Abstract
Key message
This is the first time to dissect the mechanism of NACs-mediated disease resistance in plants using metabolomic approach and discover the involvement of ABA signaling pathway in NACs-mediated disease resistance.
Abstract
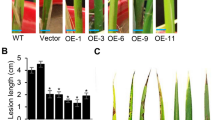
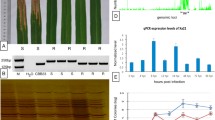
NAC transcription factors have been validated as important regulators in stress responses, but their molecular mechanisms in plant disease resistance are still largely unknown. Here we report that the NAC gene ONAC066 (LOC_Os01g09550) is significantly activated by rice blast infection. ONAC066 is ubiquitously expressed and this protein is localized in the nucleus. Overexpression of ONAC066 quantitatively enhances resistance to blast disease and bacterial blight in rice. The transcript levels of PR genes are also dramatically induced in ONAC066 overexpressing plants. Exogenous abscisic acid (ABA) strongly activates the transcription of ONAC066 in rice. Further analysis shows that overexpression of ONAC066 remarkably suppresses the expression of ABA-related genes, whereas there are no obvious differences for salicylic acid (SA) and jasmonic acid (JA)-related genes between wild-type and ONAC066 overexpressing plants. Consistently, lower endogenous ABA levels are identified in ONAC066 overexpressing plants compared with wild-type plants before and after blast inoculation, while no significant differences are observed for the SA and JA levels. Yeast one-hybrid assays demonstrate that ONAC066 directly binds to the promoters of LIP9 and NCED4 to modulate their expression. Moreover, the metabolomic study reveals that the ONAC066 overexpressing plants accumulated higher contents of soluble sugars and amino acids both before and after pathogen attack, when compared to wild-type plants. Taken together, our results suggest that ONAC066 positively regulates rice resistance to blast and bacterial blight, and ONAC066 exerts its functions on disease resistance by modulating of ABA signaling pathway, sugars and amino acids accumulation in rice.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bari R, Jones JD (2009) Role of plant hormones in plant defense responses. Plant Mol Biol 69:473–488
Beltenev V, Ivanov V, Rozhdestvenskaya I, Cherkashov G, Stepanova T, Shilov V, Pertsev A, Davydov M, Egorov I, Melekestseva I, Narkevsky E, Ignatov V (2007) Protocols on rice blast of IRRI. Internal Rice Research Institute, Manila
Cao L, Yu Y, Ding X, Zhu D, Yang F, Liu B, Sun X, Duan X, Yin K, Zhu Y (2017a) The Glycine soja NAC transcription factor GsNAC019 mediates the regulation of plant alkaline tolerance and ABA sensitivity. Plant Mol Biol 95:253–268
Cao XC, Zhong C, Zhu LF, Zhang JH, Ssjid H, Wu LH, Jin QY (2017b) Glycine increases cold tolerance in rice via the regulation of N uptake, physiological characteristics, and photosynthesis. Plant Physiol Biochem 112:251–260
Chen D, Chai S, McIntyre CL, Xue GP (2017) Overexpression of a predominantly root-expressed NAC transcription factor in wheat roots enhances root length, biomass and drought tolerance. Plant Cell Rep. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-017-2224-y
Chen M, Zhao Y, Zhuo C, Lu S, Guo Z (2015) Overexpression of a NF-YC transcription factor from bermudagrass confers tolerance to drought and salinity in transgenic rice. Plant Biotechnol J 13:482–491
Deng H, Liu H, Li X, Xiao J, Wang S (2012) A CCCH-type zinc finger nucleic acid-binding protein quantitatively confers resistance against rice bacterial blight disease. Plant Physiol 158:876–889
Ding B, Bellizzi Mdel R, Ning Y, Meyers BC, Wang GL (2012) HDT701, a histone H4 deacetylase, negatively regulates plant innate immunity by modulating histone H4 acetylation of defense-related genes in rice. Plant Cell 24:3783–3794
