Purpose
The purpose of the study was to investigate the specific mechanism by which elevated gastric pH reduces the absorption of BMS-561389, a factor Xa inhibitor, and to develop a solid formulation strategy to overcome this gastric pH interaction.
Methods
A dissolution method in an acetate buffer at pH 5.5 was used to evaluate the dissolution behavior of the tablet formulation. A precipitation model was used to screen different excipients for their potential to minimize the pH-dependent absorption of BMS-561389. Excipients that showed promise in the precipitation model were incorporated in modified tablet formulations. Dissolution rate of the modified tablets was also determined by the acetate buffer method. A canine model for pH-dependent absorption was subsequently used to evaluate the tablet formulations.
Results
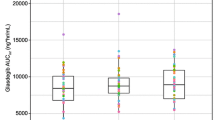
Dissolution studies suggested that the reduced absorption of the original formulation was the result of the precipitation of the poorly water-soluble free base during the initial dissolution of the salt. Modified tablets containing organic acids, sulfobutylether-β-cyclodextrin, or povidone showed enhanced dissolution as compared with the original formulation. Drug absorption from the tablet containing tartaric acid was substantially independent of gastric pH in the canine model.
Conclusion
A multitier approach was successful in identifying a solid dosage form that minimizes the pH-dependent absorption of this drug candidate.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
C. W. Abruzzo T. Macasieb R. Weinfeld J. A. Rider S. A. Kaplan (1977) ArticleTitleChanges in the oral absorption characteristics in man of dipotassium clorazepate at normal and elevated gastric pH J. Pharmacokinet. Biopharm. 5 IssueID4 377–390 Occurrence Handle19611 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaE1cXht1E%3D Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF01061697
P. Lelawongs J. A. Barone J. L. Colaizzi A. T. Hsuan W. Mechlinski R. Legendre J. Guarnieri (1988) ArticleTitleEffect of food and gastric acidity on absorption of orally administered ketoconazole Clin. Pharm. 7 IssueID3 228–235 Occurrence Handle3356120 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL1cXhsVaru78%3D
A. Grahnén B. Olsson G. Johansson S. A. Eckernäs (1994) ArticleTitleDoxycycline carrageenate—an improved formulation providing more reliable absorption and plasma concentrations at high gastric pH than doxycycline monohydrate Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 46 IssueID2 143–146 Occurrence Handle8039533 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00199878
T. L. Russell R. R. Berardi J. L. Barnett T. L. O'Sullivan J. G. Wagner J. B. Dressman (1994) ArticleTitlepH-related changes in the absorption of dipyridamole in the elderly Pharm. Res. 11 IssueID1 136–143 Occurrence Handle7908130 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2cXpsVKqsw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1018918316253
L. M. Quan P. Y. S. Lam Q. Han D. J. P. Pinto M. Y. He R. Li C. D. Ellis C. G. Clark C. A. Teleha H. Sun-Jung R. S. Alexander S. Bai J. M. Luettgen R. M. Knabb P. C. Wong R. R. Wexler (2005) ArticleTitleDiscovery of 1-(3′-aminobenzisoxazol-5′-yl)-3-trifluoromethyl-N-(2-fluoro-4-((2′-dimethylaminomethyl)imidazol-1-yl)phenyl)-1H-pyrazole-5-carboxyamide hydrochloride (razaxaban), a highly potent, selective, and orally bioavailable factor Xa inhibitor J. Med. Chem. 48 IssueID6 1729–1744 Occurrence Handle15771420 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2cXls1Kqsbk%3D Occurrence Handle10.1021/jm0497949
R. Zhou P. Moench C. Heran X. Lu N. Mathias T. N. Faria D. A. Wall M. A. Hussain R. L. Smith D. Sun (2005) ArticleTitlepH-dependent dissolution in vitro and in vivo of weakly basic drugs: development of a canine model Pharm. Res. 22 IssueID2 188–192 Occurrence Handle15783065 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2MXitlClt74%3D Occurrence Handle10.1007/s11095-004-1185-3
M. Akimoto N. Nagahata A. Furuya K. Fukushima S. Higuchi T. Suwa (2000) ArticleTitleGastric pH profiles of beagle dogs and their use as an alternative to human testing Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 49 99–102 Occurrence Handle10704891 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXhsVanurk%3D Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0939-6411(99)00070-3
C. Y. Lui G. L. Amidon R. R. Berardi D. Fleisher C. Youngberg J. B. Dressman (1986) ArticleTitleComparison of gastrointestinal pH in dogs and humans: implications on the use of the beagle dog as a model for oral absorption in humans J. Pharm. Sci. 75 IssueID3 271–274 Occurrence Handle3701609 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL28Xhsl2ks74%3D
P. H. Karpinski J. S. Wey (2002) Precipitation kinetics A. S. Myerson (Eds) Handbook of Industrial Crystallization Butterworth-Heinemann Boston 144
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the useful discussions and suggestions provided by Dr. J. Patel, Dr. J. Bogardus, Dr. R. Smith, and Dr. R. Lipper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Badawy, S.I.F., Gray, D.B., Zhao, F. et al. Formulation of Solid Dosage Forms to Overcome Gastric pH Interaction of the Factor Xa Inhibitor, BMS-561389. Pharm Res 23, 989–996 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-006-9899-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-006-9899-z