. (DOC 114 kb)
Supplementary Figure S9
Comparison of full length of deduced amino acid sequences of the ERF-B4 group proteins from apple and Arabidopsis. The black background represents conserved amino acid residues in each group. (DOC 62 kb)
Supplementary Figure S10
Comparison of full length of deduced amino acid sequences of the ERF-B5 group proteins from apple and Arabidopsis. The black background represents conserved amino acid residues in each group. (DOC 56 kb)
Supplementary Figure S11
Comparison of full length of deduced amino acid sequences of the ERF-B6 group proteins from apple and Arabidopsis. The black background represents conserved amino acid residues in each group. (DOC 110 kb)
Supplementary Figure S12
Comparison of full length of deduced amino acid sequences of the DREB-A1 group proteins from apple and Arabidopsis. The black background represents conserved amino acid residues in each group. (DOC 42 kb)
Supplementary Figure S13
Comparison of full length of deduced amino acid sequences of the DREB-A4 group proteins from apple and Arabidopsis. The black background represents conserved amino acid residues in each group. (DOC 89 kb)
Supplementary Figure S14
Comparison of full length of deduced amino acid sequences of the DREB-A5 group proteins from apple and Arabidopsis. The black background represents conserved amino acid residues in each group. (DOC 69 kb)
Supplementary Figure S15
Comparison of full length of deduced amino acid sequences of the DREB-A6 group proteins from apple and Arabidopsis. The black background represents conserved amino acid residues in each group. (DOC 77 kb)
Supplementary Figure S16
Comparison of full length of deduced amino acid sequences of the RAV subfamily proteins from apple and Arabidopsis. The black background represents conserved amino acid residues in each group. (DOC 49 kb)
Supplementary Figure S17
Comparison of full length of deduced amino acid sequences of the AP2 subfamily proteins from apple and Arabidopsis. The black background represents conserved amino acid residues in each group. (DOC 114 kb)
Supplementary Figure S18
Tissue-specific expression of the apple DREB subfamily genes. (DOC 27 kb)
Supplementary Figure S19
Tissue-specific expression of the apple AP2 and RAV subfamily genes. (DOC 27 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhuang, J., Yao, QH., Xiong, AS. et al. Isolation, Phylogeny and Expression Patterns of AP2-Like Genes in Apple (Malus × domestica Borkh). Plant Mol Biol Rep 29, 209–216 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11105-010-0227-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11105-010-0227-8