Fang Y, Liao K, Du H, Xu Y, Song H, Li X, Xiong L (2015) A stress-responsive NAC transcription factor SNAC3 confers heat and drought tolerance through modulation of reactive oxygen species in rice. J Exp Bot 66:6803–6817
Gao S, Guo W, Feng W, Liu L, Song X, Chen J, Hou W, Zhu H, Tang S, Hu J (2016) LTP3 contributes to disease susceptibility in Arabidopsis by enhancing abscisic acid (ABA) biosynthesis. Mol Plant Pathol 17:412–426
Gómez-Ariza J, Campo S, Rufat M, Estopà M, Messeguer J, San Segundo B, Coca M (2007) Sucrose-mediated priming of plant defense responses and broad-spectrum disease resistance by overexpression of the maize pathogenesis-related PRms protein in rice plants. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 20:832–842
Guo Y, Gan S (2006) AtNAP, a NAC family transcription factor, has an important role in leaf senescence. Plant J 46:601–612
Hu H, Dai M, Yao J, Xiao B, Li X, Zhang Q, Xiong L (2006) Overexpressing a NAM, ATAF, and CUC (NAC) transcription factor enhances drought resistance and salt tolerance in rice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:12987–12992
Jensen MK, Hagedorn PH, de Torres-Zabala M, Grant MR, Rung JH, Colling DB, Lyngkjaer MF (2008) Transcriptional regulation by an NAC (NAM–ATAF1, 2–CUC2) transcription factor attenuates ABA signaling for efficient basal defense towards Blumeria graminis f. sp. hordei in Arabidopsis. Plant J 56:867–880
Jespersen D, Yu J, Huang B (2017) Metabolic effects of acibenzolar-S-methyl for improving heat or drought stress in creeping bentgrass. Front Plant Sci 8:1224
Jiang CJ, Shimono M, Sugano S, Kojima M, Yazawa K, Yoshida R, Inoue H, Hayashi N, Sakakibara H, Takatsuji H (2010) Abscisic acid interacts antagonistically with salicylic acid signaling pathway in rice-Magnaporthe grisea interaction. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 23:791–798
Jiang J, Ma S, Ye N, Jiang M, Cao J, Zhang J (2017) WRKY transcription factors in plant responses to stresses. J Integr Plant Biol 59:86–101
Kaneda T, Taga Y, Takai R, Iwano M, Matsui H, Takayama S, Isogai A, Che FS (2009) The transcription factor OsNAC4 is a key positive regulator of plant hypersensitive cell death. EMBO J 28:926–936
Kauffman HE, Reddy APK, Hsieh SPY, Merca SD (1973) An improved technique for evaluating resistance of rice varieties to Xanthomonas oryzae. Plant Dis Rep 57:537–541
Kim HJ, Nam HG, Lim PO (2016) Regulatory network of NAC transcription factors in leaf senescence. Curr Opin Plant Biol 33:48–56
Kind T, Wohlgemuth G, Lee DY, Lu Y, Palazoglu M, Shahbaz S, Fiehn O (2009) FiehnLib: mass spectral and retention index libraries for metabolomics based on quadrupole and time-of-flight gas chromatography/mass spectrometry. Anal Chem 81:10038–10048
Lescot M, Déhais P, Thijs G, Marchal K, Moreau Y, Van de Peer Y, Rouzé P, Rombauts S (2002) PlantCARE, a database of plant cis-acting regulatory elements and a portal to tools for in silico analysis of promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res 30:325–327
Lisec J, Schauer N, Kopka J, Willmitzer L, Fernie AR (2006) Gas chromatography mass spectrometry-based metabolite profiling in plants. Nat Protoc 1:387–396
Liu D, Chen X, Liu J, Ye J, Guo Z (2012) The rice ERF transcription factor OsERF922 negatively regulates resistance to Magnaporthe oryzae and salt tolerance. J Exp Bot 63:3899–3911
Liu B, Zhang S, Zhu X, Yang Q, Wu S, Mei M, Mauleon R, Leach J, Mew T, Leung H (2004) Candidate defense genes as predictors of quantitative blast resistance in rice. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 17:1146–1152
Liu Q, Yang J, Zhang S, Zhao J, Feng A, Yang T, Wang X, Mao X, Dong J, Zhu X, Leung H, Leach JE, Liu B (2016a) OsGF14b positively regulates panicle blast resistance, but negatively regulates leaf blast resistance in rice. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 29:46–56
