Abstract
Background and aims
The phytoextraction efficiency of metal contaminated soil needs to be improved. Organic amendment can be used to enhance the effectiveness of phytoextraction. However, studies on how organic amendment influence the rhizosphere microbial community of hyperaccumulators are still scarce.
Methods
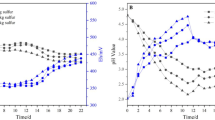
Two kinds of spent mushroom substrates (H and T) and their biochars (HB and TB) were used to facilitate the phytoextraction by Sedum alfredii Hance. The phytoextraction efficiency was monitored by measuring Cd, Zn and Pb extraction and the subsequent changes of soil microbial biomass, activity and diversity (indicators of soil health and functioning) .
Results
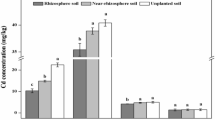
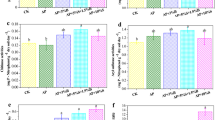
Compared to the control, the H and T amendments increased S. alfredii Cd uptake by 92% and 73%, and Zn by 106% and 67%, respectively. Organic amendments increased the microbial biomass and activities and substantially changed bacterial composition and diversity of rhizosphere soil. The relative abundances of some rhizosphere beneficial genera such as Promicromonospora, Acidibacter, Roseiflexus, Microbispora, Kribbella and Streptomyces were significantly increased under the H and T treatments.
Conclusions
Spent mushroom substrates enhanced metal extraction of S. alfredii and improved soil health by increasing microbial biomass, activity and changing microbial community composition thus providing an effective option to facilitate phytoextraction of metal contaminated soil.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad M, Ok YS, Rajapaksha AU, Lim JE, Kim BY, Ahn JH, Leed YH, Al-Wabelb MI, Lee SE, Lee SS (2016) Lead and copper immobilization in a shooting range soil using soybean Stover- and pine needle-derived biochars: chemical, microbial and spectroscopic assessments. J Hazard Mater 301:179–186
Alfonso R, Verónica A, Rubén F, Covelo EF (2016) Assessing the influence of technosol and biochar amendments combined with Brassica juncea on the fractionation of cu, Ni, Pb and Zn in a polluted mine soil. J Soils Sediments 16:339–348
Álvarez-López V, Prieto-Fernández Á, Cabello-Conejo MI, Kidd PS (2016) Organic amendments for improving biomass production and metal yield of Ni-hyperaccumulating plants. Sci Total Environ 548:370–379
Bao SD (2000) Soil and agricultural chemistry analysis. China Agriculture Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Barbafieri M, Morelli E, Tassi E, Pedron F, Remorini D, Petruzzelli G (2018) Overcoming limitation of "recalcitrant areas" to phytoextraction process: the synergistic effects of exogenous cytokinins and nitrogen treatments. Sci Total Environ 639:1520–1529
Bowles TM, Acosta-Martínez V, Calderón F, Jackson LE (2014) Soil enzyme activities, microbial communities, and carbon and nitrogen availability in organic agroecosystems across an intensively-managed agricultural landscape. Soil Biol Biochem 68:252–262
Burges A, Epelde L, Garbisu C (2015) Impact of repeated single-metal and multi-metal pollution events on soil quality. Chemosphere 120:8–15
Burges A, Epelde L, Benito G, Artetxe U, Becerril JM, Garbisu C (2016) Enhancement of ecosystem services during endophyte-assisted aided phytostabilization of metal contaminated mine soil. Sci Total Environ 562:480–492
Burges A, Epelde L, Blanco F, Becerril JM, Garbisu C (2017) Ecosystem services and plant physiological status during endophyte-assisted phytoremediation of metal contaminated soil. Sci Total Environ 584:329–338
Cang L, Zhou DM, Wang QY, Wu DY (2009) Effects of electrokinetic treatment of a heavy metal contaminated soil on soil enzyme activities. J Hazard Mater 172:1602–1607
Caporaso JG, Kuczynski J, Stombaugh J, Bittinger K, Bushman FD, Costello EK (2010) QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat Methods 7:335–336
