Abstract
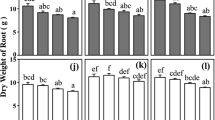
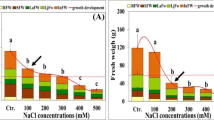
The effect of salinity on growth, ion accumulation and the roles of ions in osmotic adjustment of two populations of Suaeda salsa were investigated. Seeds were collected from an intertidal zone or a saline inland zone in the Yellow River Delta in Shandong province, China. Seedlings were exposed to 10, 100, 200, 400 or 600 mM NaCl for 18 days in a greenhouse. NO3 − concentration in the soil where S. salsa grows in an intertidal zone was much lower than that for the second population, but leaf NO3 − concentration was the same in the two populations under field conditions. When plants were cultured in a greenhouse under natural light conditions, S. salsa from the intertidal zone showed fewer main stem branches and lower relative shoot growth compared to S. salsa from saline inland. Leaf Cl− concentration of saline inland S. salsa was significantly higher than that of S. salsa from the intertidal zone, while the opposite was true for the concentration of NO3 − in leaves of plants. For S. salsa from the intertidal zone NO3 − contributed more than Cl− to the osmotic potential, whereas S. salsa from the saline inland exhibited a reverse relationship under saline conditions, indicating that NO3 − plays an important osmotic role in S. salsa from the intertidal zone in high salinity. In conclusion, S. salsa from the intertidal zone may employ superior control of ion uptake and content than S. salsa from the saline inland zone. The two populations of Suaeda salsa presented different ability in chloride exclusion and nitrate accumulation. These characteristics may affect the distributions of S. salsa in natural highly saline environments.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aslam M, Hukffaker RC, Rains DW (1984) Early effects of salinity on nitrate assimilation in barley seedlings. Plant Physiol 76:321–325
Blom-Zandstra G, Lampe JEM (1983) The effect of chloride and sulphate salts on the nitrate content in lettuce plants (Lactuca sativa L.). J Plant Nutr 6:611–628
Botella MA, Martinez V, Nieves M, Cerda A (1997) Effect of salinity on the growth and nitrogen uptake by wheat seedlings. J Plant Nutr 20:793–804
Bottacin A, Cacco G, Saccoman M (1985) Nitrogen absorption and assimilation in NaCl-resistant and NaCl-susceptible millet genotypes (Pennisetum americanum). Can J Bot 63:517–520
Carter JL, Colmer TD, Veneklaas EJ (2006) Variable tolerance of wetinland tree species to combined salinity and waterlogging is related to regulation of ion uptake and production of organic solutes. New Phytol 169:123–134
Cataldo DA, Haroon M, Schrader LE, Youngs VL (1975) Rapid calorimetric determination of nitrate in plant tissues by nitration of salicylic acid. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 6:71–80
Cerezo M, Gacía-Augustín P, Serna D, Primo-Millo E (1997) Kinetics of nitrite uptake by Citrus seedlings and inhibitory effects of salinity. Plant Sci 126:105–112
Glenn EP, Brown JJ (1999) Salt tolerance and crop potential of halophytes. Crit Rev Plant Sci 18:227–255
Greenway H, Munns R (1980) Mechanisms of salt tolerance in nonhalophytes. Annu Rev Plant Physiol 31:149–190
Greenway H, Munns R (1983) Interactions between growth, uptake of Cl and Na, and water relations of plants in saline environments. Plant Cell Environ 6:575–589
Hasegawa PM, Bressan RA, Zhu JK, Bohnert HJ (2000) Plant cellular and molecular responses to high salinity. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 51:463–499
Khan MA, Webber DJ, Hess W (1985) Elemental distribution in seeds of the halophytes Salicornia pacifica Var. utahensis and Atriplex canescens. Am J Bot 72:1672–1675
Köhler B, Raschke K (2000) The delivery of salts to the xylem.Three types of anion conductance in the plasmalemma of the xylem parenchyma of roots of barley. Plant Physiol 122:243–254
Liu Y 2006 Study on pigment accumulation and photosynthesis in Suaeda salsa under different natural conditions. MSC Thesis, Shandong Normal University, China (in Chinese).