Liu Q, Yang J, Yan S, Zhang S, Zhao J, Wang W, Yang T, Wang X, Mao X, Dong J, Zhu X, Liu B (2016b) The germin-like protein OsGLP2-1 enhances resistance to fungal blast and bacterial blight in rice. Plant Mol Biol 92:411–423
Machado RA, Arce CC, Ferrieri AP, Baldwin IT, Erb M (2015) Jasmonate-dependent depletion of soluble sugars compromises plant resistance to Manduca sexta. New Phytol 207:91–105
Moore JW, Herrera-Foessel S, Lan C, Schnippenkoetter W, Ayliffe M, Huerta-Espino J, Lillemo M, Viccars L, Milne R, Periyannan S, Kong X, Spielmeyer W, Talbot M, Bariana H, Patrick JW, Dodds P, Singh R, Lagudah E (2015) A recently evolved hexose transporter variant confers resistance to multiple pathogens in wheat. Nat Genet 47:1494–1498
Nakashima K, Tran LS, Van Nguyen D, Fujita M, Maruyama K, Todaka D, Ito Y, Hayashi N, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2007) Functional analysis of a NAC-type transcription factor OsNAC6 involved in abiotic and biotic stress-responsive gene expression in rice. Plant J 51:617–630
Nakashima K, Ito Y, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2009) Transcriptional regulatory networks in response to abiotic stresses in Arabidopsis and grasses. Plant Physiol 149:88–95
Neuman H, Galpaz N, Cunningham FX Jr, Zamir D, Hirschberg J (2014) The tomato mutation nxd1 reveals a gene necessary for neoxanthin biosynthesis and demonstrates that violaxanthin is a sufficient precursor for abscisic acid biosynthesis. Plant J 78:80–93
Noctor G, Arisic CM, Jouanin L, Valadier HM, Roux Y, Foyer CH (1997) The role of glycine in determining the rate of glutathione synthesis in poplar. Possible implications for glutathione production during stress. Physiol Plant 100:255–263
Nuruzzaman M, Manimekalai R, Sharoni AM, Satoh K, Kondoh H, Ooka H, Kikuchi S (2010) Genome-wide analysis of NAC transcription factor family in rice. Gene 465:30–44
Nuruzzaman M, Sharoni AM, Kikuchi S (2013) Roles of NAC transcription factors in the regulation of biotic and abiotic stress responses in plants. Front Microbiol 4:248
Olsen AN, Ernst HA, Leggio LL, Skriver K (2005) NAC transcription factors: structurally distinct, functionally diverse. Trends Plant Sci 10:79–87
Parker D, Beckmann M, Zubair H, Enot DP, Caracuel-Rios Z, Overy DP, Snowdon S, Talbot NJ, Draper J (2009) Metabolomic analysis reveals a common pattern of metabolic re-programming during invasion of three host plant species by Magnaporthe grisea. Plant J 59:723–737
Puranik S, Sahu PP, Srivastava PS, Prasad M (2012) NAC proteins: regulation and role in stress tolerance. Trends Plant Sci 17:369–381
Qian Y, Tan DX, Reiter RJ, Shi H (2015) Comparative metabolomics analysis highlights the involvement of sugars and glycerol in melatonin-mediated innate immunity against bacterial pathogen in Arabidopsis. Sci Rep 5:15815
Salem MA, Jüppner J, Bajdzienko K, Giavalisco P (2016) Protocol: a fast, comprehensive and reproducible one-step extraction method for the rapid preparation of polar and semi-polar metabolites, lipids, proteins, starch and cell wall polymers from a single sample. Plant Methods 12:45
Sharma R, De Vleesschauwer D, Sharma MK, Ronald PC (2013) Recent advances in dissecting stress-regulatory crosstalk in rice. Mol Plant 6:250–260
Shen J, Lv B, Luo L, He J, Mao C, Xi D, Ming F (2017) The NAC-type transcription factor OsNAC2 regulates ABA-dependent genes and abiotic stress tolerance in rice. Sci Rep 7:40641
Solomon PS, Tan KC, Oliver RP (2003) The nutrient supply of pathogenic fungi; a fertile field for study. Mol Plant Pathol 4:203–210
Song SY, Chen Y, Chen J, Dai XY, Zhang WH (2011) Physiological mechanisms underlying OsNAC5-dependent tolerance of rice plants to abiotic stress. Planta 234:331–345