Chen Y, Liu M, Deng Y, Zhong F, Xu B, Hu LM, Wang G (2017) Comparison of ammonium fertilizers, EDTA, and NTA on enhancing the uptake of cadmium by an energy plant, napier grass (Pennisetum purpureum schumach). J Soils Sediments 17:1–11
Chu Q, Sha Z, Osaki M, Watanabe T (2017) Contrasting effects of cattle manure applications and root-induced changes on heavy metals dynamics in the rhizosphere of soybean in an acidic haplic fluvisol: a chronological pot experiment. J Agric Food Chem 65:3085–3095
Ciarkowska K (2018) Assessment of heavy metal pollution risks and enzyme activity of meadow soils in urban area under tourism load: a case study from Zakopane (Poland). Environ Sci Pollut R 25:13709–13718
Ciarkowska K, Sołekpodwika K, Wieczorek J (2014) Enzyme activity as an indicator of soil- rehabilitation processes at a zinc and lead ore mining and processing area. J Environ Manag 132:250–256
Courtney RG, Mullen GJ (2008) Soil quality and barley growth as influenced by the land application of two compost types. Bioresour Technol 99:2913–2918
Cui H, Fan Y, Yang J, Xu L, Zhou J, Zhu Z (2016) In situ phytoextraction of copper and cadmium and its biological impacts in acidic soil. Chemosphere 161:233–241
Dai Z, Hu J, Xu X, Zhang L, Brookes PC, He Y, Xu J (2016) Sensitive responders among bacterial and fungal microbiome to pyrogenic organic matter (biochar) addition differed greatly between rhizosphere and bulk soils. Sci Rep 6:36101
Dimkpa CO, Svatos A, Dabrowska P, Schmidt A, Boland W, Kothe E (2009) Involvement of siderophores in the reduction of metal-induced inhibition of auxin synthesis in Streptomyces spp. Chemosphere 74:19–25
Edgar RC, Haas BJ, Clemente JC, Quince C, Knight R (2011) UCHIME improves sensitivity and speed of chimera detection. Bioinformatics 27:2194–2200
Elouear Z, Bouhamed F, Boujelben N, Bouzid J (2016) Application of sheep manure and potassium fertilizer to contaminated soil and its effect on zinc, cadmium and lead accumulation by alfalfa plants. Sustain Environ R 26:131–135
Epelde L, Becerril JM, Mijangos I, Garbisu C (2009) Evaluation of the efficiency of a phytostabilization process with biological indicators of soil health. J Environ Qual 38:2041–2049
Epelde L, Becerril JM, Alkorta I, Garbisu C (2014) Adaptive long-term monitoring of soil health in metal phytostabilization: ecological attributes and ecosystem services based on soil microbial parameters. Int J Phytoremediation 16:971–981
Fan M, Xiao X, Guo Y, Zhang J, Wang E, Chen W, Lin Y, Wei G (2018) Enhanced phytoremediation of Robinia pseudoacacia in heavy metal-contaminated soils with rhizobia and the associated bacterial community structure and function. Chemosphere 197:729–740
Fellet G, Marmiroli M, Marchiol L (2014) Elements uptake by metal accumulator species grown on mine tailings amended with three types of biochar. Sci Total Environ 468-469:598–608
Fidel RB, Laird DA, Thompson ML, Lawrinenko M (2017) Characterization and quantification of biochar alkalinity. Chemosphere 167:367–373
Fierer N, Bradford M, Jackson RB (2007) Toward an ecological classification of soil bacteria. Ecology 88:1354–1364
Golinska P, Dahm H (2011) Enzymatic activity of actinomycetes from the genus Streptomyces isolated from the bulk soil and rhizosphere of the Pinus sylvestris. Dendrobiology 65:37–46
Gómezsagasti MT, Alkorta I, Becerril JM, Epelde L, Anza M, Garbis C (2012) Microbial monitoring of the recovery of soil quality during heavy metal phytoremediation. Water Air Soil Poll 223:3249–3262
Gong X, Huang D, Liu Y, Zeng G, Chen S, Wang R, Xu P, Cheng M, Zhang C, Xue W (2019) Biochar facilitated the phytoremediation of cadmium contaminated sediments: metal behavior, plant toxicity, and microbial activity. Sci Total Environ 666:1126–1133