Mott RL, Steward FC (1972) Solute accumulation in plant cells. V. An aspect of nutrition and development. Ann Bot (Lond) 36:915–937
Munns R (2002) Comparative physiology of salt and water stress. Plant Cell Environ 25:239–250
Munns R (2005) Genes and salt tolerance: bringing them together. New Phytol 167:645–663
Nublat A, Desplans J, Casse F, Berthomieu P (2001) sas1, an Arabidopsis mutant overaccumulating sodium in the shoot, shows deficiency in the control of the root radial transport of sodium. Plant Cell 13:125–137
Peuke AD, Glaab J, Kaiser WM, Jeschke WD (1996) The uptake and flow of C, N and ions between roots and shoots in Ricinus communis L. IV. Flow and metabolism of inorganic nitrogen and malate depending on nitrogen nutrition and salt treatment. J Exp Bot 47:377–385
Ramadan T (2001) Dynamics of salt secretion by Sporobolus species (Vahl) Kunt from sites of differing salinity. Ann Bot (Lond) 87:259–266
Rubinigg M, Posthumus F, Ferschke M, Elzenga JTM, Stulen I (2003) Effects of NaCl salinity on 15N-nitrate fluxes and specific root length in the halophyte Plantago maritima L. Plant Soil 250:201–213
SAS Institute Inc (1989) SAS/STAT User’s Guide. SAS Institute INC., Cary, NC
Short DC, Colmer TD (1999) Salt tolerance in the halophyte Halosarcia pergranulata subsp. Pergranulata. Ann Bot (Lond) 83:207–213
Song J, Feng G, Tian CY, Zhang FS (2005) Strategies for adaptation of Suaeda physophora, Haloxylon ammodendron and Haloxylon persicum to saline environment during seed germination stage. Ann Bot (Lond) 96:399–405
Song J, Ding XD, Feng G, Zhang FS (2006) Nutritional and osmotic roles of nitrate in a euhalophyte and xerophyte in saline conditions. New Phytol 171:357–366
Stienstra AW (1986) Nitrate accumulation and growth of Aster tripolium L. with a continuous and intermittent nitrogen supply. Plant Cell Environ 9:307–313
Taleisnik EL, Anton AM (1988) Salt ginlands in Poppophorum (Poaceae). Ann Bot (Lond) 62:383–388
Tester M, Davenport R (2003) Na+ tolerance and Na+ transport in higher plants. Ann Bot (Lond) 91:503–527
Warwick NWM, Halloran GM (1991) Variation in salinity tolerance and ion uptake in accessions of brown beetle grass (Diplachne fusea (L.) Beauv.). New Phytol 119:161–168
Warwick NWM, Halloran GM (1992) Accumulation and excretion of sodium, potassium and chloride from leaves of two accessions of Diplachne fusca (L.) Beauv. New Phytol 121:53–61
Zhang HY, Zhao KF (1998) Effects of salinity and water stresses on osmotic adjustment of Suaeda salsa seedlings. Acta Bot Sin 40:56–61
Zhao KF, Fan H, Jiang XY, Zhou S (2002) Critical day-length and photoinductive cycles for the induction of flowering in halophyte Suaeda salsa. Plant Sci 162:27–31
Zhao KF, Fan H, Zhou S, Song J (2003) Study on the salt and drought tolerance of Suaeda salsa and Kalanchoe daigremontiana under iso-osmotic salt and water stress. Plant Sci 165:837–844
Acknowledgments
We are thankful to Professor Hans Bohnert and Dr. Lindsey Atkinson for their critical reading and revision of the manuscript. Financial support from the Foundation of Excellent Young Scientists of Shandong Province (2006BS06002), and the State High Technological Research and Development Plan of China (2007AA091701) is also greatly appreciated.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: John McPherson Cheeseman.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, J., Chen, M., Feng, G. et al. Effect of salinity on growth, ion accumulation and the roles of ions in osmotic adjustment of two populations of Suaeda salsa . Plant Soil 314, 133–141 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-008-9712-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-008-9712-3