Sun L, Zhang H, Li D, Huang L, Hong Y, Ding XS. Nelson RS, Zhou X, Song F (2013) Functions of rice NAC transcriptional factors, ONAC122 and ONAC131, in defense responses against Magnaporthe grisea. Plant Mol Biol 81:41–56
Takada S, Hibara K, Ishida T, Tasaka M (2001) The CUP-SHAPED COTYLEDON1 gene of Arabidopsis regulates shoot apical meristem formation. Development 128:1127–1135
Toki S, Hara N, Ono K, Onodera H, Tagiri A, Oka S, Tanaka H (2006) Early infection of scutellum tissue with Agrobacterium allows high-speed transformation of rice. Plant J 47:969–976
Ulferts S, Delventhal R, Splivallo R, Karlovsky P, Schaffrath U (2015) Abscisic acid negatively interferes with basal defence of barley against Magnaporthe oryzae. BMC Plant Biol 15:7
Wang X, Basnayake BM, Zhang H, Li G, Li W, Virk N, Menqiste T, Song F (2009) The Arabidopsis ATAF1, a NAC transcription actor, is a negative regulator of defense responses against necrotrophic fungal and bacterial pathogens. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 22:1227–1238
Xu J, Audenaert K, Hofte M, De Vleesschauwer D (2013) Abscisic acid promotes susceptibility to the rice leaf blight pathogen Xanthomonas oryzae pvoryzae by suppressing salicylic acid-mediated defenses. PLoS ONE 8:e67413
Yokotani N, Tsuchida-Mayama T, Ichikawa H, Mitsuda N, Ohme-Takagi M, Kaku H, Minami E, Nishizawa Y (2014) OsNAC111, a blast disease-responsive transcription factor in rice, positively regulates the expression of defense-related genes. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 27:1027–1034
Yoshii M, Shimizu T, Yamazaki M, Higashi T, Miyao A, Hirochika H, Omura T (2009) Disruption of a novel gene for a NAC-domain protein in rice confers resistance to Rice dwarf virus. Plant J 57:615–625
Yun Z, Gao H, Liu P, Liu S, Luo T, Jin S, Xu Q, Xu J, Cheng Y, Deng X (2013) Comparative proteomics and metabolomics profiling of citrus fruit with enhancement of disease resistance by postharvest heat treatment. BMC Plant Biol 13:44
Zhang Y, Su J, Duan S, Ao Y, Dai J, Liu J, Wang P, Li Y, Liu B, Feng D, Wang J, Wang H (2011) A highly efficient rice green tissue protoplast system for transient gene expression and studying light/chloroplast-related processes. Plant Methods 7:30
Zhong R, Demura T, Ye ZH (2006) SND1, a NAC domain transcription factor, is a key regulator of secondary wall synthesis in fibers of Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 18:3158–3170
Acknowledgements
This research was supported partially by the NSFC-IRRI Project (31461143019), Science and Technology Projects of Guangdong Province (2015B020231002, 2016A050502030 and 2014B070706013), the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (2014A030310489), and the Common Technical Innovation Team of Guangdong Province on Agricultural Seed Industry (2017LM2148).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
QL conducted the quantitative qRT-PCR assay, transgenic functional confirmation and chemical treatment experiments, drafting the manuscript and proposal writing. SY conducted the metabolic study, drafting the manuscript and proposal writing. WH performed the quantification of endogenous ABA. JY evaluated the blast and Xoo resistance. JD, SZ, JZ, TY and XM participated in RNA extraction and quantitative qRT-PCR assays. XZ and BL conceived of the study, drafted proposal and corrected manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Q., Yan, S., Huang, W. et al. NAC transcription factor ONAC066 positively regulates disease resistance by suppressing the ABA signaling pathway in rice. Plant Mol Biol 98, 289–302 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-018-0768-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-018-0768-z