Gregorich EG, Carter MR, Angers DA, Monreal CM, Ellert BH (1994) Towards a minimum data set to assess soil organic matter quality in agricultural soils. Can J Soil Sci 74:367–385
Gregory SJ, Anderson CWN, Arbestain MC, Mcmanus MT (2014) Response of plant and soil microbes to biochar amendment of an arsenic-contaminated soil. Agric Ecosyst Environ 191:133–141
Gremion F, Chatzinotas A, Harms H (2003) Comparative 16S rDNA and 16S rRNA sequence analysis indicates that Actinobacteria might be a dominant part of the metabolically active bacteria in heavy metal-contaminated bulk and rhizosphere soil. Environ Microbiol 5:896–907
Guan SY (1986) Soil enzymes and its methodology. Agricultural Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Har-Peled S, Sharir M, Varadarajan KR (2015) The effects of biochar and compostamendments on copper immobilization and soil microorganisms in a temperate vineyard. Agric Ecosyst Environ 201:58–69
Hou D, Wang K, Liu T, Wang H, Lin Z, Qian J, Lu L, Tian S (2017a) Unique rhizosphere micro-characteristics facilitate phytoextraction of multiple metals in soil by the hyperaccumulating plant Sedum alfredii. Environ Sci Technol 51:5675–5684
Hou J, Liu W, Wu L, Hu P, Ma T, Luo Y, Christie P (2017b) Modulation of the efficiency of trace metal phytoremediation by Sedum plumbizincicola, by microbial community structure and function. Plant Soil 421:1–15
Houben D, Sonnet P (2015) Impact of biochar and root-induced changes on metal dynamics in the rhizosphere of Agrostis capillaris and Lupinus albus. Chemosphere 139:644–651
Huang XF, Chaparro JM, Reardon KF, Zhang R, Shen Q, Vivanco JM (2014) Rhizosphere interactions: root exudates, microbes, and microbial communities. Botany 92:267–275
Jones D, Willett V (2006) Experimental evaluation of methods to quantify dissolved organic nitrogen (DON) and dissolved organic carbon (DOC) in soil. Soil Biol Biochem 38:991–999
Juan LI, Li YT, Yang XD, Zhang JJ, Lin ZA, Zhao BQ (2015) Microbial community structure and functional metabolic diversity are associated with organic carbon availability in an agricultural soil. J Integr Agr 14:2500–2511
Kang SM, Khan AL, Hamayun M, Hussain J, Joo GJ, You YH, Kim JG, Lee IJ (2012) Gibberellin-producing Promicromonospora sp. SE188 improves Solanum lycopersicum plant growth and influences endogenous plant hormones. J Microbiol 50:902–909
Kim BY, Kshetrimayum JD, Goodfellow M (2011) Detection, selective isolation and characterisation of Dactylosporangium strains from diverse environmental samples. Syst Appl Microbiol 34:606–616
Kramer C, Gleixner G (2008) Soil organic matter in soil depth profiles: distinct carbon preferences of microbial groups during carbon transformation. Soil Biol Biochem 40:425–433
Lee JS, Lee KC, Kim KK, Lee B (2016) Complete genome sequence of the Variibacter gotjawalensis GJW-30T from soil of lava forest, Gotjawal. J Biotechnol 218:64–65
Li Z, Wu L, Hu P, Luo Y, Zhang H, Christie P (2014) Repeated phytoextraction of four metal-contaminated soils using the cadmium/zinc hyperaccumulator Sedum plumbizincicola. Environ Pollut 189:176–183
Liang S, Jin Y, Liu W, Li X, Shen S, Ding L (2017) Feasibility of Pb phytoextraction using nano-materials assisted ryegrass: results of a one-year field-scale experiment. J Environ Manag 190:170–175
Lou Z, Sun Y, Bian S, Ali BS, Hu B, Xu X (2017) Nutrient conservation during spent mushroom compost application using spent mushroom substrate derived biochar. Chemosphere 169:23–31
Lu KP, Yang X, Shen JJ, Robinson B, Huang HG, Liu D, Bolan N, Pei JC, Wang HL (2014) Effect of bamboo and rice straw biochars on the bioavailability of cd, cu, Pb and Zn to Sedum plumbizincicola. Agric Ecosyst Environ 191:124–132
Marin-Benito JM, Rodriguez-Cruz MS, Andrades MS (2009) Effect of spent mushroom substrate amendment of vineyard soils on the behavior of fungicides: 2. Mobility of penconazole and metalaxyl in undisturbed soil cores. J Agr Food Chem 57:9643–9650
