Abstract
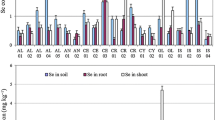
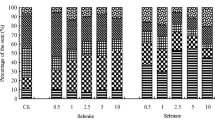
Various extraction methods have been used to determine selenium (Se) concentrations in soils and plants in the second seleniferous regions of China. Our results show tea Se contents in the study area range from 1.009 to 2.6 mg/kg, which reveal that the tea areas in Ziyang County are in seleniferous regions. The four extraction methods evaluated in this study provide different information concerning soil and plant Se levels. The quality control/quality assurance program for this project indicated there is excellent agreement between total soil Se and extractable Se. For example, phosphate extractable Se results from the field investigation and greenhouse study were found to be highly correlated (R 2 > 0.91) by linear regression analyses. Results from rye seedling experiments further show phosphate extractable Se has significant correlations with plant Se uptake and that a 0.1 M solution of KH2PO4 can be used as the extractant of soil available Se. In the acid soil, the Brassica campestris yield could be significantly reduced when the content of Se6+–Se ≥ 0.5 mg/kg, and the influence on the yield was not as obvious when the content of Se6+–Se reached up to 2.0 mg/kg. The uptake by Brassica campestris of Se6+–Se is higher than that of Se4+–Se. The main factors influencing the biological availability of soil Se, in order of their importance are CaCO3, the presence of silt grains, organic matter and the presence of clay grains. pH could affect KH2PO4 extractable Se through CaCO3.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
D Y Boon (1989) Potential selenium problems in Great Plains soils L W Jacobs (Eds) Selenium in Agriculture and the Environment Spec. Publ. 23. SSSA Madison, WI 107–121
M L Berrow A M Ure (1989) Geological materials and soils. Chapter 6 M IHNAT (Eds) Occurrence and Distribution of Selenium CRC Press Boca Raton, FL 132–145
K Borowska J Koper (2000) ArticleTitleThe effect of long-term organic fertilization on the selenium content in lessive soil Polish J. Soil Sci 33 21–27 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXislykt7o%3D
E E Cary G A Wieczorek W H Allaway (1967) ArticleTitleReactions of selenite-selenium added to soils that produce low-selenium forages Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc 31 21–26 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaF2sXktFSktbc%3D Occurrence Handle10.2136/sssaj1967.03615995003100010010x
E E Cary G G Nielsen (1973) ArticleTitleEffect of fertilizer anions on the solubility of native and applied selenium in soils Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc 37 590–593 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaE3sXltVCis7Y%3D
D Z Chen (1984) ArticleTitleSelenium in soils in Shaanxi Province Acta Pedologica Sinica 21 247–257 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL2cXmtlemsLc%3D
X S Chen et al. (1980) ArticleTitleStudies on the relation of selenium and keshan disease Biological Trace Element Research 2 91–107 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL3cXmtlOgu74%3D
B E Davies (1980) Applied Soil Trace Element John Wiley and Sons. Chichester. Academic Press New York 80–97
S J Fritz S D Hall (1988) ArticleTitleEfficacy of various sorbic media in attenuation of selenium J. Environ. Qual 17 480–484 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL1cXlsFGmsbs%3D Occurrence Handle10.2134/jeq1988.00472425001700030023x
R Jump B Sabey (1985) Evaluation of the NH4HCO3−DTPA Soil Test for Identifying Seleniferous Soils American Society for Surface Mining and Reclamation Proceedings Eexington, KY 87–90
R Jump B Sabey (1989) Soil test extractants for predicting selenium in plants E W Jacobs (Eds) Selenium in Agriculture and the Environment SSSA Madison WI 95–106
S Q Li (1984) ArticleTitleSelenium in environment and the Se-toxic disease on people and livestock in Ziyang County Shaanxi Agric. Sci. 3 35–38
Z Q Mei (1980) ArticleTitleThe second high Selenium area in China Shaanxi Agric. Sci 6 36–37
H Neubauer W Schneider Die (1923) Nahrstoffaufnahme der Keimpflanzen und ihre Anwen dung auf die Bestimmung des Nahrstoffgehates des Boden Z Pflanzene Dung u Bodenk. AZ, 329–362
A B Orrille (1964) Selenium Academic Press New York and London 27–50
I E Oldfield (1998) Environmental implications of uses of selenium with animals W T Frankenberger SuffixJr R A Endberg (Eds) Environmental Chemistry of Selenium Marcel Dekker, Inc New York 129–142
O E Olson E I Whitehead A L Moxon (1942) ArticleTitleOccurrence of soluble selenium in soils and its availability to plants Soil Sci 54 47–53 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaH38Xjsl2msQ%3D%3D
A L Page (1982) Methods of Soil Analysis. Part 2. Chemical and Microbiological Properties EditionNumber2 Agronomy Society of America. Agronomy 9 Madison WI
R A Prodgers FF Munshower (1991) ArticleTitleAB-DTPA extractable soil selenium as a predictor of seleniferous vegetation. Proceeding of the Billings Reclamation Symposium Proc., Billings MT.U.S. Geol. Survey Circ 1064 65–71
K I Penny (1996) ArticleTitleAppropriate critical values when testing a single multivariate outlier by using a mahalanobis distance Appl. Stat. 45 732–781
D J Reuter J B Robinson K I Peverill G H Price (1986) Guidelines for collecting, handling and analyzing plant materials D J Reuter J B Robinson (Eds) Plant Analysis an Interpretation Manual Inkata Press Melbourne, Australia 20–35
R A Shamberger (1983) Biochemistry of Selenium Plenum Press New York 89–120
S Sharmasarkar G F Vance (1995a) ArticleTitleCharacterization and correlation of soil and plant selenium in some range and coal mine environments of Wyoming Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 26 2577–2591 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2MXns12jur4%3D Occurrence Handle10.1080/00103629509369469
S Sharmasarkar G F Vance (1995b) ArticleTitleFractional partitioning for assessing solid-phase speciation and geochemical transformations of soil selenium Soil Sci 160 43–55 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2MXnt1Grtbw%3D
M Singh N Singh (1978) ArticleTitleSelenium toxicity in plants and its detoxification by phosphorus Soil Sci 126 255–262 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaE1MXjsVKhuw%3D%3D
P N Soltanpour S M Workman (1980) ArticleTitleUse of NH4HCO3-DTPA soil test to assess availability and toxicity of selenium to alfalfa plants Commun Soil Sci. Plant Anal 11 1147–1156 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL3MXmsVartQ%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1080/00103628009367111
L K Spackman G F Vance L E Vicklund PK (1994) Standard operating procedures for the sampling and analysis of selenium in soil and overburden/spoil material Research Publication MP−82, University of Wyoming Laramie, WY 71–82
SPSS. Inc. SPSS base syntax reference guide. USA, 1999, 400–447.
N Terry A Zayed (1998) Pytoremediation of selenium W T Frankenberger R A Engberg (Eds) Environmental Chemistry of Selenium Marcel Dekker, Inc New York 633–655
Vance, G. F. 2000. Problems associated with selenium leaching from waste shale. In W L Daniels and S G Richardson (ed.) A new era for land reclamation. Vol. 17. Am. Soc. for Surface Mining and Reclamation, Lexington, KY.
H F Wan (1989) ArticleTitleAbsorption and accumulation of soil Se by wheat and other four crops Acta Pedologica Sinica 26 3–7
H F Wan R L Mikkelsen A L Page (1988) ArticleTitleSelenium uptake by some agricultural crops from central California toxic soils J. Environ. Qual. 17 269–272 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL1cXit1Srt74%3D Occurrence Handle10.2134/jeq1988.00472425001700020018x
P L Wanek G F Vance P D Stahl (1999) ArticleTitleSelenium uptake by plants: effects of soil steaming, root addition, and selenium augmentation Soil Sci. and Plant Anal. 30 265–278 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXhtlGhsrs%3D
C Williams I Thomton (1973) ArticleTitleThe use of soil extractants to estimate plant available molybdenum and selenium in potentially toxic soils Plant Soil 39 149–159 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00018053 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaE3sXltFCgurc%3D
G Q Yang et al. (1981) ArticleTitleResearch on the etiology of an endemic disease characterized by loss of nails and hair in Enshi County J Chinese Acad. Med. 3 1–6 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL38XlsVOks7s%3D
B J Zhou (1984) ArticleTitleSelenium in soil–plant system Adv. in Soil Sci. 5 1–3
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, C., Ren, J., Xue, C. et al. Study on the Relationship between Soil Selenium and Plant Selenium Uptake. Plant Soil 277, 197–206 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-005-7011-9
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-005-7011-9