Medina E, Paredes C, Bustamante MA, Moral R, Moreno-Caselles J (2012) Relationships between soil physico-chemical, chemical and biological properties in a soil amended with spent mushroom substrate. Geoderma 173-174:152–161
Mendez MO, Maier RM (2008) Phytostabilization of mine tailings in arid and semiarid environments-an emerging remediation technology. Environ Health Persp 116:278–283
Mitchell PJ, Simpson AJ, Soong R, Simpson MJ (2015) Shifts in microbial community and water-extractable organic matter composition with biochar amendment in a temperate forest soil. Soil Biol Biochem 81:244–254
Moameri M, Khalaki MA (2017) Capability of Secale montanum, trusted for phytoremediation of lead and cadmium in soils amended with nano-silica and municipal solid waste compost. Environ Sci Pollut R 3:1–8
Mohamed BA, Ellis N, Kim CS, Bi X (2017) The role of tailored biochar in increasing plant growth, and reducing bioavailability, phytotoxicity, and uptake of heavy metals in contaminated soil. Environ Pollut 230:329–338
Nie C, Yang X, Niazi NK, Xu X, Wen Y, Rinklebe J, Yong SO, Xu S, Wang H (2018) Impact of sugarcane bagasse-derived biochar on heavy metal availability and microbial activity: a field study. Chemosphere 200:274–282
Paula FS, Tatti E, Abram F, Wilson J, O'Flaherty V (2017) Stabilisation of spent mushroom substrate for application as a plant growth-promoting organic amendment. J Environ Manage 196:476–486
Peregrina F, Larrieta C, Colina M, Mariscalsancho I, Martín I, Martínezvidaurre JM, García-Escudero E (2012) Spent mushroom substrates influence soil quality and nitrogen availability in a semiarid vineyard soil. Soil Sci Soc Am J 76:1655–1666
Pratas J, Favas PJ, D'Souza R, Varun M, Paul MS (2013) Phytoremedial assessment of flora tolerant to heavy metals in the contaminated soils of an abandoned Pb mine in Central Portugal. Chemosphere 90:2216–2225
Pudjiraharti S, Takesue N, Katayama T, Lisdiyanti P, Hanafi M, Tanaka M, Sone T, Asano K (2011) Actinomycete Nonomuraea sp. isolated from Indonesian soil is a new producer of inulin fructotransferase. J Biosci Bioeng 111:671–674
Rajput R, Prasad G, Chopra AK (2009) Scenario of solid waste management in present Indian context. Caspian J Env Sci 7:45–53
Rees F, Germain C, Sterckeman T, Morel JL (2015) Plant growth and metal uptake by a non-hyperaccumulating species (Lolium perenne) and a Cd-Zn hyperaccumulator (Noccaea caerulescens) in contaminated soils amended with biochar. Plant Soil 395:57–73
Rodríguez-Vila A, Asensio V, Forján R, Covelo EF (2016) Assessing the influence of technosol and biochar amendments combined with Brassica juncea L. on the fractionation of cu, Ni, Pb and Zn in a polluted mine soil. J Soils Sediments 16:339–348
Rue M, Rees F, Simonnot MO, Morel JL (2019) Phytoextraction of Ni from a toxic industrial sludge amended with biochar. J Geochem Explor 196:173–181
Schellenberger S, Kolb S, Drake HL (2010) Metabolic responses of novel cellulolytic and saccharolytic agricultural soil bacteria to oxygen. Environ Microbiol 12:845–861
Steffen KL, Dann MS, Fager K, Fleischer SJ, Harper JK (1994) Short-term and long-term impact of an initial large-scale SMS soil amendment on vegetable crop productivity and resource use efficiency. Compost Sci Util 2:75–83
Stewart DPC, Cameron KC, Cornforth IS, Stewart DPC, Cameron KC, Cornforth IS (1998) Effects of spent mushroom substrate on soil chemical conditions and plant growth in an intensive horticultural system: a comparison with inorganic fertilizer. Soil Res 36:185–198
Tan Z, Lin CS, Ji X, Rainey TJ (2017) Returning biochar to fields: a review. Appl Soil Ecol 116:1–11
Tan X, Machmuller MB, Wang Z, Li X, He W, Cotrufo MF, Shen W (2018) Temperature enhances the affinity of soil alkaline phosphatase to cd. Chemosphere 196:214–222
Trivedi P, Anderson IC, Singh BK (2013) Microbial modulators of soil carbon storage: integrating genomic and metabolic knowledge for global prediction. Trends Microbiol 21:641–651
Van der Ent A, Baker AJM, Reeves RD, Pollard AJ, Schat H (2013) Hyperaccumulators of metal and metalloid trace elements: facts and fiction. Plant Soil 362:319–334
Vance ED, Brookes PC, Jenkinson DS (1987) An extraction method for measuring soil microbial biomass C. Soil Biol Biochem 19:703–707
Vogeler I, Vachey A, Deurer M, Bolan N (2008) Impact of plants on the microbial activity in soils with high and low levels of copper. Eur J Soil Biol 44:92–100
Volchko Y, Norrman J, Rosén L, Bergknut M, Josefsson S, Söderqvist T, Norberg T, WibergK TM (2014) Using soil function evaluation in multi-criteria decision analysis for sustainability appraisal of remediation alternatives. Sci Total Environ 485-486:785–791
Wood JL, Tang C, Franks AE (2016) Microbial associated plant growth and heavy metal accumulation to improve phytoextraction of contaminated soils. Soil Biol Biochem 103:131–137
Wu L, Li Z, Akahane I, Liu L, Han CL, Makino T, Luo Y, Christie P (2012) Effects of organic amendments on cd, Zn and cu bioavailability in soil with repeated phytoremediation by Sedum plumbizincicola. Int J Phytoremediat 14:1024–1038
Wu C, Shi L, Xue S, Li W, Jiang X, Rajendran M, Qian Z (2019) Effect of sulfur-iron modified biochar on the available cadmium and bacterial community structure in contaminated soils. Sci Total Environ 647:1158–1168
Xu M, Xia H, Wu J, Yang G, Zhang X, Peng H, Qi H (2017) Shifts in the relative abundance of bacteria after wine-lees-derived biochar intervention in multi metal-contaminated paddy soil. Sci Total Environ 599:1297–1307
Yang X, Long XX, Ni WZ, Fu CX (2002) Sedum alfredii H: a new Zn hyperaccumulating plant first found in China. Chin Sci Bull 47:1634–1637
Yang W, Li H, Zhang T, Lin S, Ni W (2014) Classification and identification of metal-accumulating plant species by cluster analysis. Environ Sci Poll R 21:10626–10637
Zhang RH, Duan ZQ, Li ZG (2012) Use of spent mushroom substrate as growing media for tomato and cucumber seedlings. Pedosphere 22:333–342
Zhang C, Clark GJ, Patti AF, Bolan N, Cheng M, Sale PW, Tang C (2015) Contrasting effects of organic amendments on phytoextraction of heavy metals in a contaminated sediment. Plant Soil 397:331–345
Zhang C, Mora P, Dai J, Chen X, Giusti-Miller S, Ruiz-Camacho N, Velasquez E, Lavelle P (2016) Earthworm and organic amendment effects on microbial activities and metal availability in a contaminated soil from China. Appl Soil Ecol 104:54–66
Zhao X, Huang J, Lu J, Sun Y (2019) Study on the influence of soil microbial community on the long-term heavy metal pollution of different land use types and depth layers in mine. Ecotox Environ Safe 170:218–226
Zheng J, Chen J, Pan G, Liu X, Zhang X, Li L, Bian R, Cheng K, Zheng J (2016) Biochar decreased microbial metabolic quotient and shifted community composition four years after a single incorporation in a slightly acid rice paddy from Southwest China. Sci Total Environ 571:206–217
Acknowledgements
This research was financially supported by the Foundation for Distinguished Young Scholars of Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University (Nos. XJQ201628) and the Major Scientific and Technological Projects of Fujian Province (2017NZ0001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Antony Van der Ent.
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, W., Wang, S., Ni, W. et al. Enhanced Cd-Zn-Pb-contaminated soil phytoextraction by Sedum alfredii and the rhizosphere bacterial community structure and function by applying organic amendments. Plant Soil 444, 101–118 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-019-04256-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-019-04256-x